UAZ 469
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
Truck (1972-2007) - c1,000,000 built
The UAZ-469 is a Russian, ex-Soviet off-road vehicle developed in the late 1960s for the military to replace the GAZ-69. Serial productios started in 1972 and lasted continuously until 2007, restarted for the provate sector in 2010 at the Ulianovsk plant. Powered by a single R4 2.4 liters engine rated for 70 hp with a 4-speed manual gearbox and all-wheel drive it had more power, better suspension, while still amazingly rugged, reliable and dirt stupid to maintain. of the entire structure. Deployed with the Soviet Army and Warsaw Pact troops as well as numerous uniformed services of communist countries in the Cold War it was also largely exported and was featired in almost every armed conflict after 1970. Its most famous deployment by the Soviet Union was in Afghanistan in 1979-1989. It's mostly veterans nostalgy that pushed to resume production. Today a used UAZ-469 is worth 5,000$ on the market in relatively good conditions.
Development History
 UAZ 460 in trials, 1960.
UAZ 460 in trials, 1960.
The UAZ 469 is perhaps not well known in the west, but for USSR and the warsaw pact, it was (and still is) an institution. As well known as the Jeep was for WW2. Not only because of the duration of its production, but also because it is still running today in the civilian market, an for many years to come. This vehicle is essentially the first-born of the UAZ plant, not counting the post-war one-and-a-half ton diesel Ul ZIS-253, which never passed the prototype stage, as an independent design. UAZ was "Ulyanovsky Avtomobilny Zavod", founded in 1941 on the Volga, far from German tanks, to take on the production of other vehicles in wartime, notably and mainly ZIS. No tanks. But the location at Ulyanovsk was a perfect one, with a nascent industrial center, sufficiently developed infrastructure and good supply of skilled workers.
Work on the UAZ 469 started under the direction of chief designer P. I. Muzyukin; back in the second half of the 1950s. Everyone understood that the plant, which had almost been excluded from the automobile industry before the GAZ69 was put into production, would succeed only by looking into future (and proper) designs. In 1958, the first prototype of the UAZ-460 appeared. Externally, it was very much a Soviet version of the
British Land Rover, which already was a massive success across the world, a worthy successor of the Jeep.
But the UAZ 460 had independent suspensions and in 1959, the 460B appeared with a shortened three-door body, and started its first tests. Ulyanovsk designers worked not only quickly, but also tinkered with the compact V4 engine. Gradually the concept stafted to acquire more down-to-earth outlines. This was largely due to the fact that the main customer was the Ministry of Defense, which did not tolerated much tricks and deviations from their pre-set views on military hardware.
The model 460 these went through a cure of austerity and simplified designs for mass production. It was given for example an old fashioned canvas roof and folding windshield in order to be carried inside an early air transport, or sued by paratroopers, inside the glider. It also had similar forward and rear doors to streamline production. The suspensions were extremely rugged and simple, using tested longitudinal springs. Unlike the GAZ-69, the UAZ 469 was produced in a seven-seater configuration with folding chairs at the rear to store cargo, 600 kg, and whe used as troop carrier with seven infantry, 100 kgs of gear. That was also a seducive proposition for collective farms.
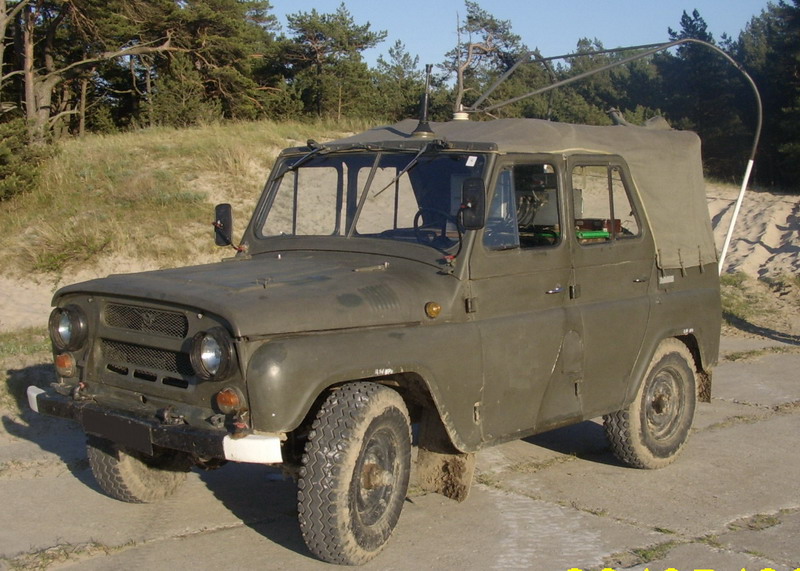 RD-115 UAZ 469 radio car
RD-115 UAZ 469 radio car
The engine was swapped back to the common "Volga" air-cooled 4-cylinders, and its manufacture was entrusted to a local Ulyanovsk plant, which previously produced boat engines. Incidentally, this company had been founded in the 19th century by the Simbirsk merchant Andreev, and transferred to the Russian Automobile Plant of I. P. Puzyrev in 1916. The UAZ-469 prototype was the last of the initial lineage in 1959, already very close to the production vehicle, and this led to a first pre-bproduction batch assembled in 1961, tested in 1962. But still, 10 years will passe before it was put into production.
The UAZ-469 was designed carry staff, troops, cargo and tow a light trailer on as well as light payload on all types of roads and terrain. Development went on between 1950 and 1958, and the first prototype UAZ-460 was a strong utilitarian SUV, useful but not very comfortable. In 1965, the first UAZ-469 were found in the Soviet press, but it was still a long way before full production. A long, long way indeed.
The first UAZ-469 rolled off the assembly line at Ulyanovsk by... December 15, 1972. The vehicle, started as a radical improvevement of the GAZ-69, also made at UAZ, ultimately replaced it. The GAZ-21 Volga, a best seller well known by Russian mechanics in those years, utterly reliable procured a design with some safety margin, and neded largely used as a powertrain base. The military index UAZ-469 saw a first production until 1985, but in 1966 already it received a four-digit number, 3151 (31512 was given to the UAZ-469B).
In August 1974, UAZ delivered three completely standard (without winches and anti-skid chains) UAZ-469. On a well-publicized test run, they reached the glacier on Mount Elbrus at 4200 meters. In 1985, production of the modernized model UAZ-3151 started. Production in 2003 was limited to the gearbox (3151) and export (31512, 31514 and 31519) versions as the army made a transition to the modernized model UAZ-315195 "Hunter", itended for the domestic market. Indeed, between a civilian market that exploded after the first decade following the collapse of USSR and plenty of veterans of the Afghan war nostalgic of the vehicle (something well known in the US for the Jeep and other utility types, largely behind the rise of pipularity for SUVs in the 1990s.
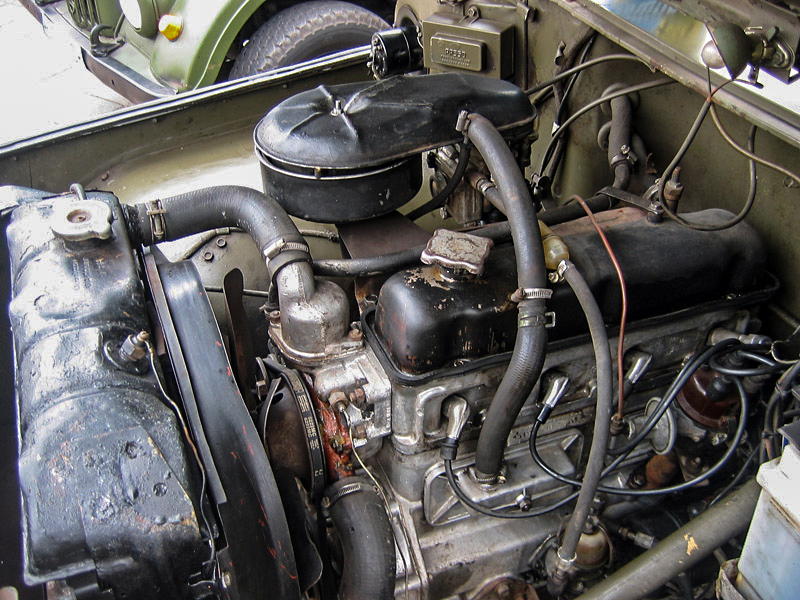 "Volga" air-cooled 4-cylinders
"Volga" air-cooled 4-cylinders
In February 2010, the Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant announced resuming production of the "469" in a limited edition simply called the "UAZ-469" (index UAZ-315196). This civilian only design was les rough than the original, with efforts to improve comfort like a spring front suspension, front disc brakes, power steering and even an optional metal roof. The engine, the new ZMZ-4091 engine developed 112 hp to compenate for the extra weight and bring some modernity to a design ill-suited for modern traffic. But the solutions used in the original design were still there, albeit with significant changes such as split Timken axles, steering knuckles from Spicer axles, new metal bumpers with plastic "fangs", a proper drop side, previously from the UAZ Hunter Classic.
From April and throughout 2010, a limited series as produced as the "469", to coincide with the 65th anniversary of the Victory in the "Great Patriotic War" with an announced serie limited to 5,000 units, which apparently sold well in the first week. In January 2011, the UAZ-469 disappeared from the Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant catalog, with all the 5000 vehicles sold. In its place, the UAZ "Hunter Classic" returned into production with a much steeper price but all modern comfort.
In October 2011, the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation announced its intention to refuse further purchases of the UAZ-3151 but did not completely rule out the possibility of purchasing small batches in the future for some special services.
Design Minutia
 RD-115 UAZ 469 radio car
RD-115 UAZ 469 radio car
Compared to GAZ-69, the UAZ-469 was much more modern, with a 75 hp overhead, 4-speed gearbox and decent heating. Two 39-liter tanks provided a good range as well. But the interior remained spartan to say the least. It was purely a military machine, that could be given to any peasant trained in a single day. There were, for 1972-74, none of the special amenities and benefits of civilization known in the civilian market. This simplicity raduced in smaller costs and simplifed maintenance, it was thus very popular at export, with USSR selling licenced left, front and center.
By the way, military requirements were for some aspects, very peculiar. One was the obligation of placing all instruments in the middle of the dahsboard so that the "senior in the vehicle" could see them. Those who served in the army in the 1950s were OK wih this, as it was current practice. The military also wanted wheel reducers, but were provided for an option without. In terms of cross-country ability, the UAZ 469 was arguably as good as the Land River, and evern better as claimed by the Soviets in many aspects.
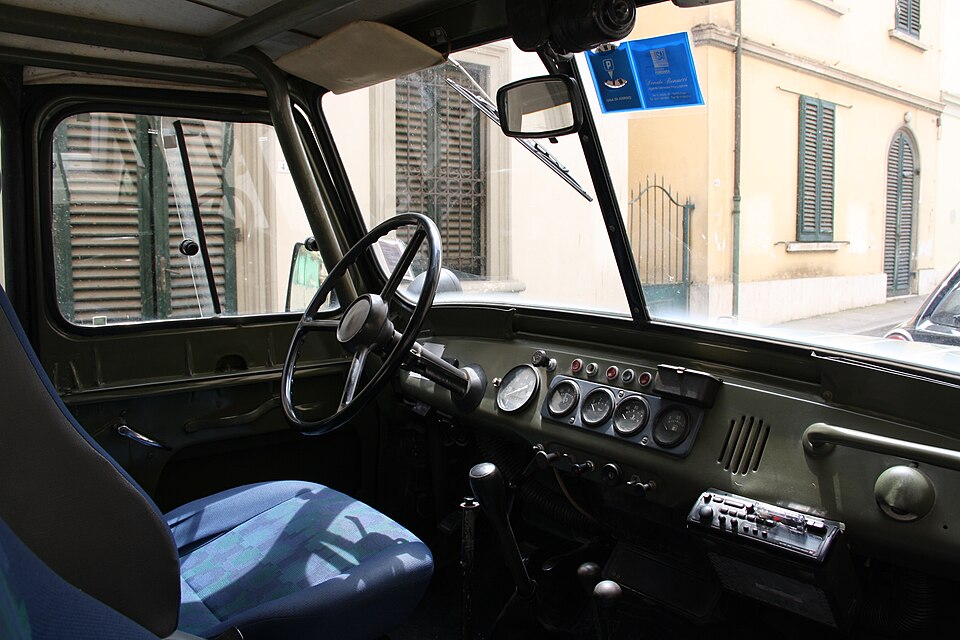 Dashboard and interior cab
Dashboard and interior cab
The ground clearance of the version using geared reduction was 300 mm, and without gears of 220 mm. The reduction gear was 1.940, with the first of the highest row is 4.124. The approach and departure angles of the army version were 52 and 42 degrees respectively. Engineers explained the lack of differential locks by the fact that the UAZ's cross-country ability was already excellent. But to respect the Army requirements, it was required to be as cheap and simple as possible for production and in maintenance.
Serial production of 1972 coincided wit the second year of the ninth 5-year plan, with a modification without gears, index 469B. In 1974, factory testers drove an almost standard 469 to Elbrus without much fanfare and hype with small notes in newspapers and magazines, but proving to the army the ruggedness of the design. At the time, the UAZ 469 was certainly not sold to private owners, just like the GAZ-69. Individual citizens could hope to obtain after a decade of less, some battered, or even completely written-off cars. But from 1969, UAZs quickly became familiar at parades and in military units but also on collective farms and later in various state organizations which needed a dependable out-door car typical in a planned economy.
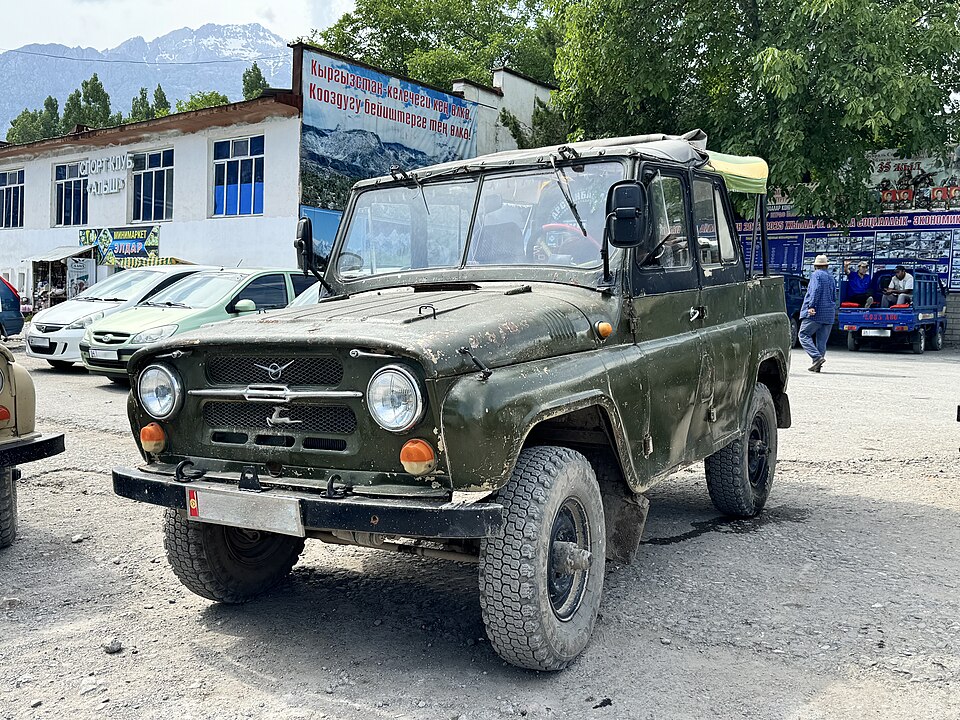 Original 1970s UAZ 469 in Jalalabad, Kyrgistan
Original 1970s UAZ 469 in Jalalabad, Kyrgistan
The vehicle was not exempt from critics. On potholes, it bounced so much that a drive would loose pedals. Experienced drivers coped with this bouncing without much difficulty however. Compared to the GAZ-69 it was judged far better controllable still. However soldiers improvized drivers were not always not able to competently handle the car. Old-timers of the Dmitrov toures units to procure advices from their additional tests of the UAZ in stability and controllability. The Ministry of Defense was forced to publish a notice also, as an internal statistic told the vehicle had the habit of killing Soviet officers, quite a serious accusation.
The "469" had high tires that broke on turns and tests on proving ground recommended at least changing tires more often than prescribed. But the military wanted the car not only not to roll over, but also to overcome insurmountable obstacles such as railroad tracks. The industry did not produce suitable tires for such exercises through, and it was out of question importing those. Effort thus were made instead to better train drivers.
Body Design & General Layout
The body was that of an open, 5-seater, with removable canvas, four doors, side doors with removable metal and glass extensions, usually folded down, but at first simpl removed. The rear side folding down like on a pickup, was used to load up to 500 kgs, but two more passengers could be accommodated here on two folding seats, making for a total of 7 (2 forward, 3 middle, 2 on jump seats at the rear). The tarpaulin frame were removable, and windshield frame could folds down onto the hood, to facilitates camouflage and transportation. The vehicle was notably light enough to be towed by the standard Mil Mi-8 general purpose helicopter. I could not be loaded inside though. four or more could be stored however in a Mi-6.
The UAZ 469 had a light metal body made in treated rolled steel, quite thin, mounted on a strong and torsionally rigid side member frame. The engine used a clutch with a dry single-disc type, and the gearbox had 4-speeds with synchronizers on 3rd and 4th gears. The transfer case was two-stage, and it was rigidly attached to the gearbox without intermediate cardan shaft, also to simplify production.
The payload as already seen was 7 passengers and 100 kg of personal gear, everything needed for an infantry section in campaign, or when used as cargo pickup, with two passengers and 600 kg. Both the middle bunk and rear seats could be folded, or even removed, and free the entire rear section to store all sorts of payload, upt to the weigh above, but it could tow in addition a trailer, weighing up to 850 kg. So in cargo configuration this was as much as 1.45 tons.
To increase ground clearance to 300 mm, drive axles with double final drive, extended housing of reduced vertical size as well as reduction final drives were fitted between the axle shaft and the hub, a pair of cylindrical gears with internal engagement; the direction of rotation of the axle shaft and hub is the same) were used. The UAZ-469B was equipped with drive axles with a single final drive, designed on the basis of the axles from the GAZ-69. The final drives were absent, and ground clearance of the "civilian" UAZ was only 220 mm.
The cardan shafts on the UAZ-469B were also slightly longer and total gear ratio of the drive axles, both geared and gearless, was almost the same (5.38 for the geared one and 5.125 for the gearless one). The "geared" UAZ-469 (UAZ-3151) cold only be distinguished from the UAZ-469B (UAZ-31512) by looking under. But from the outsid, torque was transmitted to the hub through a conical "cap". On the "gearless" version, the axle flange was visible. The gearbox was lubricated by a 300 ml oil tank.
The UAZ-469/UAZ 3151 had 215/90 R15 model Ya-192 (later Ya-409) tyres.
The UAZ 469B/UAZ 31514 of civilian production had 215/90 R15 model Ya-245 tyres
The front axle hubs could be disconnected for a slight reduction in fuel consumption on good roads. The driver unscrewed the protective cap with a socket wrench, same used to adjust the hub bearings, and connected or disconnected the coupling, with a 12 mm Allen key. Since the 1990s, quick-disconnect or self-locking couplings were installed on vehicles. In 1980, the exterior lighting was modernized, the front and rear turn signals were made into orange diffusers, turn signal repeaters placed on the hood's sides. There were hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers added on the suspension instead of levers. From 1983, the new 414 engine rated for 77 hp became standard, and in 1984, an expansion tank and sealed radiator cap were added for the cooling system.
UAZ-3151
In 1985, a further modernization brouht a new geared version indexed 3151. They were equipped with:
- Hydraulic clutch release drive
- Cardan shafts with radial-face sealed bearings
- New lighting, with 2-section sidelights, 3-section rear lights FP-132, side repeaters
- Windshield washer with electric drive;
- Suspended clutch and brake pedals;
- High-reliability drive axles with new gear ratio, wheel reduction gears;
- Brake system with dual-circuit drive and signal lamp
- Split stabilized steering column;
- More efficient and reliable heater;
- Fully synchronized 4-speed gearbox and vacuum brake booster (option)
- UMZ-417 engine rated for 90 hp, top speed 120 km/h
Variants
- UAZ-315196: Patrol police version of the UAZ-469AP
- UAZ-469: Base army version with 2-stage final drive, 300 mm GC, index UAZ-3151 in 1985.
- UAZ-469B Main, "civilian" version, single-stage final drive, 220 mm GC, index UAZ-31512*
- UAZ-469BI: Shielded electrical equipment like the R-403M radio relay transceiver VHF.
- UAZ-469BG: Medical variant with stretchers, index UAZ-3152 in 1985.
- UAZ-469 WZMot-4: Polish Ambulance variant in Wroclaw, local longer body, higher roof.
- UAZ-469RH: Radiation and chemical reconnaissance variant.
- UAZ-469AP: Base patrol police version, all-metal roof, fixed rear seat row, rear door locked from the outside, grilled window.
- UAZ-3151: UAZ-469 name from 1985.
- UAZ-2315: Cargo pickup.
*Metal top: UAZ-31514. 2.89-liter UMZ-4218 engine: UAZ-31519.
Prototypes and one-offs
- UAZ-460 pre-production with a different radiator grille with three slits.
- UAZ-3907 "Jaguar" amphibious variant, with 2 propellers fwd of the rear axle.
- UAZ-Martorelli (exported to Italy only, declined into the following versions below:
- UAZ-Explorer: Petrol engine UMZ-451M (2500 cm3, 75 hp)
- UAZ-Marathon: Diesel Peugeot XD2 (2500 cm3, 76 hp)
- UAZ-Dakar: Turbodiesel from Vittorio Martorelli VM (2400 cm3, 100 hp)
- UAZ-Racing: FIAT (2000 cm3, 112 hp) engine for comprition.
Awards
In 1978, in San Remo, Martoletti won the Silver Jack award for winning the Italian Autocross Championship in a UAZ-469.
A production UAZ-469 set a world record for passenger capacity, tested with 32 people, a total weight of 1900 kg. It traveled 10 meters with this full load as required by the record setup conditions, registered on June 2, 2010 by the International Agency.
Operators & Exports
 Chinese "Beijing" BJ2020S with recoiless rifle.
Chinese "Beijing" BJ2020S with recoiless rifle.
 Italy
Italy
The 469 was mostly exported to friendly, mainly socialist countries and their armies, but in total several dozen other countries were concerned. The Italian case is quite remakable.
The three Martorelli brothers, sons of a car dealer, discovered the GAZ-69 and became fascinated with the model. They participated in and won the Italian autocross championship in a UAZ. They decided to sell it locally, and this was just when UAZ was started to export the 469, so they made an agreement to purchase it, but they were significantly modified. The vehicle were repainted in more "funky" colors, had different wheel rims and new tires were had more reliable tarpaulins and hard tops and modern seats. In addition they were tinkered with a large variary of local engines. Martorelli soon offered modifications with imported vehicles, and it was sold locally and on other markets under the name Explorer. The most spoke about version at the time had an Italian VM engine rated for 100 hp called "Dakar", and intended for the African rally of the same name. Another had a 76-horsepower diesel Peugeot engine and was called the Marathon, another had the 112 hp Fiat and was intended for rally, called the "Racing". These successes inspired the UAZ management to adapt the model to western markest, primarily European.
 China
China
The BJ212/BJ2020, the PLAN SUV "Beijing" was derived from the UAZ 469 with licence was acquired, they were produced in 1965-2005, as a local version of the army model, but without any participation of UAZ for the chassis and instead was derived from the licensed GAZ-69 and only body elements of the UAZ-469, procured by intermediaries. There was no other way after the Sino-Soviet split of 1968.
 Cuba
Cuba
In April 2006, Zavolzhsky Motor Plant and the Cuban Ministry of Defense signed an agreement to produce locally the ZMZ-5143 diesel engine for the UAZ "Hunter" after testing in Cuba. It was planned to re-motorize the remaining Cuban UAZ-469 with these new engines. The economic crisis from 2008 prevented the project to go further. But in 2019-2020, the Minsk Motor Plant proposed to re-motorize Cuban UAZ-469s with the new 4-cyl. diesel MMZ-4DTI. The first demonstrator model was presented in October 2020 at the BelAgro-2020 exhibition, first 100 vehicles ordered by Cuba. In 2021 they were offered for export at large.
Late UAZ export for the civilian market

In 1977, at the proving ground near Dmitrov, prototype UAZ 469 were tested with a hardtop in plastic and steel roofs, as well as modified lighting equipment, one-piece windshield and other improvements. Tests were positive bu the army was not interested. The Soviet auto industry at the time however presvented further development. Because of this and modest improvement over a product unlikely to sell outside freindly counties and the warsaw pact, the compzany was in no urge of any modernization.
Modifications remained modest, with the only option between a "geared" and "non-geared" variant. A postal van with an increased base and rear overhang was developed but remained as a prototype. In the early 1980s, a dozen and a half UAZ-3907 "Jaguar" were tested by the army as possible amphibious vehicles. But the army demanded a better integrated frame witl a fully sealed body and this never went further. The other project of amphibian, VAZ, also petered out. production went on still with all-metal bodies made by specialized plants, mainly for the police, or medical teams for remote places notably in Siberia, special government agencies as well. In the early 80s, the front and rear lights were changed, an expansion tank installed in the cooling system, and other modifications.
| Specs UAZ 469 |
| Dimensions: | 4,025 x 1,785 x 2,050 mm (158.5 in x 70.3 in x 80.7 in) |
| Weight: | 2,380 mm (93.7 in) |
| Crew: | 7 |
| Propulsion: | 2445 cc UMZ 451 MI |
| Speed: | 70 kph road |
| Range: | c600 km |
| Payload: | 6 passengers/400 kgs |
| Production: | Unknown, 1,000,000 est. |
The UAZ 469 in action
How many soldiers, policemen, and collective farmers were transported by the “469”... Seen also in movies, the vehicle became an insititution. They saw action as well, transporting border guards in 1969 along the border with China and afterwards, and carried officer staff during all manpeivers, but also plant staff, rural leaders concerned about production plans, or district police officers of forgotten, remote oblasts. Technically, this history ended in 1985. At that stag it received a brake booster, better engine rated for 78 hp and other improvements under the new UAZ-3151 index. It saw heavy action in Afghanistan being light and easy to deploy, arled in a very of ways, with heavy machine guns or even autocannons, converted as "technicals" for this war. It was appreciated by its high capacity, sometimes carrying as much as ten soldiers, and despite "bumpy" roads and tracks, they prove well at ease on these landscapes. The could be also heliborne by the common Mi-8, so some tactics were developed to drop entire "fast attack units" composed of armed UAZ-469s carried under slings, dropped in the supposed rear of Mudjahideen positions. It saw action as well in all the conflicts in which export users were concerned in the 1970-80s, notably the African Angola war, Iraq-Iran war, Lebanon war, and countless others, sometimes used in very unusual ways.
In 1989, so a few years after the production was shut down, few realized then that this was the beginning of a new, even longer era, in which the "469" finally acquired a hard roof, adopted modern engines, and get a host of modifications for consumers. Two decades later, the plant offered a simplified version, returning to the roots of the original rugged vehicle. Nostalgia did not cause alone widespread demand however. The UAZ "Hunter" became the new flagship of the brand, a rugged yet modern SUV able to tacked the most demainding terrains and yet not loosing its original qualities.
There are few such cars left in the world with this pedigree, and the "hunter" is often compared to the Land Rover Defender, Jeep Wrangler and Mercedes G-clas (Gelandewagen). In any case, the UAZ-469 will go down in history and continue to generate interest in the years to come.