Sd.Kfz.11
 Germany (1934-45) - Utility Half Track - 9,000 built
Germany (1934-45) - Utility Half Track - 9,000 built
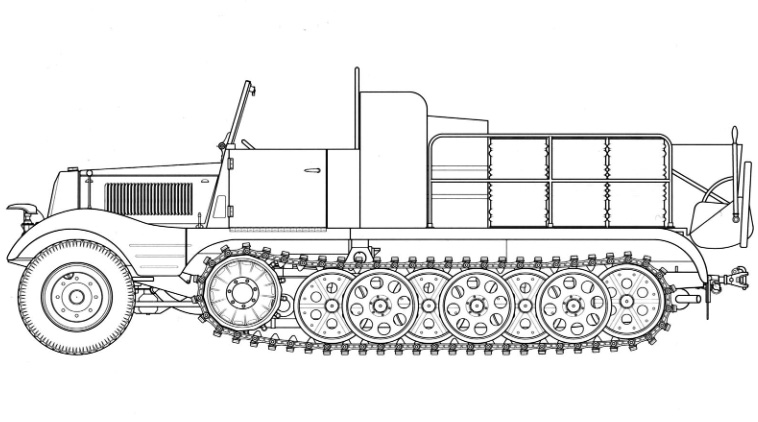
The Sd.Kfz. 11 (Sonderkraftfahrzeug or "special motorized vehicle" type 11) was a German half-track in heavy used during World War II. It was a relatively "light" prime mover, towing medium guns, from the nimble 3.7 cm FlaK 43 anti-aircraft gun, up to the 10.5 cm leFH 18 field howitzer and carry either their crew, equipment and ammo, or six fully equipped infantry troops and trailer, in addition to the driver/co-driver. Not among the costiest vehicles it was deployed in the Wehrmacht as the main version H kl 6, its chassis being so successful it was reused by the armored Sd.Kfz.250, also built by Hanomag. With 9,000 delivered until 1945, it saw action with many units on all battlefields in WW2, but especially the eastern front.
Design development 1934-38

The vehicle's basic engineering was developed during the Weimar-era, at the the Reichswehr's Military Automotive Department, and many prototypes were deliovered to test the concept, like the Marienwagen above. The French carried ou similar developments. The final design, and testing, was made at low cost, by reusing all possible commercial parts, and with the ultimate understanding that production was to be shared between multiple companies, with "open source" policy of copyrights and patents.
Borgward was chosen to develop the second light model of half-tracks, as required in 1934, the first one being the
Sd Kfz 10. Borgwards then delivered a series of prototypes from 1934, until 1937. However since it had limited production capabilities and was already committed on other projects, production was taken over in 1938 by Hanomag, which refned the last prototype and created fro there a more practicable model for production. This one was called the H kl 6, sixth and last prototype evolution, considered as a pre-production model.
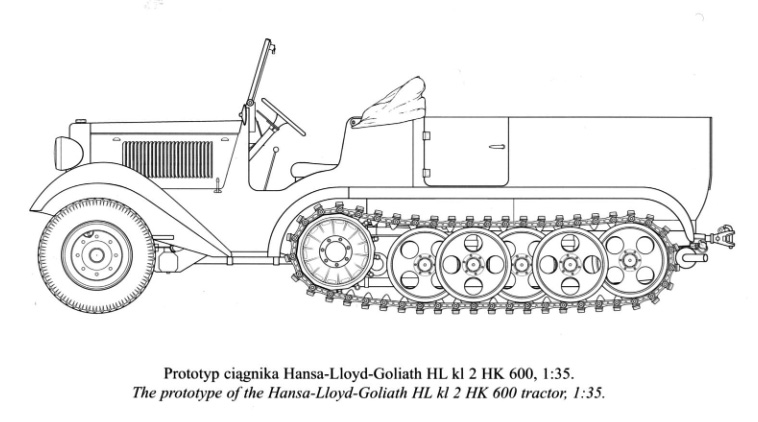
Preliminary design made by Dipl.Ing. Ernst Kniepkamp, working for the Military Automotive Department (Wa Prüf 6) was turned over to commercial firms, and Borgward was assigned the 3 tonnes towing prime mover. HL. kl. 2 was its first prototype in 1933. it was given a six-cylinder petrol engine Hansa-Lloyd 3500L which developed 3.485 litres (212.7 cu in) for an output of 71 horsepower (72 PS). Front-mounted, it was coupled with a four-speed Hansa-Lloyd-Goliath transmission. However its tracked section was fairly short, which just four unterleaved roadwheels per side, and 5 tonnes (4.9 long tons; 5.5 short tons) in all. The HL. kl. 3 prototype of 1936, differed only in details.
The first production model, HL.kl.5 which was given the early Type 3500 L engine and transmission, but was lengthened, adding two roadwheels per side for better traction over soft terrain, which auglented its overall weight bby 1.5 tons, to 6.5 tonnes total (6.4 long tons; 7.2 short tons). It could this time carrying a more honorable military payload of 1,500 kilograms (3,300 lb), and as required, tow a 3 tonnes load, trailer or ordnance. In all, 505 were made by Borgward, between 1936 and 38, with a price tag of 20,000 Reichsmarks.
Nevertheless, the vehicle was considered over complicated and Borgward did not have the capacity for more, so Hanomag was designated to take over the final development in 1938, tasked to delver a better production models, which was the H kl 6. Initially it was given a Maybach HL 38 TUKR engine, replaced later in production in 1940 by the HL 42 TUKRM. Hanomag also had the original Hansa-Lloyd-Goliath transmission replaced by a more sturdy, own four-speed U 50 transmission.
Among other modifications, the fuel tank was enlarged to accept 110 litres (29 US gal), improving its range. With all these modificatons, the total weight of the vehicle, with its body, but unloaded, reached 7,200 kilograms (15,900 lb). It was however capable of carrying a payload of 1,800 kilograms (4,000 lb) and towing four tonnes.
Design
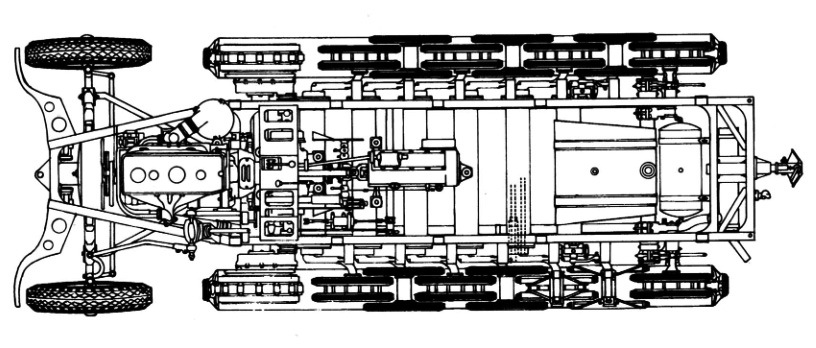
Chassis and engine
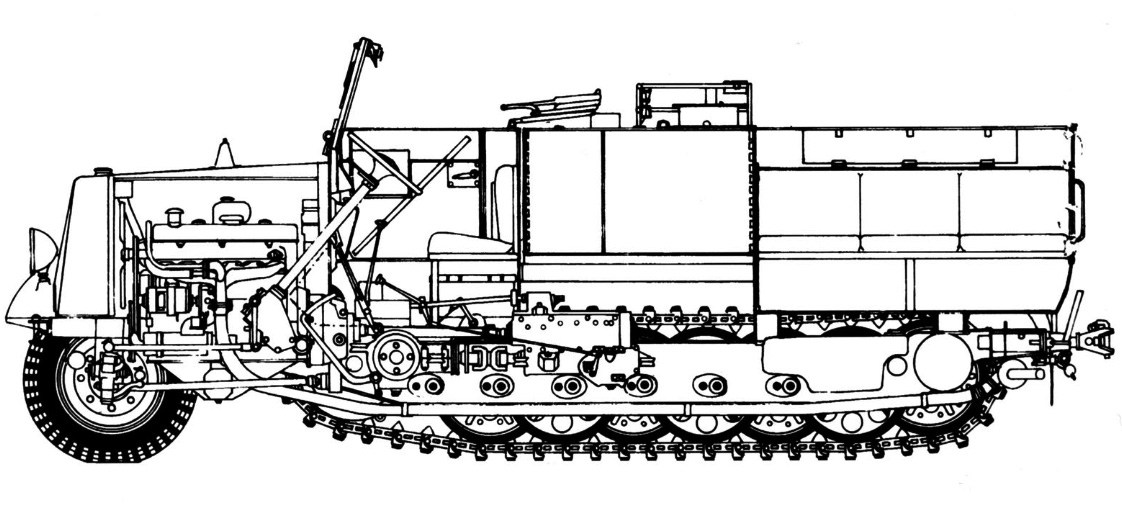
The Sd.Kfz. 11 used a conventional ladder frame, consider the most sturdy for its tracks. Power came from a front-mounted Maybach six-cylinder, water-cooled, 4.17 litres (254 cubic inches) HL 42 TRKM gasoline engine. It developed 100 horsepower (100 PS). It was connected to the Hanomag U 50 transmission, given four forward gears and one reverse gear. Top speed was not stellar, but accurate for a half-track, having a lot of friction; peaking at 52.5 km/h (32.6 mph) on road, and down to 25-30 kph () off-road. It could also ford a 50 cm (1.6 ft) deep river without preparation. However its seven tonnes made it compatible with most bridges in Europe.
Motricity
 Chassis of a standard model HL KI 6, Sd Kfz 3 tons, showing the Maybach engine
Chassis of a standard model HL KI 6, Sd Kfz 3 tons, showing the Maybach engine
Tracks and wheels were powered, and used for steering. The front axle was used for shallow turns, while braking the track would provide and even farther steering than obtained wit the front axle alone, for al almost complete U-turn in a span of 15 meters or less. Drive sprockets mounted at the front of the tracks, close to the engine, had rollers rather than teeth. it was seen having many advantages for friction, less retaining mud, but was also more fragile.
 Construction of the vehicle
Construction of the vehicle
The suspension comprised six double roadwheels overlapping, interleaved (Schachtellaufwerk system) to give the best motricity and weight rest on uneven terrain. They were all mounted on swing arms, themselves sprung by torsion bars. There was an idler wheel at the rear used both a track tensioner and traction as it was placed at the same level as the others. The front wheels were placed on a rigid front axle with transversely mounted leaf springs, doubled by shock absorbers dampening impacts. The whole system allowed civilian truck drivers to quicky train on these machines.
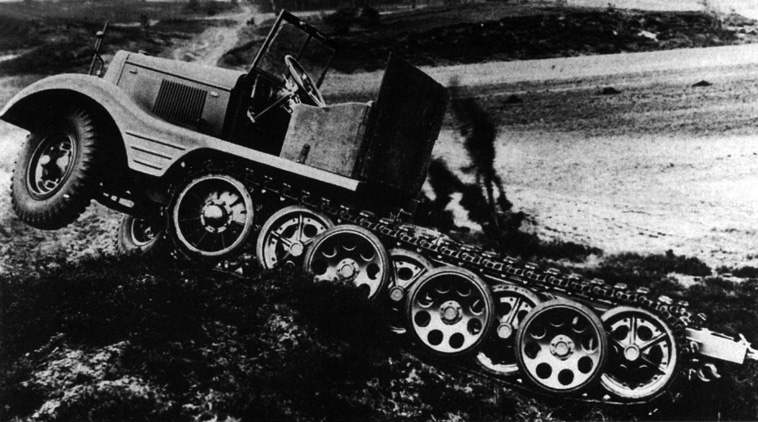 Kh L 6 SdKfz 11 in motricity tests 1940
Kh L 6 SdKfz 11 in motricity tests 1940
Body types and specificities
 The 10.5 cm Howitzer carrier version, with the six benches open top body, able to carry 11 men.
The 10.5 cm Howitzer carrier version, with the six benches open top body, able to carry 11 men.
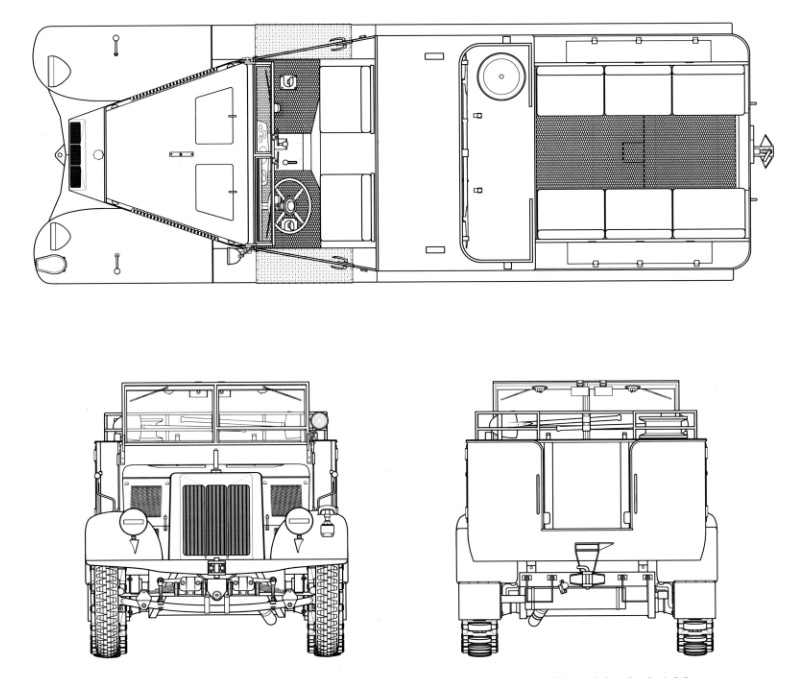
It was decided to fit the production Sd.Kfz. 11 with two different upper bodies:
The "artillery" body was given a rear ammunition compartment with side twon doors, completely separating the driver's compartment from the crew compartment at the rear and reducing it two benches. The ammunition compartment could be configured with various ammunition holders, coming in many calibers. The two rear Bench seats could accomodate three men with little space to spare, seating on the sides and facing each others, each with under-seat storage. Access was from the two-doors at the rear of the vehicle.
The "engineer" body had three bench seats for the crew, convertible canvas top on the rear body and storage compartment at the rear of the vehicle and underneath the crew seats.
On both vehicles, the windshield could fold forward and could be removed entirely, which was done in North Africa. By default, the vehicle was open top, and thus covered by a tarpaulin without windows, strapped on three series of foldable frames, all stored at the rear when not in use, with the packed and folded tarp. This convertible waterproof canvas top could also be mounted over the ammunition compartment only. In both case, it was fastened to the windshield when erected, with optional side pieces for better weather protection.
Production
it was rationalized after Hanomag took over: Both Borgward and Hanomag created the chassis, but soon Adlerwerke (Frankfurt-am-Main), Horch (Zwickau) and even Škoda (Mladá Boleslav) added the model to their own production plan and by 20 December 1942 the production reached 4,209 total, with 2,133 built 1943, then 1,308 in 1944 for over 9,000 in 1945. The declining production was the result of several factors, notably the urge for larger vehicles. The usefulness of small half-tracks was no longer garanteed in 1944, with heavier ordnance and a large part of the materials and workforce used for offensive vehicles instead.
Main variants
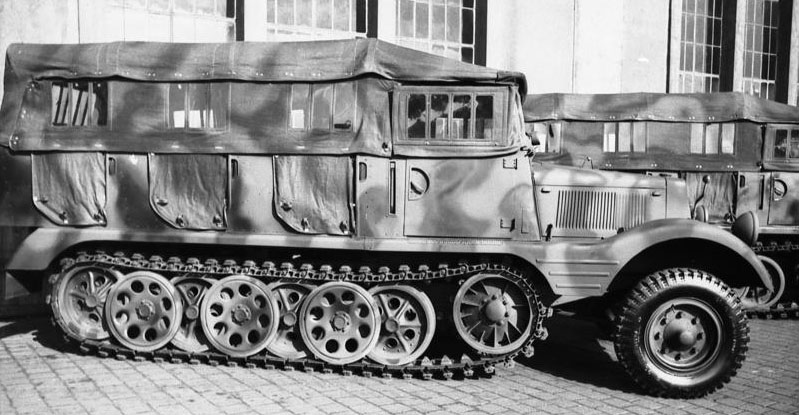 The infantry carrier body for towing the 10.5 cm Howitzer and crew
The infantry carrier body for towing the 10.5 cm Howitzer and crew
Sd.Kfz. 11/1
Two vehicles types in fact shared this waffenamt designation:
-The early one was an ammunition carrier, for the 10 cm Nebelwerfer 35/40 mortar. Compartment's racks were specific to hold the shells and propellant, with side-opening doors.
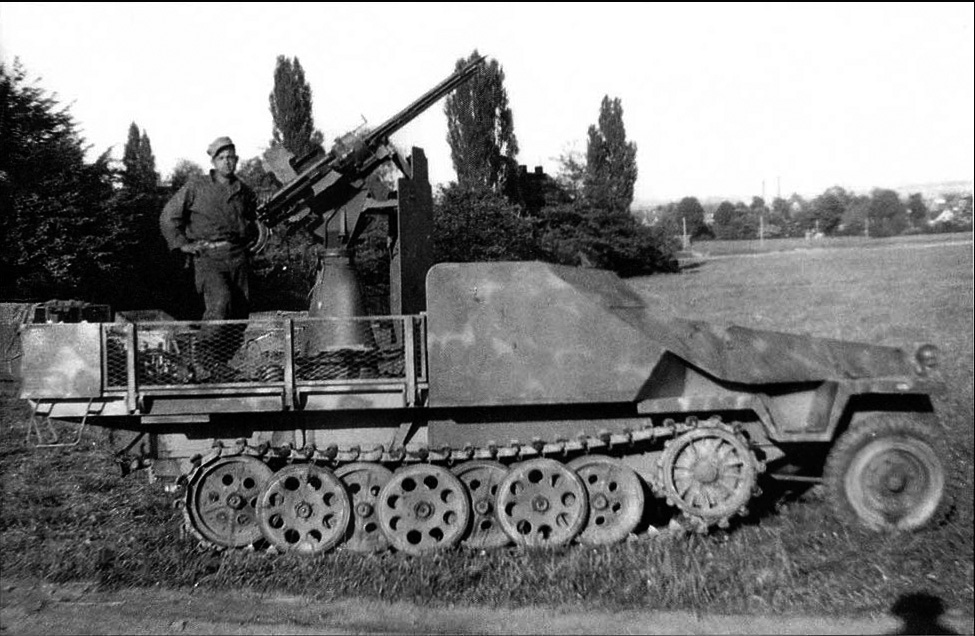
-The 1944 version was an armoured anti aircraft vehicle using a front plating scheme similar to the Sd.Kfz. 251, but mounting a 2 cm Flak 38 gun on the flatbed. Production circa 600.
Sd.Kfz. 11/2
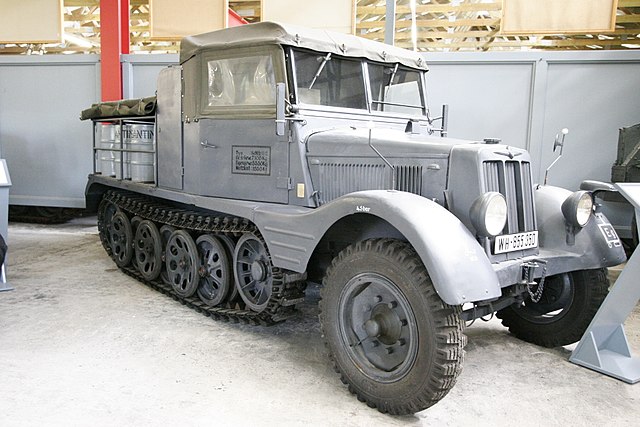
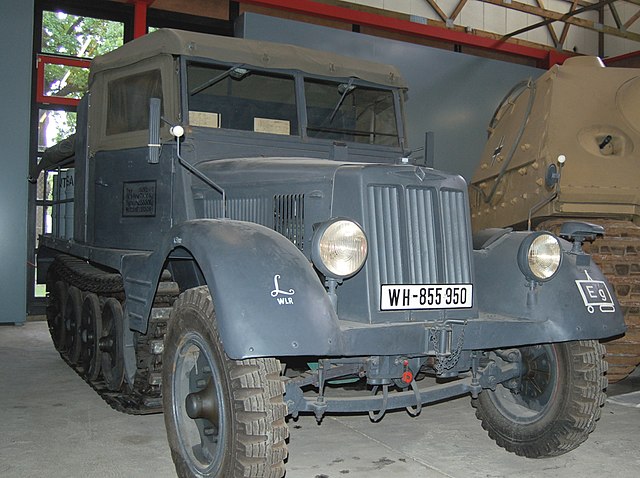
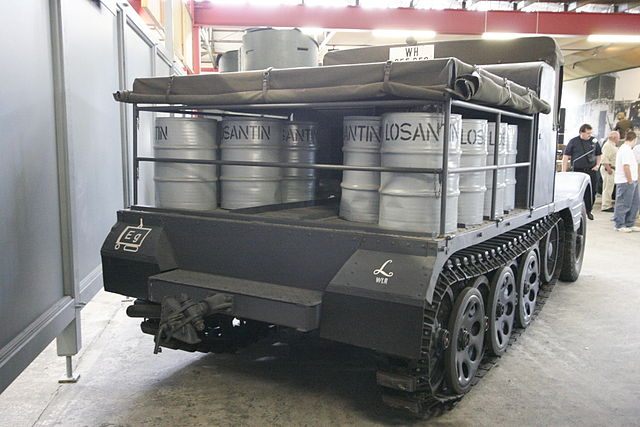

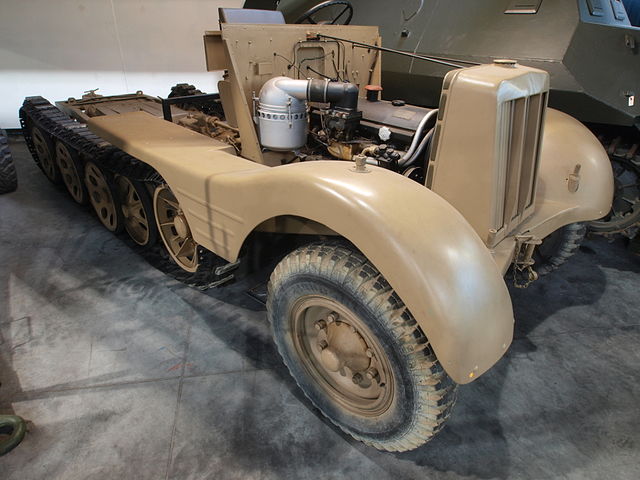
 11/2 vehicle in the xxx museum.
11/2 vehicle in the xxx museum.
The Sd.Kfz. 11/2 was the 1939 chemical decontamination vehicle: It was fitted with a 70 kg (150 lb) spreader, place just behind the rigid wooden cabin, and enough space on the flatbed for eight barrels full of decontamination chemicals. The three crewmen were seated in the cabin. Barrels were stowed on platforms over tracks and foldable outer rails for easy manipulation.
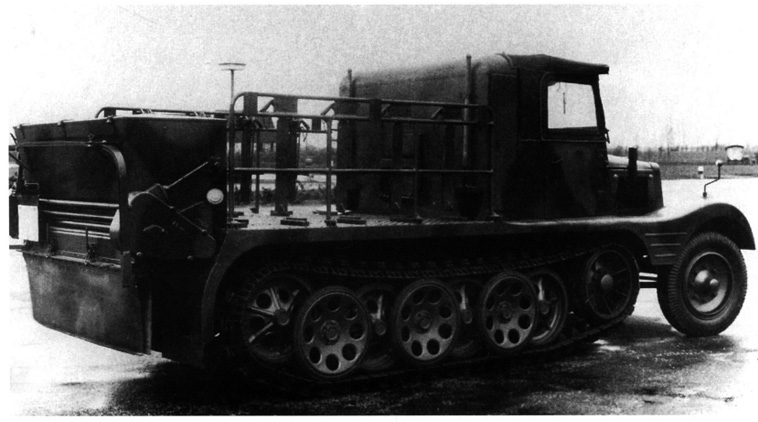
Using 760 kilograms (1,680 pounds) of bleach, with a density of 300 gr. (0.66 Ibs)/m2 (up to 600), a strip 1.7 m (5 feet 7 inches) wide, 1.4 km (mile) long could be decontaminated. Density was independent to speed. 16 decontamination canisters could also be carried, fill with 22 Ibs (10.0 kg) each of the same for hand spreading. Since the feared chemical warfare never materialized these vehicles were soon converted for other uses, but at least one survived to this day, now in a museum. Production unknown.

Sd.Kfz. 11/3
The other chemical warfare vehicle. The 11/3 had a 500 litres (130 US gal) tank and spray system, but this time, to sent poison gas barriers. The spray nozzle swung back and forth, covering an area of 16 metres (52 ft). 125 vehicles of this type were allegedly built in 1937.
Sd.Kfz. 11/4
The standard ammunition vehicle towing the 15 cm Nebelwerfer 41 rocket launcher. The ammunition racks with side doors could carry larger rounds, 10.5 centimetres (4.1 in) mortar shells, or 36x 15 centimetres (5.9 in) up just 10x 21 centimetres (8.3 in) rockets and a six man crew (2 in cabin, the rest seated on benches at the rear). Production unknown.
Sd.Kfz. 11/5
The third type of ammunition vehicle for Nebelwerfer units. It had a wooden upper body with two compartments, with an open top forward cargo compartment without racks racks and rear crew compartment with a bench seat facing the rear and rifle racks on each side. Production unknown.
Sd.Kfz. 250
The chassis was considered sturdy enough to be armored, and formed the basis for the Panzergrenadiers Sd.Kfz. 250, specialized armored personnel carrier, the second most common of the German Army during WW2, declined to around 6,630 vehicles, comprising also a host of variants
See the armored version on Tank Encyclopedia.
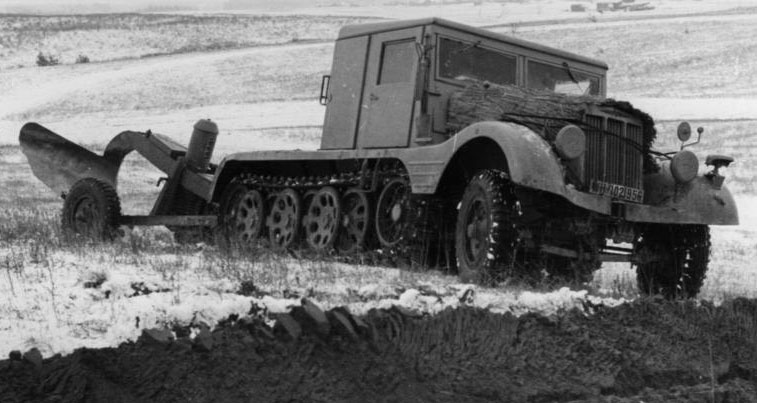
 Light wooden cabin version towing a ditch plow, in action (Grabenpflug im Einsatz)
Light wooden cabin version towing a ditch plow, in action (Grabenpflug im Einsatz)
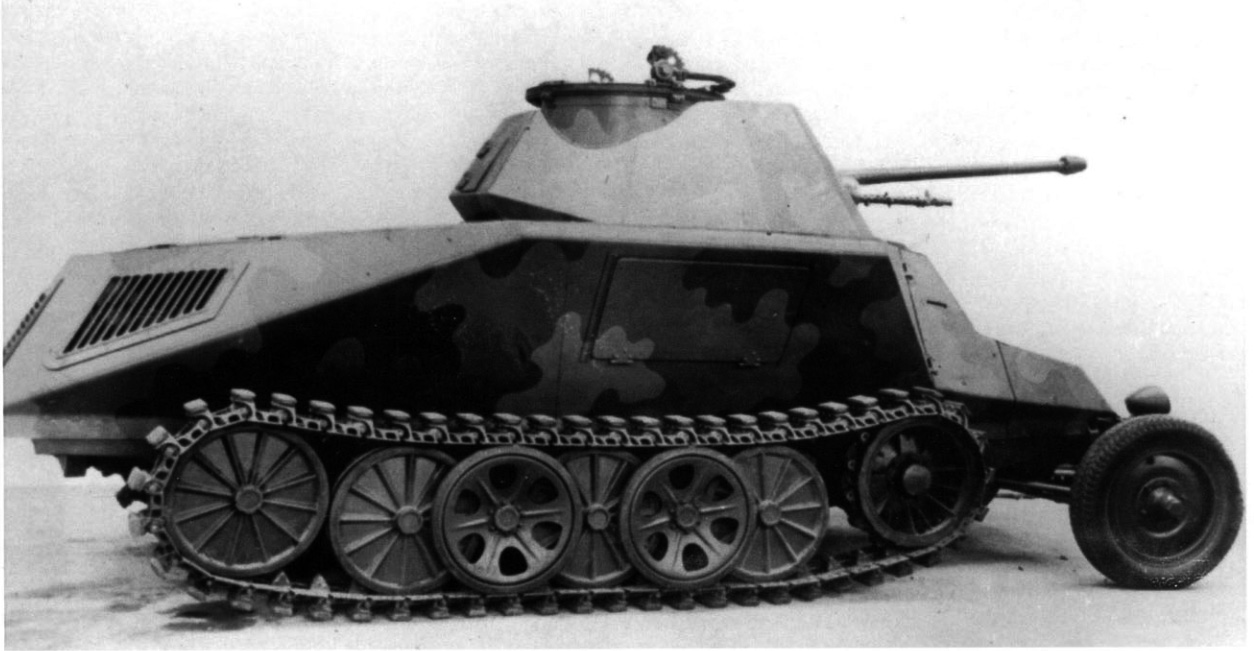 prototype 37cm Selbstfahrlafette auf J Lkl3 H, 1936
prototype 37cm Selbstfahrlafette auf J Lkl3 H, 1936
Other Variants
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11 (normal Artillerie Aufbau) Typ A (Tractor)
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11 (normal Artillerie Aufbau) Typ B (Tractor)
- Raupenraketenwagen, Raupenfeuerwehrwagen, Seerettungsfahrzeug auf 3t Sd.Kfz.11 (Van)
- Prototyp für Nachrichtentruppen Sd.Kfz.11 (Troop carrier, trainer, prototype)
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11 (Artillerie Dachaufbau) (Tractor)
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11 mit Holzpritsche (Tractor)
- Schneeschaufelkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11 (Snow cleaning vehicle)
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11 M-Aufbau (Engineering Carrier Vehicle)
- Leichte Feld-Haubitze 18 auf Zugkraftwagen 3t (Sd.Kfz.11) (Armored Artillery Vehicle)
- Mittlere Nebelkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/1 (Tractor)
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/1 Workshop Carrier (Carrier)
- Leichte Zugkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/1 Pionier (Engineering Vehicle)
- 20 mm Flak 38 auf Selbstfahrlafette Zgkw.3t (Sd.Kfz.11/1) (Anti-Aircraft Vehicle)
- Munitionsschlepper für Selbstfahrlafette Zgkw.3t (Sd.Kfz.11/1) (Anti-Aircraft Vehicle)
- 20 mm MG/151/21 Drilling auf Selbstfahrlafette Zgkw.3t (Sd.Kfz.11/1) (Anti-Aircraft Vehicle)
- 30 mm Bordkanone Mk/103 auf Selbstfahrlafette Zgkw.3t (Sd.Kfz.11/1) (Anti-Aircraft Vehicle)
- 75 mm PaK 42 L/70 auf Zgkw.3t (Sd.Kfz.11/1) (Tank Destroyer Prototype)
- Mittlere Entgiftungskraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/2 (Chemical Decontamination Vehicle)
- Mittlere Sprühkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/3 (Chemical Decontamination Vehicle)
- Schwere Nebelkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/4 (Tractor)
- Schwere Nebelkraftwagen 3t Sd.Kfz.11/5 (Tractor)
Sd.Kfz.11 with Van Bodies
Called Raupenraketenwagen, Raupenfeuerwehrwagen, and Seerettungsfahrzeug (auf 3t Sd.Kfz.11 (Van)) these vehicles completely replaces the original low hull with spaces for ammunitions lockers by a brand new, longer and extra-long chassis and a new box body wih windows. There are two variants depicted here, one having a taller cab. These were confidential vehicles. The "long chassis", company for the rescue of shipwrecked, and a control vehicle for V2 launches. The elevated cab had side storage bins. The others had vertical lockers for the firemen's equipment, as main vehicle for combat airfield.
More to come !
The Sd.Kfz.11 in combat
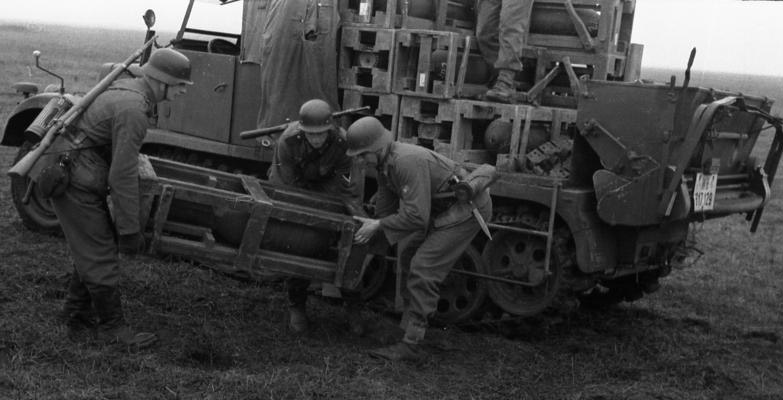 Bundesarchiv_Russia_Nebelwerfer-Sdkfz11
Bundesarchiv_Russia_Nebelwerfer-Sdkfz11
With Approximately 9,000 produced from 1938 to 1945, thi model was the second most common light half-track of the German Army and a well used German tactical vehicles, soldiering through the Invasion of Poland, Battle of France and the low countries, Balkans Campaign and Eastern Front, as North Africa and Italy. The Romanian Army also received six in late 1942 to help its effort on the eastern front. Both body versions as shown by photographic evidence were used by artillery units.
The vehicle was organically the prime mover of the 10.5 cm leFH 18, from Poland onwardsn and was present in Leichte Artillerie Regimnt (Mot.) in two battalions of such towed howitzers, with three each, each having itself two gun platoons with two tractors and two howitzer, so 24 total per regiment. It was also used for towing medium mortar and ammunition trailers, and in September 1939, three Nebel Abtailung (Mot.), the 1st, 4th and 5th had three batteries each, subdivided into two platoon each, all with the 10 cm Nebelwerfer 35. Weighting one ton, they could reach 3000 meters, and fire either smoke, explosive or chemical rounds. Each crew comprised seven, with a commander, three gunners and three loaders. On long distance, the crew's gear was packed into one or even two trailers.
The Panerjäger units started to use also the vehicle (simplified as Zgkw 3t) from 1942. They were towing the 7.5 cm Pak 40. The Motorized division mixed the equal number of 10.5 cm Howitzer vehicles and Pak 40 tank hunters. The typical Panerdivison on paper in 1943 called for 24 Zgkw 3t, including three in the Divisional HQ. The panzergrenadier Regiment also had three. Reconnaissance Bataillions also had three Pak 40 vehicles. Panzerartillerie Regiments had three batteries of four 10.5 cm howitzer each, also including two Mg.34 teams for protection.
 Sd.kfz.11 with an SS Division, Nebelwerfer unit, southern russian front, late 1943
Sd.kfz.11 with an SS Division, Nebelwerfer unit, southern russian front, late 1943
In 1944 a new reform had these vehicles rose to 29 per Division, a Panzergrenadier Regment having 3 and the Panzerjäger zug and one independent Abt. with two companies each with 6 vehicles, and the same AT guns. The Panzer Artilleri Rgt. retained 12 vehicles and same howitzer, and the replacement field battallion had a mix of Howitzer and Pak 40 units as well as the smaller 5cm Pak 38, they had interchangeable ammo racks betwen these and the 10.5 cm howitzer rounds.
Luftwaffe units also operated the type, for towing the 2 cm Flakvierling 38 nut also the 1.7 cm Flak 18/36. Some were even found towing the 8.8 cm Pak 43/41, but at 5 tons, this was only an interim measure, wearing the nimbled half-track quickly. The towing hooks were standardized. It also happened that these vehicles were found bogged despite their tracks (which were narrow) and called for small chains attached to them, in particular to deal with snow and ice, and these were generally fitted on each third link.
The H kl 6 was developed in 1940 as a much simplified replacement, using wood whenever possible and a much simplified engine hood. This new model was also supposed to replace the Mittere SPW Sd Kfz 251. They were suppose to come in both armored and unarmored versions. The H 7 was the armored version of the Kl 6, and the H8(H) was a rear-engine prototype developed by Hanomag that went nowhere. In truth, in 1942, the HKp 606 by Demag was supposed to replace all existing platform, but never entered production. The Sd Kfz 11 went on soldiering until the end of the war, often with transformations that were not planned, mostly using wood paneling.
Links about the Sd.Kfz.11
Commons, cc photos
On lexikon-der-wehrmacht.de
On worldwarphotos.info
On kfzderwehrmacht.de
On militaryfactory.com
The Sd.Kfz.11 on Wikipedia
The Sd.Kfz.10 on weaponsandwarfare.com
Overloon museum - Militracks, SWS halftrack
On lonesentry.com, German Chemical Warfare Vehicles
On cybermodeler.com
Axworthy, Mark (1995). Third Axis, Fourth Ally: Romanian Armed Forces in the European War, 1941–1945.
Chamberlain, Peter, and Hilary L. Doyle. Thomas L. Jentz (Technical Editor). Encyclopedia of German Tanks of World War Two
Niehorster, Leo W. G. German World War II Organizational Series, Vol. 4/II: Mechanized GHQ units and Waffen-SS Formations
Spielberger, Walter J. Halftracked Vehicles of the German Army 1909-1945. Atlgen, PA: Schiffer
Hanomag Sd.Kfz.11 specifications |
| Dimensions | 4.75 m (15 ft 6 in) x 1.93 m (6 ft 3 in) x 2 m (6 ft 6 in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 3,400 kg (7,500 lb) |
| Crew | 2 (driver, co-driver) + 8 troops |
| Propulsion | Maybach HL42 TRKM 4.2L 6-cyl. water-cooled petrol 99 hp |
| Top speed | 65/25 km/h (40/16 mph) road/off-road |
| Payload | 1,250 kg (2,650 lb) |
| Transmission | 7 + 3 speed Maybach Variorex SRG 102128H |
| Suspension | Torsion Bars |
| Maximum range (on/off road) | 300/150 km (190/93 mi) |
| Armament | None, see notes |
| Armor | 6 mm (0.2 in) |
| Production | Hanomag, 1938–1945 - 22,000 Reichmark |

Hep support this site !