Sd.Kfz.6 Zugkraftwagen 5t
 Germany (1936-45) - Utility Half Track - 3,640 built
Germany (1936-45) - Utility Half Track - 3,640 built
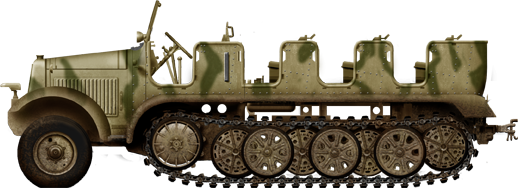
The Sonderkraftfahrzeug 6 ("special motorized vehicle 6") was a German half-track of World War II, prime mover for the 10.5 cm leFH 18 howitzer, manufactured to 3,640 vehicles by Büssing-NAG, Mercedes Bens and BMM. It was also used as supplier and troop carrier, and declined into the armed/armored variants such as the 37 mm FlaK36 auf Fahrgestell Zugkraftwagen 5t and 7.62 cm FK 296(r) Selbstfahrlafette auf Zugkraftwagen 5t (Sd.Kfz. 6/3) tank hunter.
Design development
Already during the First World War, half-track vehicles had been developed by Germany. In the interwar J.A. Maffei AG developed the agricultural wheeled tractor ZW 10, which was converted to a half-track for testing purposes. 24 of the total production were delivered to the Reichswehr for evaluation, in an improved version called MSZ 201 in 1930. Dürkopp works was developing on its side a new half-chain tractor and soon fell specifications for a use on Central and Western European road conditions by the Reichswehr. The office asked for high speeds on road, good traction off-road.
However, no track drives could do both yet. Development work led to a more sophisticated system, the Kettenlaufwerke and later Schachtellaufwerk (overlapping and interleaved main road wheels) introduced to the German army in 1936 and enabling speeds of up to 50 km/h on road. Fast road travel caused steering problems which were resolved also by the half-track directional front axle. Steering was further developed so that at a certain angle in one direction, the inside curve chain was automatically braked for chain steering, allowing better turning radius and more power while doing this.
As part of rearmament program, Wa Prüf 6 department (headed by chief engineer Kniepkamp) commissioned Krauss-Maffei to develop a "light all-terrain traction vehicle", leading to the production of the prototype KM I 4 in 1934. Kraftfahr- und Motorisierungsabteilung (Wa Prüf 6) or "Automotive and Motorization Department" was part of the larger Office Group for Development and Testing setup as part of the Heereswaffenamt (Wa A) in 1933. It was a long derived organization derived from the quartermaster system and Rifle Testing Commission, Artillery Testing Commission which were all dissolved in 1918 and grouped into the Waffenamt or "Weapons Office" (inspectorate for weapons and equipment) founded in the Reichswehr Ministry under Colonel Wurtzbacher. On May 5, 1922, it became the Army Weapons Office or Heereswaffenamt (HWA).
From September 1, 1939 if fell under the Chief of Army Armaments, Commander of the Reserve Army, namely Friedrich Fromm headquartered in Berlin, Hardenbergstraße 29. Tests were performed at the army research institutes in Kummersdorf and Peenemünde and other locations.
Krauss-Maffei was a 1838 founded steam locomotives manufacturer founded by J. A. Maffei in Munich-Hirschau, bankrupt in 1930 and taken over by its competitor Krauss & Comp. (1860, Allach). The company was also know for its Steam rollers have from 1908 and in 1927 Maffei made a road tractor under French license, and trucks with the Swiss company Berna. Krauss-Maffei was born and settled in Munich-Hirschau from 1938 with a 60-hectare site in Munich-Allach. It was tasked to developed the KM 1/4 prototype.
About Büssing-NAG

The vehicle was eventually approved for production in 1936 after many tests, and manufacturer chosen for the task was to be Büssing-NAG. The company was founded in 1903 by Heinrich Büssing, and started production of trucks, motor buses and engines, in Braunschweig's Elmstraße after designing a successful 10-seats bus in 1900. In 1908 the company was closed to the Viennese mechanical engineer Anton Fross and by 1909 a machinery factory was established in Vienna-Brigittenau producing as Fross-Büssing from 1915 under license, after WWI relocated in Prague, Továrna, active until 1931.
From 1920 Heinrich Büssing Automobilwerke KG was founded but in limited partnership with Hermann Fischer designed its new logo, a stylized Braunschweig lion. The company was rebranded in 1922 Heinrich Büssing Automobilwerke AG, HQ Salzdahlumer Strasse and started production of an American Bus from 1926. The 1929 economic crisis struck when a new three-axle cab-over-control bus was presented (Trambus) becoming the company's trademark until 1971.
From 1931 Büssing-NAG, United Commercial Vehicles AG was just a subsidiary of AEG but offered a large range commercial vehicles and industry leader. Facilities were relocated in Elbing, East Prussia as Büssing-NAG Werk Ost.
Trucks had a specific chrome-plated radiator face for better brand identification from 1933 and 1938 new underfloor motors were tested. The company was a major manufacturer of Trucks for the Wehrmacht in WW2.
Final Vehicle
 Wehrmacht tractors on a Popular Mechanics article
Wehrmacht tractors on a Popular Mechanics article
Only one prototype of the "leichter geländegängiger Zugkraftwagen" (Vskfz. 616) type KM I 4 was made by Krauss-Maffei in 1934. Eight serial vehicles by Büssing-NAG (BN l 4) had many similarities to the m. Zgkw. 8t, type KM m 8 also developed by Krauss-Maffei but larger (future Sd.Kfz.8). Contrary to the KM m 8, the KM l 4 and BN l 4 only three road wheels per side and its front mudguards were not swung to the rear. The vehicle was finalized with the right engine as the le. gl. Zgkw. (Sd. Kfz. 6) early in 1936. The production version of the chassis however had one more axles for four central roadwheels axles instead of three per side. The final had seven axles suspended by torsion bars, three outer wheels, four inner wheels in the interleaved scheme. The last axle acted as track tensioner.
During development, the use of the Sd.Kfz. 6 was planned for the engineer and artillery units of the army. Several modifications were made to the chassis and new engine adopted, until the final engine chosen. Responsibility for the development transferred to Büssing-NAG was a manufacturing decision as the latter could deliver the awaited output for the army. The company started in 1936 to produce a first small serie of 8 vehicles designated BN I-4 and in 1937 Daimler-Benz was included in licensed production.
Design
The Sd.Kfz.6 was a typical German half-track of this generation, with a ladder frame chassis, engine at the front, and transmission to the drive sprockets at the start of the tracked section of the chassis to the rear. The front wheels were not tracted in any way and just used for direction only. The traction was all made by the tracks, enabling the required off-road caracteristic wanted for a half-track. The same system was used by the whole range of such vehicles. Its overall Weight depending on its use and modifications, from 8.8 to 8.5 tons and even 9 tons, although the armoured and armed versios such as the 6/3 tank hunter reached 12 tonnes.
In the forward hood was installed the engine, the Maybach NL 38 TR Spezial, later replaced in production by the more powerful NL 38 TUK and NL 54 TUKRUM. They were all six-cylinder in-line models, which deplaced, dependong of the respective versions 3.791 Liters or 3.791 Liters or 5.420 liters, for a final output from 100 hp to 150 hp on the NL 54 TUKRUM.
Classed as "medium" these vehicles had a useful paylopad on the rear flatbed of 5 t whatever the version. The engine was started by a Bosch BJH 1.4/12 ignition system, later replaced by the BJH 1.4/12 and BJH 1.8/12 magneto for late production (wartime). The engine was coupled with a single carburettor Solex JFF 40 II. In WW2 with the NL 54 TUKRUM these were two Solex JFF 40 II for a twin downdraft off-road system, self-regulating starter.
Engine consumption was 50 or 60 liters every 100 km and 90 liters when off-road as tested. The Range was 300 km on road and 130 off-road, but of course using it on roads was not recommanded due to excessive vibrations, although the track links were padded. Top speed on flat went at best to 55 km/h. Al other half-tracks these vehicles traded speed for better off-road caracteristics.
Superstructures for its two basic tasks varied, to carry large or smaller teams on bunks, depending if they were engineers (pioneers) or artillery crews, which included specially made storage areas for the ammunition rounds, in standby behind closed doors. Unlike smaller half-tracks like the Sd.Kfz.11 and 10 which had different bunks arrangement for maximizing payload, the model 6 was the first to really stack bunks tranversally, reather than seats, enabling more potential seating. No les than four bunks were arranged, the first one being stopped where the driver's seat started, but larger enough to carry two men side by side. This made for a total of twelve seats, but it was pushed in reality up to 16. The artillery vehicle 6/1 had less seats, having one missing bunk at the rear, replaced by the ammunition storage. This still made for potentially 9-11 personal. It should be noted that the crew of a 10.5 cm leFH 18 howitzer was just six, so the more reasonable caacity was nine, with an officer and two extra hands supplying ammunitions.
As the war progressed, the Sd.Kfz.6 was planned as a towing vehicle for the 8.8 cm PaK 43 (K.St.N. 1146 for heavy tank destroyer companies) with two vehicles of the 12 m.Zgkw 5t each as linked tractors "zug", but nothing came of it.
Weapons:
The basic SdKfz.6 and 6/1 carried no onboard weapon (no pintle-mounted LMG for example). But the crew's individual weapons, Mp38 pistols and mp40 LMGs or rifles. However there were three "armed" versions, one towed, and two in portee (carried over it). The artillery towing vehicle had the 10.5 cm leFH 18 as designed (but more were towed in WW2). The 10.5 cm leFH 18 was considered a "light field howitzer", standard artillery piece of the Wehrmacht adopted in 1935, used by all divisions and artillery battalions. 11,848 were produced plus 10,265 of the leFH 18/40 variant. It was also horse-drawn and used on many self-propelled versions using as base the Panzer 2, H35, Char B1 or 37L chassis. Max range was 10,675 m (11,674 yd) at 6-8 rpm.
The portee 3.7 cm FLAK 36/37 was fully automatic and effective up to 4,200 m. It was also used in ground support roles but 1944 a German copy of the Bofors 40 mm started to appear as well as the replacing 35-mm AA from Switzerland, developmed from the Oerlikon. As the PAK 36 was also a 37mm, the FLAK 36 just used a few common parts, and on its standard mount can elevate -8° to +85° and had a rate of fire of 160 rpm cyclic with 6-round clips. Max range was 4,200 m (4,600 yd) for cailing and against ground targets,7,995 m (8,743 yd).
As for the the "Diana" tank hunter, they used only ten captured Soviet guns 76.2 mm which were dedicated anti-tank guns of excellent performances.
Production
From the fist large serie of the BN l 5 (184 units), followed the BN l 7 (281), BN l 8 (464), BN 9 (617), BN 9 V (2nd serial prototype, for wartime production), and wartime BN 9b (1,167) at Büssing-NAG. Mercedes BMM joined the production for the BN 9b (300), BN 11 V (one prototype), DB l 5 (313), DB l 7 (228) and DB l 8 (272) which production ending globally in November 1943. Indeed Speer wanted to rationalize haff-track production towards a unique model to lower costs and allow better interchangeability.
The rough early production ratio was 1/3 engineer, 2/3 artillery for the 6 and 6/1, making the bulk of the production. Conversions were made from standard vehicle. Production figures were insufficiently documented however. Only the army's inventory provide information on speed delivery rates, and from 1 September 1939, 1,506 vehicles has been registered in the Wehrmacht already and 68 vehicles for the Luftwaffe. Büssing-NAG was given the task of developing the Sd.Kfz. 6 "standard" from 1943 using a new heavy Wehrmacht tractor but ot went nowhere so production of the time was as good as terminated at this point.
The next schwere Wehrmachts Schlepper (s.W.S.) saw a small production though, five pre-production vehicles in December 1943 followed by 851 vehicles up to March 1945 by Büssing-NAG and Ringhofer-Tatra. This was nowhere near what Speer expected, around 60,000 yearly from all manufacturers in the new standard. As for the Sd.Kfz.6 somes sources states 4,000, others 3,500 but the more often stated figure is 3,640. Perhaps variants are added to the mix, or those from BMM. The 3,640 are based on plate numbers as recorded by the Waffenamt.
Variants
Typically, the Sd.Kfz.6 was to be used by bridgelaying units and divisional artillery. The vehicle was declined in four versions total, although the first two shared the same denomination for clarity: The Sd.Kfz.6/1 Pioneerswagen. The prime mover was called Sd.Kfz.6/1 artillerie, and the two later ones developed whhen WW2 broke out with the "flak" and "PzJg" with specific superstructures and equipments, performed by a conversion specialist.
Sd.Kfz. 6 pioneerwagen
Also called Zugkraftwagen 5 t mit Pionier-Aufbau and this version was towing typical trailer loads which were medium "pontoons" Pf.10 or Pf.11 and light pontoons Pf. 14 and 15 for pioneers (engineers). These "pontoons" were in reality storm boat trailers, and the engineering vehicles PF. 10, 11 and 12 carried engineering equipment. The rest accomodated extra equipments in their storage areas instead of ammunition and personal, plus their personal gear. This was a common vehicle for the river crossing/assault teams in 1939, a first wave enabling to install pontoon bridges afterwards.
Sd.Kfz. 6/1 artilleriewagen
Also called Zugkraftwagen 5 t mit Artillerie-Aufbau: Standard half-tracked prime-mover used for towing various artillery pieces in addition to the regular 10.5 cm leFH 18 howitzer, able to transporting anything up to 15 gun personal/troops seated on three bunks.
Sd.Kfz. 6/2 FLAK
37 mm FlaK36 auf Fahrgestell Zugkraftwagen 5t (Sd.Kfz. 6/2): Sd.Kfz. 6 fitted with a 3.7 cm Flak 36 anti-aircraft gun, sides would fold down to allow space to work on a crew of seven. Its weight was 10,400 kg and length was about 6.5 meters. Like the SdKfz 6, the SdKfz 6/2 had a top speed of about 50 km/h and could carry around 190 liters of gasoline. It should be also noted than the previous Sd.Kfz.11 was also chosen as a base to install a 20 mm FLAK, almost fully armored, but the 3.7 cm was too heavy for it. Thus, the Sd.Kfz.6 became the first half-track to carry the standard medium AA gun.
More on the dedicated page.
Sd.Kfz. 6/3 "Diana"
7.62 cm FK 296(r) Selbstfahrlafette auf Zugkraftwagen 5t (Sd.Kfz. 6/3). Sd.Kfz. 6 carrying a captured Soviet 76 mm F-22 gun portee in an armoured superstructure. However only 11 were so converted, a pinprick in the Jadg. Abteilungs and nine sent in operational service with the Afrika Korps. The gun was redesignated FK 36(r) or PaK 36(r) and its weight and dimensions varied slightly depending on the production model, early ones being 10,500 kg, aberage lenght 6.1 meters with the rear section protected by 5mm of armor plating. The crew of 5-6 had to share space with a hundred 76.2 mm rounds.
More on the dedicated page.
Combat Records
With 3,600 vehicles, the Sd.Kfz.6 was certainly not the most common German half-track of the war, Costly and small, it was mostly replaced in 1943 by the larger Sd.Kfz.7.
Pioneers vehicles
German Sd.Kfz.6 Halbkettenzugmaschine Pionierausfuhrung: As said above, it was attributed to pioneer units tasked of crossing river (Sturmpionierbataillon or assault pioneer battalion, performing engineering tasks during an infantry assault). They used assault boats for the first wave, the next carrying in trailer the larger pontoons to be used as provisional pontoon-bridges. They were used prominently during the invasion of Poland in 1939 as bridges were all dynamited by Polish troops to cross the Warta and reach Lodz, and later the Vistula to reach the capital Warsaw and for subsequent river crossings like the Meuse in May 1940.
They were also in action in the Balkans and Russia. Sd.Kfz. 6 pioneerswagens were intended to procure a beach-head for the engineers, to be followed by cable-towing and setting the main axles on which were hooked the serial pontoons. When all were pushed transversally across the river, a new set of cables was stretched to hook on metal and wooden frames that wood contitute the flexible "road" usable by Wehrmacht tanks of reasonable weight (up to Panzer IV).
Prime Movers
Towing the 10.5 cm leFH 18 was also a task given to the Sd.Kfz.11 also. Both were pressed into the many artillery batallions assigned to various motorized and standard infantry divisions as well as Panzerdivisions. The main problem with the SdKfz 6 was that it was expensive to produce and that it is why other half-tracks were used more often. They coped however well as expected to the taxing autumn conditions on the eastern front, less bogged down than standard trucks as expected. Production was terminated in 1943 after an adjustement towards a simpler, cheaper version in 1942, but the vehicle was replaced altogether by the SdKfz 7/2. Therefore with lack of maintenance and parts as well as fatigue, wear and tear, they became a rare sight by 1945. It was also considered a bit too small to be a good self-propelled platform, only seeing two conversions. The 9 SdKfz 6/3 converted went all in North Africa, whereas the Luftwaffe obtained the earlier Sd.Kfz.6/2.
Links/Books about the Sd.Kfz.6
Lepage, Jean-Denis (2007). German Military Vehicles of World War II. McFarland.
Bishop, Chris, ed. (1998). The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II. Aerospace Publishing.
The prototype KM I 4 on kfzderwehrmacht.de
The Sd.Kfz.6 on wikipedia.com
The SdKfz 6 kfzderwehrmacht.de
1/72 3D printer model
List of SdKfz designations
Bussing-Nag Sd.Kfz.6 (HL 54 TUKRM) specifications |
| Dimensions | 6.325 x 2.26 x 2.50 m () |
| Gauge (wheeltrack) | 1,825 cm wheels and 1,700 cm () tracks |
| Track width | 32 cm () |
| Special gauge | 200 cm with track extensions |
| Ground clearance | 32 cm () |
| Total weight, battle ready | 9.0 t (max.) |
| Payload | 1.5 t, 5 tons utility flatbed |
| Crew | 2 (driver, co-driver) + 14 troops |
| Propulsion | Maybach HL 54 TUKRM 115 hp (85 kW) |
| Power-to-weight ratio | 12.8 hp/t |
| Top speed | 50 km/h (road) |
| Off-road Performances | Climb 24° sloped, ford 60 cm water |
| Transmission & suspension | 4+1 speed ZF, Torsion Bars, see notes |
| Maximum range | 190 ltr tank, 300 km (road) |
| Armament | None 1-1/1, but 37 mm and 76 mm 2/3 versions |
| Armor | None, but /2 and /3 versions (partial) |
| Production | |