Komintern (1933)
 Heavy Artillery Tractor 1933-1940: 1,800 produced.
Heavy Artillery Tractor 1933-1940: 1,800 produced.
Origins

Searching for a new heavy artillery tractor in the early 1930s, officials of the Red Army combined the suspension the T12 tank, combined with a ZiS-5 truck cabin. The result was called the "Komintern" tractor powered with a 131 hp 4-cyl. engine for 30 km/h, 220 km range and able of towing the 18 ton B-4 howitzer and a whole range of heavy ordnance. In 1940 production ceased after c1,800 delivered, and replacement by the more modern Voroshilovez. A post coupled with the latest howitzer entry.
Development
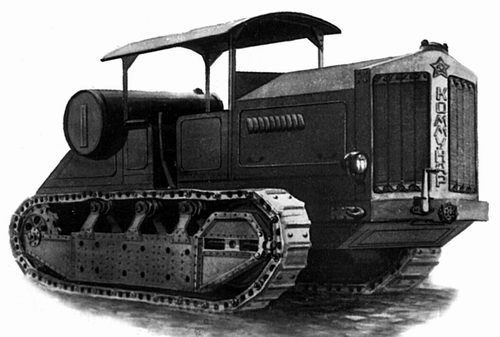 The previous Kommunar, a better proposition than the Stalinets.
The previous Kommunar, a better proposition than the Stalinets.
The industrial tracked tractor "Kommunar", was manufactured by the Kharkov Locomotive Plant (KhPZ) from 1924 onwards. It was very much modeled after the German tractor Hanomag VD-50 widely since the late 1920s in the Red Army for towing the heaviest artillery systems, those that can't be horse-pulled. The plant continuously increased the engine power and speed, up to the model “3-90” rated for 90 hp and 15 km/h.
But this was already the limit of this artillery tractor. It could be still improved in terms of traction properties, mobility, reliability and usability. The army required a special new high-speed medium tracked tractor for ten tons artillery, as well as towing troops via a train of wagon carriages. It needed also to protect the driver from the elements. In 1930, on instructions of the Main Artillery Directorate, KhPZ started development of such a tractor under the leadership of B.N. Voronkov assisted by leading designers D.M. Ivanov, D.F. Bobrov. By November 7, 1931, three prototypes were built at the plant.
The new tractor was called Comintern and proved able to reach 18 km/h altogether with a new suspension and chassis ofering a much better ride, but low weight (7 tons) and power (65 hp). In tests it showed insufficient towing capacity and was rejected. Like the Kommunar it still lacked the requested cargo platform, winch and enclosed cabin. After field tests of 1932, the model was fine-tuned at the Tractor Design Bureau (TRK) by a new team led by N.G. Zubarev, assisted by engineers A.G. Gulita and V.P.Kaplin.
The cornerstone of the design was it brand new, tailored designed engine capable of a considerably higher output, whereas the chassis and suspension were changed again, adopted from the T-24 tank also previously produced at the same plant. In early trials it showed clearly superior speed and range as well as flexibility thanks to a brand new transmission. To protect the driver and even manage a cos-driver seta, an automobile-type cabin was installed as well as a platform on the rear flatbed allowing to ransport the gun crew and ammunition. This was a great progress as previously the troops just had to walk alongside the vehicle or were carried by trucks not able to follow the tractor on muddy ground.
For the first time also a winch rated as strong in pulling power as the trailer was installed. The new tractor soon met and outrun all specs. The artillery corps officers were amazed at it and requested permission for mass production as soon as practicable. The Komintern at that time was indeed estimated as the world's best tracked artillery tractor anywhere. Fastest, ablme of towing the largest ordnance in service and transport its nine-strong (+1) crew and ammunition, dispensing of trucks off-road in the worst imaginable conditions. It was accepted by the Red Army and the factory started to setup mass production.
Production

Mass production began in 1934 and in total, between 1934 and 1940, some 1,798 vehicles were manufactured, entering service with all artillery units of the Red Army as standard for heavy artillery. In 1940, production was discontinued as a more advanced, more powerful artillery tractor was accepted as successor, the Voroshilovets. Before WW2, the Komintern started to be switched to the Far East, and many were passed on gradually to the wood industry and other public services. The Komintern knew no variants or known improvements, apart better optional tracks.
Design
Hull, Chassis, General design
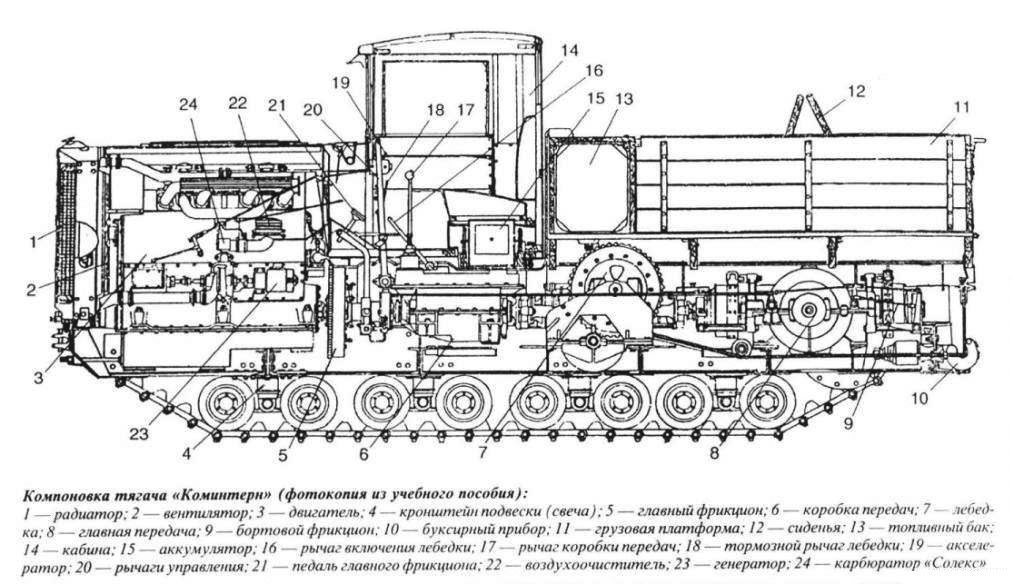 cutaway technical
cutaway technical
The wooden cabin had metal lining shared from the
ZIS-5 truck with minor modifications. Notably the driver's seat was located on the right. All windows could be opened also for better ventilation in summer. Behind the cabin, two metal gas tanks of 275 liters each were installed, fuelling the engine by gravity. The whole crew was located on the rear flatbed with an area of 5.36 m3, folding sides and removable awning. There were bunks, and two transverse seats above the gas tanks. In all, the Komintern could carry ten men in the flatbed. An optional tarpaulin was provided for winter conditions.
Electrical equipment comprised a 12-volt battery, enough to power all lighting and alarm systems as the dashboard. The winch was installed close to the engine gearbox. It consisted in an horizontal drum with the pulling force up to 10,000 kgf, a 30 m long, 22 mm diameter steel cable, connected to the power take-off of the gearbox through a worm gearbox and open cylindrical pair. The drum was also braked from the cab. The towing device was strapped using a spring-loaded swivel hook.
Engine and Performances
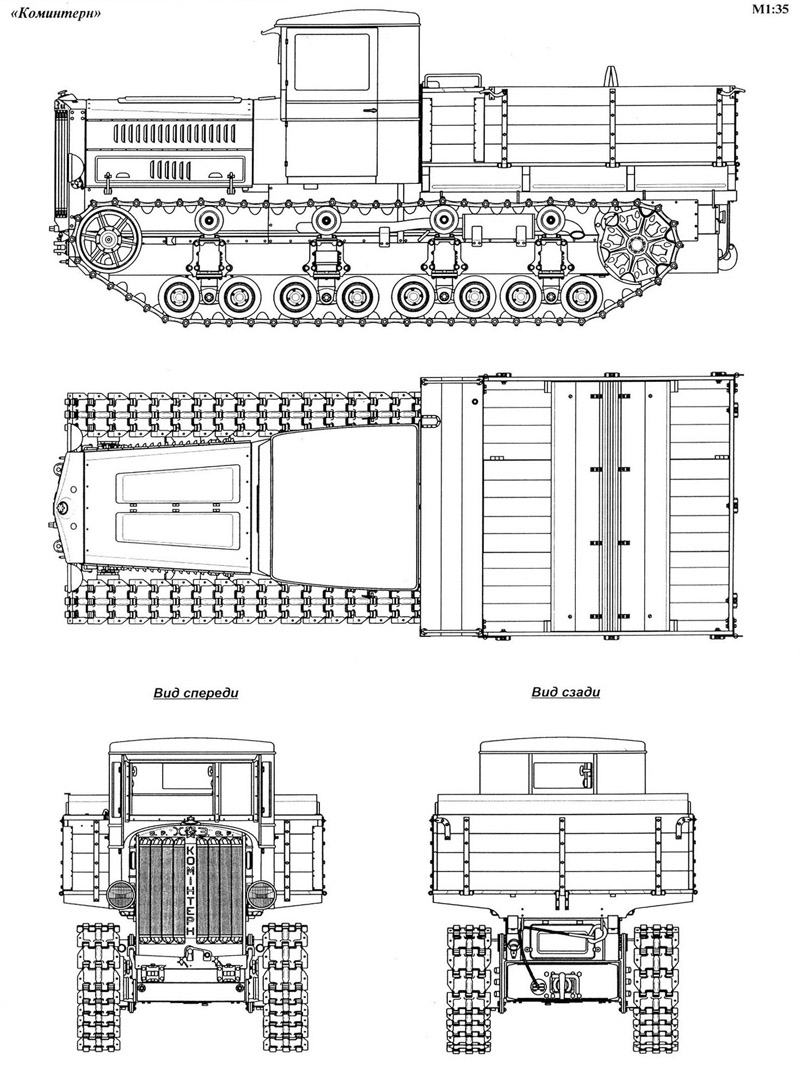 blueprint
blueprint
The Komintern was convenient to operate and maintain with a mixed tank/truck layout, front-mounted engine witn truck cab, cargo platform, rearwheel drive. The robust chassis ladder type framed the transmission and traction winch with its cable extending completed to back for towing. This tractor frame was all-welded and made of two longitudinal beams connected by cross members, gussets and braces.
The KIN engine was a four-cylinder, four-stroke displacing 15.095 liters gasoline engine. It was liquid cooled and had overhead valve plus two removable heads. It was pretty tolerant of the grade of the gasoline, but preferably second-grade gasoline mixed with kerosene, due to a low compression ratio of 4.65. It used a powerful electric starter backup by a safe starting handle with reduction gear for low temperatures.
Due to its relative low speed, low vibrations, it had great endurance and reliability, and could withstand continuous towing missions of the heaviest loads over 2000 km in the most demainding terrainand under the wost weather conditions. The carburetor used was the Solex KhPZ model ignited from a magneto with starting accelerator. The lubrication system was specially adapted for stable operation on slopes up to 40°. Auxiliary drive units were of the gear-type and the engine lacked any belt drives which caused failures in the past. Fuel came from tanks with manual air pump. From 1939 the ZIS-5 fuel pump was added.
The main clutch was of the double-disc type, steel on ferrodo, with brake making shifting easier. The gearbox was a five-speed with a power range of 7.61 (3.81 for Kommunar) and provided a “creeping” speed of 2.6 km/h, traction force of 6800 kgf and best top speed withiut load oin good road of 30.5 km/h.
The gearbox was connected to the main drive by a cardan shaft with Makenik joints, not requiring precise alignment. Onboard clutches and brakes were located on lightly loaded longitudinal drive shafts part of the main gear. They reduced the transmission bulk and crawler tracks. The Komintern's side clutches operated at a minimum input torque and had cast iron driven disks plus steel drive disks, as well as high wear resistance. They did not require much effort from the driver when disengaged.
The suspension was the same as the T24 early tank, spring loaded, on four balancing bogies. It was very elastic as authorizing a travel of 72 mm, which, in combination with rubber-coated wheels and support rollers, made it possible to move off-road at high speed without much vibrations. Army tests carried out in August-November 1937, showed that the vehicle had pretty solid performances, with 21 km/h on flat when towing a heavy load, 16 kph on average down to 12 km/h off road, cross country 6-8 km/h. It could negociate sloped up to 30°, 17° with trailer and up to 25° in descent or negociate 19° side slopes, cross 1.3 m gaps and ford with preparation up to 1 m, as well as climbing a 0.7 m vertical obstacle.
The track system was the same as the tank again, lightweight, with ridge engagement and 50 mm links. It provided traction on muddy/snowy ground but was cushioned enough to be usable on paved roads. The gun crew was seated behind on three transvers bunks, three wide on three rows. This left little space for rounds however. The gun commander was seated close to the driver in the cabin.
Limitations
When driving on soft soils, icy roads, it was however found the traction properties insufficient as the tractor skidded sidways on 5-6° sloped to the side of the road, but later single and double grousers were installed on the tracks for added traction. During operation, high fuel consumption was noted also, up to 5 kg per 1 km and low lateral stability due narrow track, high center of gravity. This cause it also to understeer over 4.5 m and it generally had excessive directional stability
There were isolated cases of tracks falling off also due to poor design of the drive sprocket. Also noted, the excessive wear of the main clutch, and twisting of the gearbox input shaft. Maintenance was made a bit more difficult by all the lubrication points. The plain bearings and weak seals in the chassis also complicated it and cause oil losses and more labor-intensive maintenance and care in general, far more than initially stated.
Komintern |
| Total weight, battle ready | 12t |
| Lenght | 5765 mm |
| Width | 2208 mm |
| Height | 2538 mm |
| Ground Clearance | 400 mm |
| Tracks | Width 360 mm, center track 1530 mm, roller base 3278 mm |
| Ground Pressure | 0.495 kgf/sq.cm |
| Payload | 15 cwt (1 ton) |
| Crew | 2+6 in troop configuration |
| Propulsion | 131 l. 15,095 cm³ 4 cyl overhead valve, comp. ratio 4.65, 1280 rpm. Carburetor petrol, KIN (131 hp) |
| Suspension | Torsion Bars, Leaf Springs |
| Speed (road) | 30.5 km/h |
| Range | 220 km road, 170 km off road |
| Armament | None |
| Production | 1,800 |
The Komintern in service
 Komintern as prime mover for the massive tracked 203mm howitzer B-4 M1931
Komintern as prime mover for the massive tracked 203mm howitzer B-4 M1931
From April until the end of 1934, the first pilot batch of 50 tractors was produced and hard tested. From 1935, mass production commenced and fitting out work, was carried out by bench assembly to reach 25-32 monthly deliveries. They first took part in the parade on Red Square on May 1, 1937. By November 30 were sent from Sevastopol to China by sea.
A total of 1,798 Komintern tractors entered service until 1940. 1,712 joined artillery units of the Red Army, and for long they were successfully and rightfully considered one of the best medium artillery tractors of the interwar. With their help, artillery corps tactical and operational mobility sharply increased. These vehicles were use for towin the following:
-76 mm anti-aircraft gun model 1931
-85 mm anti-aircraft gun model 1939
-122 mm gun model 1931/37
-122 mm howitzer moedel 1938
-152 mm howitzers model 1934/36
-152 mm cannon model 1935 (BR-2)
-152 mm howitzer-gun model 1937 (ML-20)
-203-mm howitzer model 1931 (B-4).
In parades she was shown towing in general the 122 mm M1931/37 A-19 and 152 mm howitzer M1937 ML-20. By January 1, 1941, there were still 1,017 Kominterns in the Red Army which amounted to only 4.7% of special artillery tractors (this showed the mass of vehicles used by Soviet artillery !). By April 1941, the Red Army had a total of 6,891 tracked tractors alone. By June 22, 1941, there were still c1,500 all types combined, and by 1945 only 568 Komintern tractors survived with only 56 lost since September 1, 1942 and many other captured.
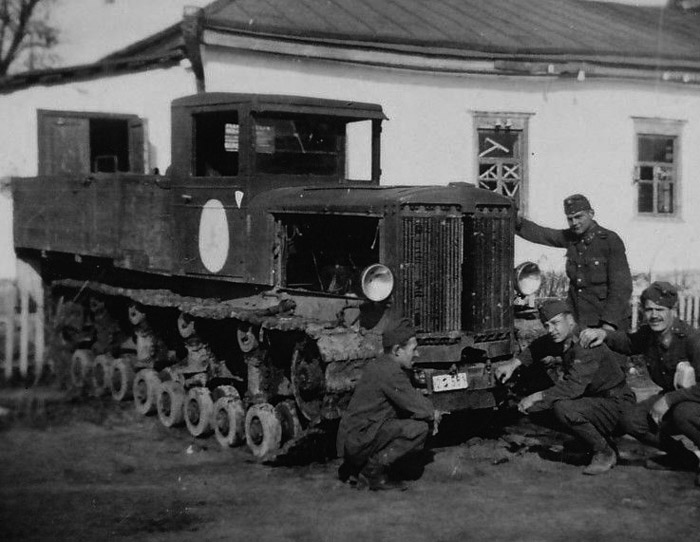
 Stalinets and Kominterns used by the Germans on the eastern front
Stalinets and Kominterns used by the Germans on the eastern front
During the "Great Patriotic War" these tractors saw hostilities, while taking small losses. Spare parts were no longer produced, but their reliability ensure good duration with poor maintenance. The rock solid engine could withstand the most severe frontline conditions and after 2000 km only some wakness was observed on the connecting rod bearings. On January 1, 1943, 385 tractors remained and some were used for towing damaged or broken down tanks.
In the summer-autumn of 1943, new tests were carried out at NATI center with worn out engines, and they could still pull out 126 hp at 1250 rpm. Fuel consumption remained however a constant issue despite the low pressure of 4.65 or 326 g/e.h.h.. In fifth gear they consumed up to 1.4 kg of gazoline. Ground pressure was as low as 0.593 and this corresponded to other high-speed tracked tractors with larger tank tracks.
Gear ratios proved to have been setup correctly, ensuring a traction reserve of more than 20% when driving in all gears, 40% in fifth gear. The Kominterns thus could tow a standard trailer in fifth gear on roads of any class at 340 kgf and 27.8 km/h. Maximum traction force with overload in first gear was even greater than tested at 7500 kgf at 2.3 km/h. But overload meant severe slipping of the tracks; Still this was considered a good traction-speed balance. Towards the end of the war, 568 were still active given than by September 1, 1942 only 56 units were lost since the summer of 1941. Only one tractor has survived to this day.
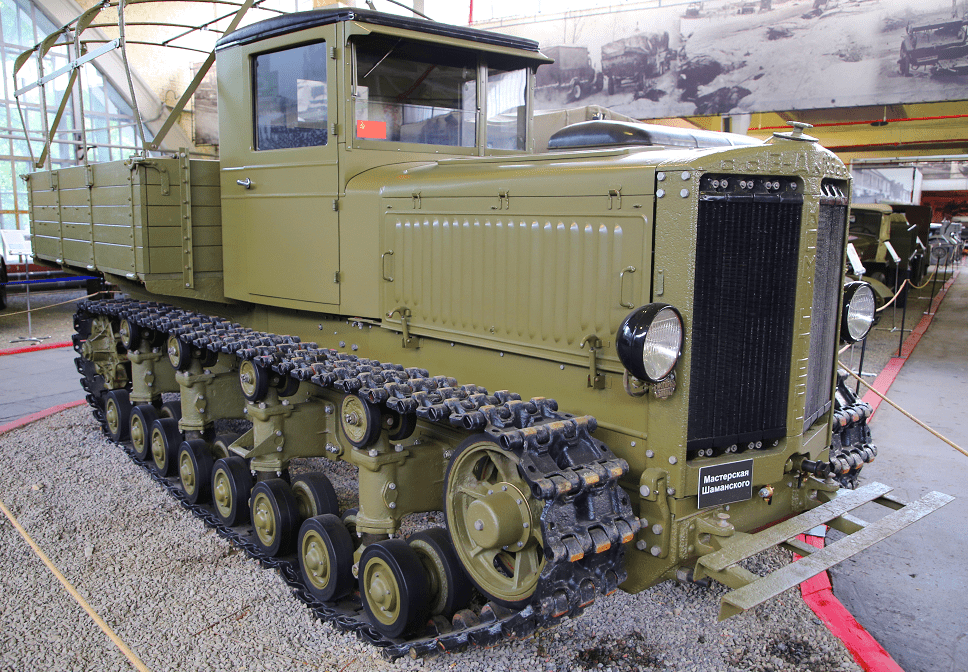
Today it is being restored to running condition in the “Battle for Leningrad” museum named after Zinovy Grigorievich Kolobanov (Leningrad region, Vsevolozhsk city, Narodnaya street 5). Completion of work is scheduled for December 2018. As of today, one Komintern survived long enough to be restored to running condition, to be displayed in the "Battle for Leningrad" museum Zinovy Kolobanov (a famous Soviet tank ace). It was completed allegedly by 2018. Another is restored at the Workshop Evgeniy Shamansky in full working condition.
Sources/Read More
THE RUSSIAN BATTLEFIELD (September 20, 2005). Access date: July 13, 2012.
E. Prochko. Comintern // magazine “Technology-Youth”, No. 3, 1993. pp. 18-19
A. Beskurnikov, M. Svirin. The first Soviet tanks // "Armada", No. 1, 1995
bronetehnika.narod.ru
battlefield.ru
armchairgeneral.com B3 B4 heavy arty
tehnikapobedy.ru
o5m6.de
Wiki ru Stalinets 2 tractor
On ru.wikipedia.org
www.scalemates.com
Video