Sd.Kfz.10
 Germany (1938-45) - Utility Half Track - 14,000 built
Germany (1938-45) - Utility Half Track - 14,000 built
The smallest German half-track prime mover of WW2 (apart the kettenkrad), the Sd.Kfz.10 revealed itself the most affordable and suitable for mass production, and also able to carry most light to medium weaponry. During the war it proved also capable to carry these weapons directly on its flatbed, creating a very efficient self-propelled fast-firing dual purpose artillery. The chassis was such as success that Demag's vehicle was also reused for the production of the fully armored Sd.Kfz 250 and 251, standard APCs of the Panzergrenadiers and specialists on the frontline. The vehicle was produced until the end of the war and was seen on all fronts.
Design development 1934-38
One of the most important half track of the Wehrmacht during WW2 was also the smallest. In fact, it was just above the Sd.Kfs.3 Kettenkrad in terms of prime mover. Its main durty was to bring all sorts of guns on all terrains, from the 2 cm Flak 30, 7.5 cm leIG mountai gun, 3.7 cm Pak 36 to name a few, as well as mortars and trailers. In addition the rear flatbed when fitted with transverse bunks or seats could carry three rows of two, so eight troops or gun servants.

 First Wa Prüf 6 prototypes under the German Republic: The 1920 Marienwagen (top) and Mechanische Werke Cottbus 201 model of 1928 (bottom). One of the main driving force between these was the similar effort made by the French.
First Wa Prüf 6 prototypes under the German Republic: The 1920 Marienwagen (top) and Mechanische Werke Cottbus 201 model of 1928 (bottom). One of the main driving force between these was the similar effort made by the French.
The base project was relatively recent as the vehicle's proper studies and design started in 1936, but the engineering for all half-tracks was developed under the Weimar Republic, by the Reichswehr's Military Automotive Department. Like the others of the serie, the "special vehicle 10" (Sonderkraftfahrzeug 10) fninal conception related to a specificcation of the smallest of thes eprime movers was given to a commercial firm geared for production but with other companies and suppliers, under licence, to rapidly met a critical mass. Demag was chosen as the lead manufacturer after preparing and submuitted a design, which was approved after a long serie of prototypes started just after Hitler accession to power, in 1934 until 1938 when production was launched. Demag at each iteration improved its prototypes.
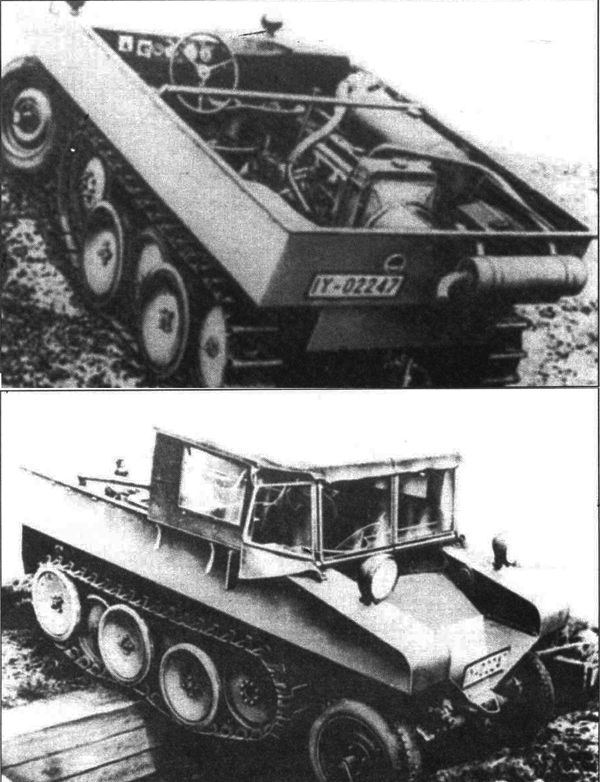 Demag D 11 in 1934 (rear mounted engine)
Demag D 11 in 1934 (rear mounted engine)
Preliminary design not for the current model, but for all German half-tracks, was Dipl.Ing. Ernst Kniepkamp's work. His was the chief engineer at the Military Automotive Department (Wa Prüf 6). The Nazis took power in 1933 but did not changed its direction and allocated more funds to reach production status. That way, his designs were then turned over to the private manufacturing sector for final development and testing. Demag was chosen for the smallest one in the new imagined range of half track prime mover, tasked to develop the "Liliput", or
Kleinster geländegängiger Kettenschlepper ("smallest cross-country tracked towing vehicle"). In 1934 the first D ll prototype was ready and started testing. It had a six-cylinder, 28 horsepower (28 PS) BMW Type 315 engine mounted in the rear. It also had three roadwheels per side. The D ll 2 followed in 1935 with the same engine, but using an extra roadwheel, for 2.56 tonnes.
 Demag D 11 2 1936 in testing, now with a front-mounted BMW engine.
Demag D 11 2 1936 in testing, now with a front-mounted BMW engine.
-The D ll 3 (D 3) 3.4 tonnes went closer to actual production. First off, to be used as prime mover it needed more power, and was so fitted with a 42 horsepower (43 PS) BMW Type 316 engine, this time mounted in the front. It also had five roadwheels, and a troop utility compartment ar the rear, large enough to carry six personal.
-The D 4 prototype never left the drawing board.
-No D 5 was developed.
-The D 6 prototype was in fact the first of a field test preserie of eight vehiles ("Versuchs-Serie") in 1937. This one weighed 3.85 tonnes for a 90 horsepower (89 hp) Maybach NL 38 TRK engine. The transmission was also new, but its general construiction still ressembled the D ll 3. D 6s and extra D ll 3 prototypes were heavily tested and modified for service, intended at the start to be used by the Chemical Troops (Nebeltruppen) and Air Defense Troops (Luftschutztruppen).
In the end, 60 pre-production (0-serie) D 6s were ordered from Demag in 1937. Adler and Mechanische Werke Cottbus (MWC) own vehicles were to be produced in parralel, only differing in details. On 17 March 1937, the waffenamt designation was chosen: "Leichter Zugkraftwagen 1" abbreviated to Sd.Kfz. 10, light 1 ton semi-tracked towing vehicle. The whole D 6 ausf 0 was delivered by November 1938 to be delivered in active units and obtain better feedback.
Production versions 1938-45
The D 7 was the final evolution of the type and mass-production model. Its main difference was different tracks, and a more powerful Maybach NL 38 TRKM engine. The latted however had too much compression for the 74 octane (OZ 74) mandtory gasoline type for use after 1 October 1938. It was modified with a new cylinder head, and shorter pistons. Deliveries began in October 1938. The first vehicle off the production line was tested on 11 October 1938.
Design of the Demag Sd.Kfz. 10
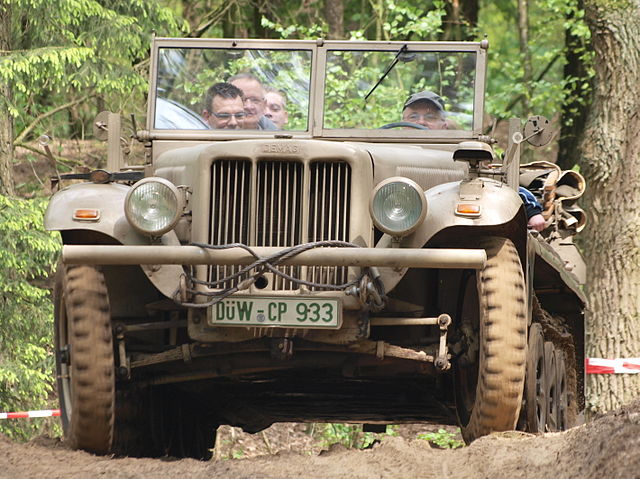 Demag D7 front
Demag D7 front
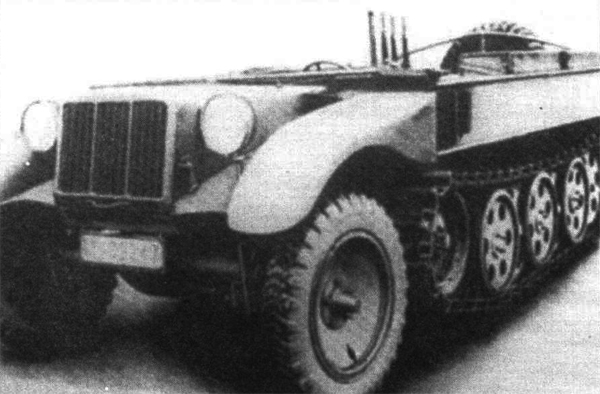
-Construction called for a standard ladder beam chassis, all-welded, with a flatbed aft and the engine and driving compartment at the front. The front axle was used for steering. Each rear wheeltrain system comprised a set of nine stamped, rubberized roadwheels, three axial (running at the center of the track) and three pairs running on both sides of the track, in beteen external teeth. The aftermost one was used as idler/tensioner and higher than the others. All also rested on torsion bars fior suspension. There was a drive sprocket at the front. The engine was connected, via the transfer case, to this drive sprocket axis. The front axle was not actioned and only was there for direction. The vehicle was unarmoured, although many versions were made during the war with partial armored plates (see variants).
The Maybach NL 38 TRKM powerplant had 4.2L chamber volume and ran on petrol. It was 6-cylinder, water-cooled unit which developed 89 metric horsepower, for a Power/weight ratio of 28 HP/ton. It was connected to a transmission 7 + 3 speed Maybach Variorex SRG 102128H. This enabled a top speed on road of 65 kph (40 mph), the best of all half-tracks developed at the time. However that kind of vehicle were likely to be brought by train close to the front (like tanks) and not proceeding on their own power all the way to it to spare the wear and tear of the tracks and mecanical components. Off road, they were capable of around 15-35 kph (mph). The interleaved roawheel system allowed for a low ground pressure, so this vehicle was at ease on snow and mud.
Early versions were fitted with two fuel tanks: One of 58 litres (15 US gal) and the other of 32 litres (8.5 US gal) for a total autonomy of 250 km, but this was deemed complicated and the final production version was given a unique 110 litres (29 US gal) at the end of 1939. It enable a range (road) of 300 km or 190 miles, down to 150 (93 miles) off road.
Also the NL 38 TRKM engine was replaced in late 1939 by the HL 42 TRKM, with a cylinder stroke increased to 110 mm, so a better cubic displacement from 3.8 to 4.2 litres (260 cu in). This improved also the output to 100 metric horsepower (99 hp). At the tart of 1940, stronger stamped road wheels were installed and the hull rear was modified for towing heavier loads, like the 7.5 cm PaK 40 anti-tank gun or the 15 cm sIG 33. But most often, it carried the 10.5 cm leFH 18 howitzer, the others taking quite a toll on the engine.
The Sd.Kfz.10 engine was also later fitted with a air compressor for air brakes trailers and other loads, designated Ausf B. In 1943 the semi-automatic transmission was replaced by a manual one. The D7p reinforced chassis was eventually chosen to develop the armoured Sd.Kfz. 250 light armored personnel carrier, with a shortened suspension.
1944 production version
Demag was tasked to rework the design completely in 1944: The vehicle was to be fitted with the following:
- Ten road wheels
- Strengthened front axle
- Strenghtened idler crank arm
- Improved track tensioner
- Increased ground clearance
Three prototypes were completed, but only the first two were delivered in September 1944 for field tests, the last remained a the factory. Its Development did not went any further. In between a new version of the Sd.Kfz. 10 was proposed as part of the Emergency Development Program (Entwicklungs-Notprogramm) on 20 February 1945. It was given an armored engine and driver's compartment, the development was scheduled to be completed in June 1945, but of course was stopped in May.
Production Facilities
Six factories, outside Demag, were contacted to assemble various models and more suppliers in the loop. Demag alone built only 1,075 vehicles until November 1942. Adler-Werke completed 3,414 mdels, started also in 1938 and until December 1943. Büssing-NAG built 750 vehicles until December 1942, MWC 4,750 (starting 1939) until November 1944, Mühlenbau (MIAG) 324 vehicles also between 1939 and 1941. Maschinenfabrik Niedersachsen Hannover (MNH) delivered 600 vehicle between 1939 and November 1942 and Österreichische Saurerwerke 3,075 vehicles from 1940 to December 1943. Demag and MWC produced the D7p chassis also for the Sd.Kfz.250 in 1945 but only 276 were completed, and with wooden upper bodies... 80 were delivered by 1 March 1945, including 310 chassis for the Sd.Kfz.252 and Sd.Kfz.253 specialized vehicles.
Main variants
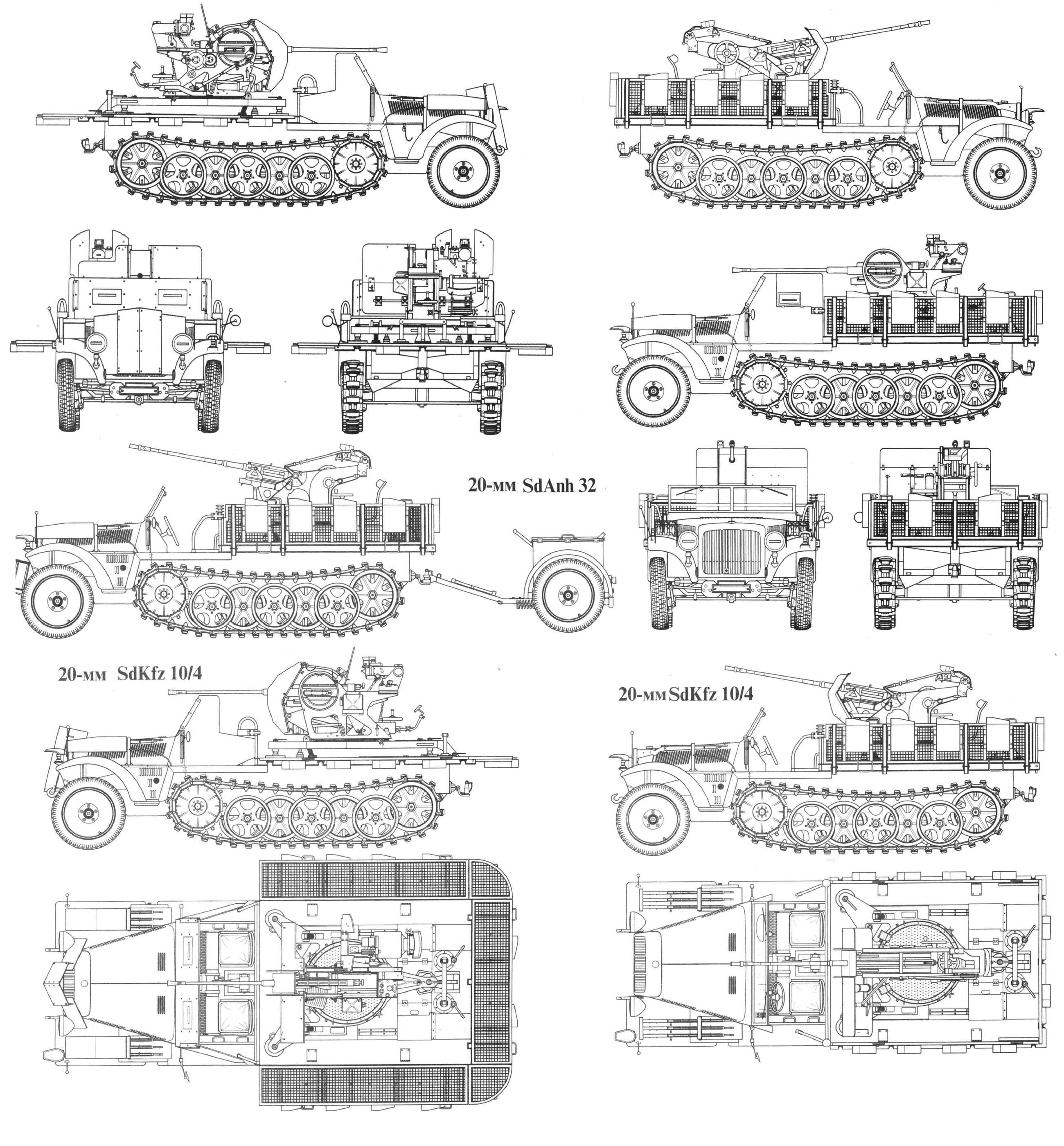
Sd.Kfz. 10/1
Chemical detection vehicle, one of the first tasks of the vehicle, planned in 1938: 90 were planned for delivery in 1940–42 as primary vehicle of the Nebeltruppen, but on 3 May 1940 production was revised for 30 vehicles monthly to reach 400, instead of 10 per month. MWC was tasked of this, but a report later mentuions only ten vehicles delivered by 15 January 1943 and few more afterwards, until cancelled.
Sd.Kfz. 10/2
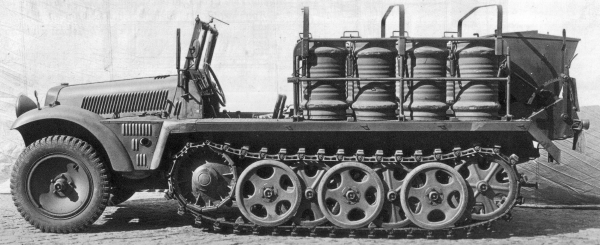 SdKfz10-2S_chemical_decontamination_vehicle
SdKfz10-2S_chemical_decontamination_vehicle
Chemical decontamination vehicle: Complementary to the Nebeltruppen, it was fitted with a 200 kg (440 lb) capacity spreader and carrying 50 kg (110 lb) barrels of decontamination chemicals, served by two crewmen on a bench seat between barrels on the rear chassis wall. Each barrel covred around 160 m2 (1.1 by 175.0 yd). They were stowed on suspended platforms to avoid vibrations and foldable outer rails. The 10/2 also was modified with two fuel tanks for 86 litres (23 US gal) in all and a tunnel to accommodate an auxiliary driveshaft powered the spreader. Range was only 250 km (160 mi). The 10/2 measured 4.83 metres (15.8 ft) long, 1.9 metres (6.2 ft) wide, 1.95–1.7 metres in height. Weight was 3,890 kg and up to 4,900 kilograms (10,800 lb) fully loaded with the barrels and crew. The spreading was done at around 10–20 km/h (6.2–12.4 mph). Sixty vehicles built in 1938–39.
Sd.Kfz. 10/3
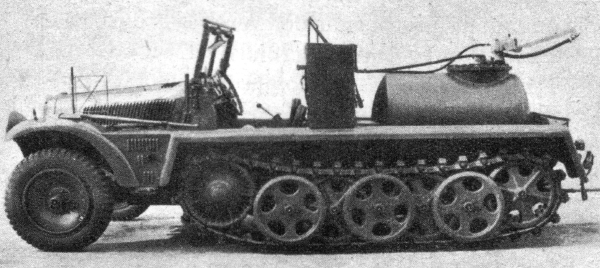 SdKfz10-3_chemical_sprayer-vehicle
SdKfz10-3_chemical_sprayer-vehicle
Another chemical batallion vehicle, fitted with a 500 litres (130 US gal) tank and a spray system, to create poison gas barriers. The spray nozzle swung back and forth and spread the gasified liquid over 16 metres (52 ft). 67 vehicles were built in 1938–39. On 15 April 1942, the Oberkommando des Heeres orfered these in storage modified completely to carry instead 216 rounds of anti-tank ammunition, and later issued to recreated Nebeltruppen units at the front, used as carriers for the Nebelwerfer rocket launchers, units with organic anti-tank guns.
Sd.Kfz. 10/4
The first SPAAG or FLAK vehicle, with a 2 cm FlaK 30 mounted on a special platform aft, with fold-down side and rear panels to allow the gun servants to walsk around. This platform was specifically tailored for the 20 mm and could not be used for a Flak 38 mount. The vehicles was also wider and taller 2.02 metres (6.6 ft) wide, 2 metres (6.6 ft) high, for 4,075 kilograms (8,984 lb) empty. It was iven four folding seats for the crew on the platform as well. During the war, gun shields were fitted on these mounts as the vehicles were used more and more as close support for the infantry, notably in urban theaters.
Ready ammunition bins were fastened to the side and rear panels, six in all, containing each a single 20-round magazine, so 120 rounds total. To carry more round and gun service maintenance tools it also towed the ammunition trailer Sd.Ah. 51 (Sonderanhänger), called a special single-axle trailer. It was loaded with a total of 640 rounds but also te sensible gun's sights when travelling, as well as its rangefinder and spares.
Those built in 1940 had removable loading ramps and cable rollers (pulleys) to dismount the 20 mm FLAK, as well as a reinforced tail gate. The Flak 30 could then be mounted on the Sd.Ah. 51 trailer. They also were given welded-on rifle racks over the front fenders. From 1942 they were partially armored, with light sheet metal covers as protection. Production went on a greater pace in 1941 and gun shields became mandatory in 1942 also, but swapped on the 10/5.
Sd.Kfz. 10/5
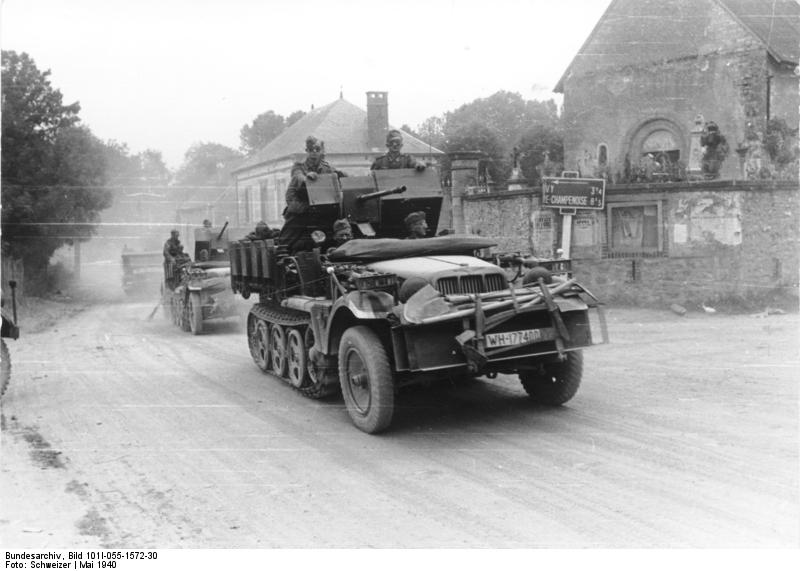 Sd.kfz 10/5 2cm PAK 30 FlAK at Ortschaft france, 1940
Sd.kfz 10/5 2cm PAK 30 FlAK at Ortschaft france, 1940
Improved SPAAG, 2 cm FlaK 38 carrier: The platform was wider and lighter compared to the Flak 30 while the platform itself was enlarged. Production started in 1942 with the vehicle width increased to 2.156 metres (7.07 ft). The first specific denimonation was given in 1 September 1943, although the OKH still called it the 10/5 until 1 December 1944. The Luftwaffe on its part was interested to acqyire the vehicle to cover the approaches of its advanced airfield and ordered 293 sets of armor plate (Behelfspanzerung) in 1943 to be fitted on the field. They covered the radiator, windshield and both sides of the driver's cabin. Some also were retrofitted to the 10/4.
Production of the 10/5 started in 1939 for both the Army and Luftwaffe but production figures are still ellusive to this day. Adler listed 1054 until February 1943, some as 0/4 and others as 10/5s in 1942. MWC order was 975 10/5s but in 1944, only 13 were delivered, completed as regular Sd.Kfz. 10s instead.
Pak36/38 Auf Sd.Kfz. 10
 Kettenfahrzeug 3.7 cm Pak36
Kettenfahrzeug 3.7 cm Pak36
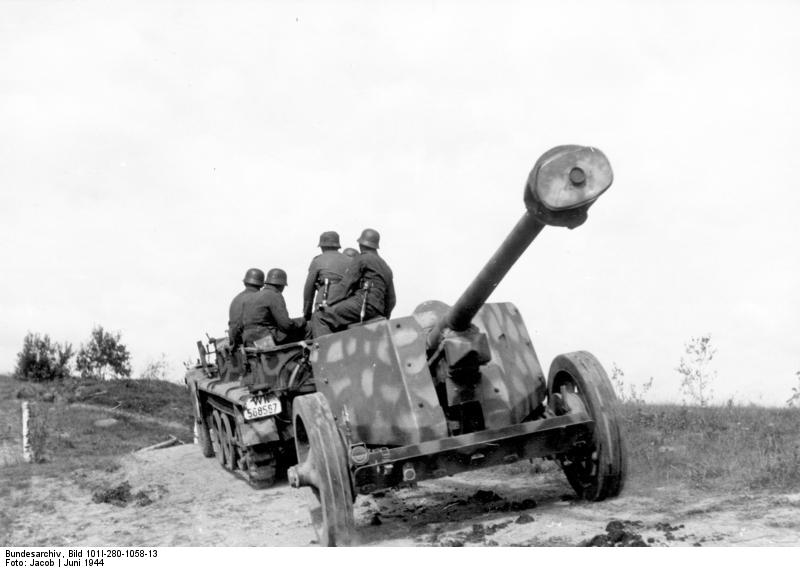 Halbkettenfahrzeug mit 7,5 cm Pak in Russia 1942
Halbkettenfahrzeug mit 7,5 cm Pak in Russia 1942
These were never given official names but stayed as field modifications: Some vehicles were fitted with a 3.7 cm PaK 36. Others with a 5 cm PaK 38 anti-tank gun installed on a special mount over the rear flatbed. Some also received cab and armored engine compartments, on site and without following a centralized scheme so they diverged greatly in appearance. The Pak 36 was small enough to be mounted complete, and so to be dismounted with ease, but the Pak 38 was stripped of its wheels and legs and instead placed on a pivot mount. In 1945, a few were reconverted to carry the triple-mount ("Drilling") MG151 autocannon, placed on a conical pivot, identical to the one used on the Sd.Kfz. 251/21 (no photo found).

Up-armoured Sd.Kfz.10 mit 3.7 cm PAK 36 tank hunter, Krueger Horst, Flickr
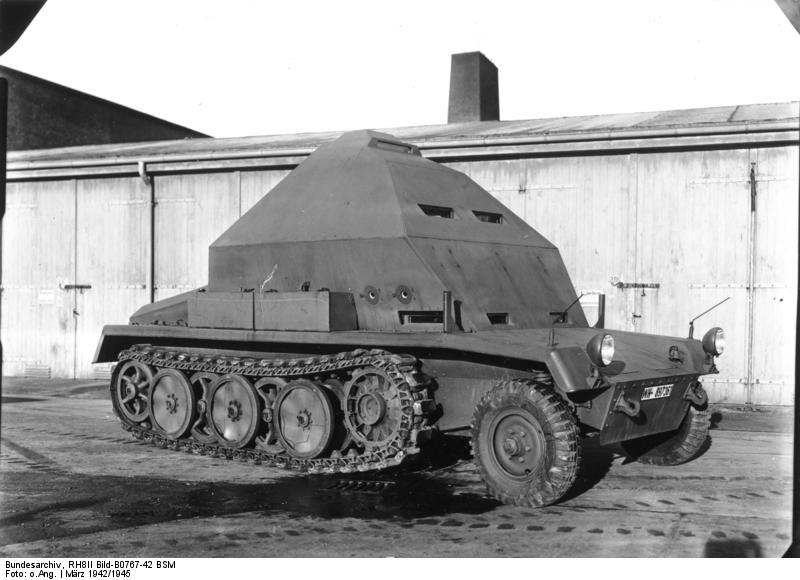

RH-8 II derived from the SdKfz 10 as Feuerleitpanzer (Rocket Launch command vehicle) at Pennemunde
The Sd.Kfz.10 in combat
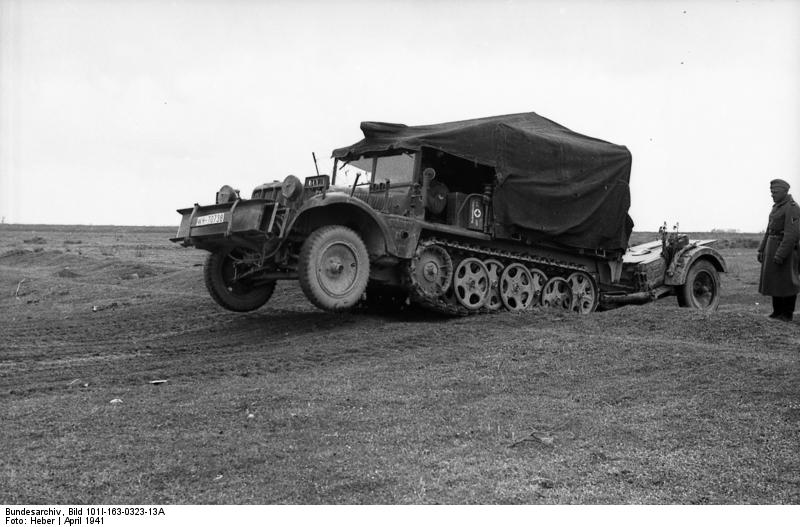 SdKfz 10 in Greece, May 1941
SdKfz 10 in Greece, May 1941
Needless to say with as many vehicle as the better known Sd Kfz 251, the Sd.Kfs.10 was present on all fronts during the war, from Poland to France and the low countries, the Balkans, Russia, and North Africa.
Organic antitank units:
Initially, the Sd.Kfz.10 was a specific light gun prime mover, using trailers carrying ammunition, but later it became an ersatzkraftwagen, a substitute for the Sd.Kfz.250 by the fall 1939. It filled the same role in the same units. The Sd.Kfz.10 Ausf.B was reinforced for towing the 5 cm PaK 38 and its ammunition trailer. Others Sd.Kfz.10 were used on the maintenance and supply companies in motorized ad Panzer units. Nine were also exported to Romania in 1942, as tractors for their anti-tank guns and service in Russia.
Nebeltruppen:
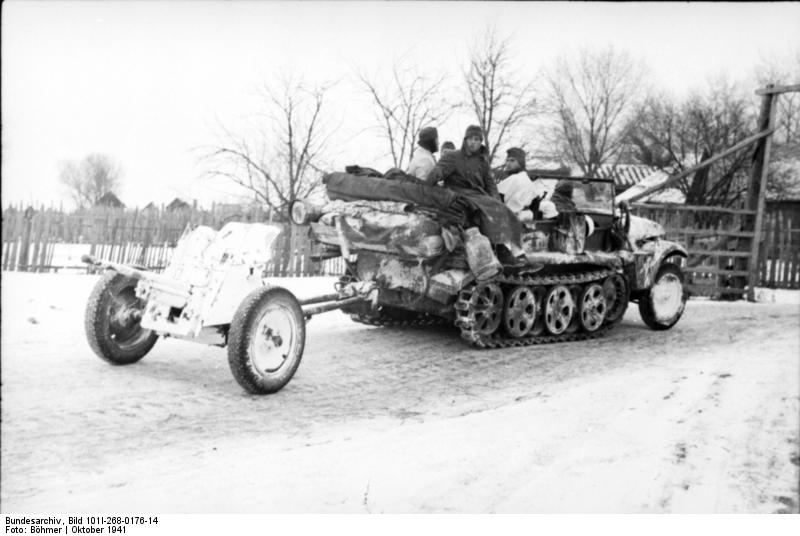
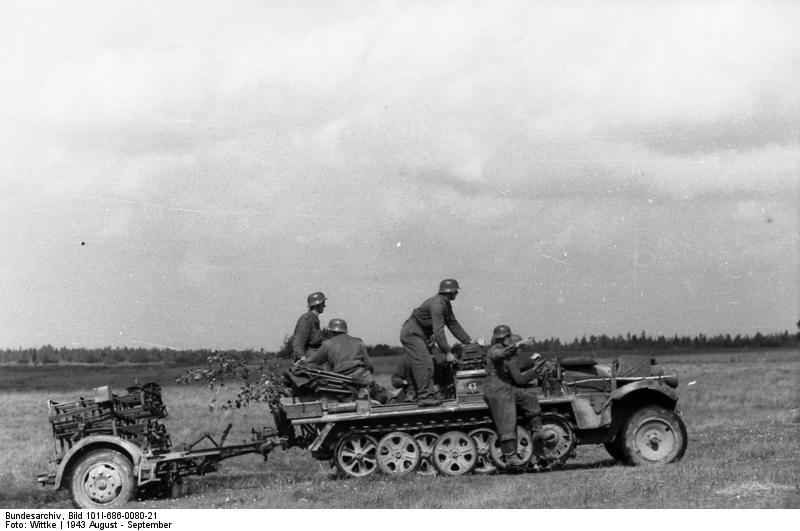 Russia, sdk.fz.10/1 mit Nebelwerfer
Russia, sdk.fz.10/1 mit Nebelwerfer
Another known user was the Chemical Troops, or "Nebeltruppen". They were the prime movers of decontamination battery ("Entgiftungs-Batterie") and each was given six Sd.Kfz. 10/1 and six Sd.Kfz. 10/2. Another eighteen Sd.Kfz. 10/3 were held at battalion level to replace their Sd.Kfz. 10/2s in case. The Sd.Kfz. 11s could also be used as substitutes. By November 1941, chemical warfare was no longer a priority and all batallion were reconverted as rocket launcher ones for support. This time, each unit had seven Sd.Kfz. 10/1s towing the 28/32 cm Nebelwerfer 41. One more was used as platoon leader vehicle, towing an anti-tank gun to defen the perimeter in case of a counter attack. Decontamination units retained their Sd.Kfz. 10/2s also but also used for toiwing rocket launchers, stripped of all their special equipment.
FLAK Batteries:
Another early-war role was for the anti-aircraft company (Flugabwehr-Kompanie). Each was organized in three platoons sharing eighteen Sd.Kfz. 10/4s between them, not all mountng a 20 mm FLAK 30. Only 12 were so indeed, the remainder six carrying ammunition. In 1941, the four-barrel 2 cm Flakvierling 38 arrived and 1941, each platoon had also four Sd.Kfz. 10/4s towing guns and ammunition in trailers. They were reorganized with eight Sd.Kfz. 10/4s each plus two towing Flakvierlings and three with ammunition. In 1942 also, Sd.Kfz. 10/5s were substituted for 10/4s. It is unclear how the Luftwaffe organized its light anti-aircraft units, most likely in 9-12 vehicles units.
Exports: The Swedish Artilleritraktor m/40
In September 1939, Sweden although still strickly neutral wanted a rapid upgrade of its military and imported from Germany Artillery guns, notably the 10.5 cm leFH 18 for which towing vehicles were necessary. The deal to acquire the Sd.Kfz.10 was secured in the winter of 1939/1940, deliveries starting in 1940. Part of the order was also filled by classic Klöckner-Deutz A330 4x4 trucks. The rest was made of earlier D7 halftracks. They were slightly adapted to act in sub-arctic climate. These twelve Demags were delivered in the autumn of 1940, along with twelve guns for 8th Artillery regiment based in Boden (arctic circle).
They were locally called "Artilleritraktor m/40" abbreviated "Arttrak m/40". The Swedes were pleased with them and ordered more in 1941 but it proved impossible. Volvo was tasked to reverse-engineer the vehicle to be called the "Artilleritraktor m/43" or internally "Volvo HBT". They were obliged to have common track links, interchangeable with the Demag vehiicles. Although they were produced they were stored, as well as the twelve surplus vehicles purchased in 1946, for a total of 24 Sd.Kfz. 10 used for training gun crews until the early 1960s. In 1966 they were all sold to avid collectioners at the Kalix airfield. The was sold in 1992, fourteen since were repurchased by private collectors and museums.
Links about the Sd.Kfz.10
The Sd.Kfz.10 on Wikipedia
The Sd.Kfz.10 on wikipedia.com
On panzerserra
Commons
ww2 photos gallery
On forosegundaguerra.com
On asphm
The Sd.Kfz.10 on weaponsandwarfare.com
D.B. Sd.Kfz.10 specifications |
| Dimensions | 4.75 m (15 ft 6 in) x 1.93 m (6 ft 3 in) x 2 m (6 ft 6 in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 3,400 kg (7,500 lb) |
| Crew | 2 (driver, co-driver) + 8 troops |
| Propulsion | Maybach HL42 TRKM 4.2L 6-cyl. water-cooled petrol 99 hp |
| Top speed | 65/25 km/h (40/16 mph) road/off-road |
| Payload | 1,250 kg (2,650 lb) |
| Transmission | 7 + 3 speed Maybach Variorex SRG 102128H |
| Suspension | Torsion Bars |
| Maximum range (on/off road) | 300/150 km (190/93 mi) |
| Armament | None, see notes |
| Armor | 6 mm (0.2 in) |
| Production | Demag, Adler-Werke, Büssing-NAG, MWC, MNH, MIAG, Saurerwerke 1938–1945 - 15,000 Reichmark |