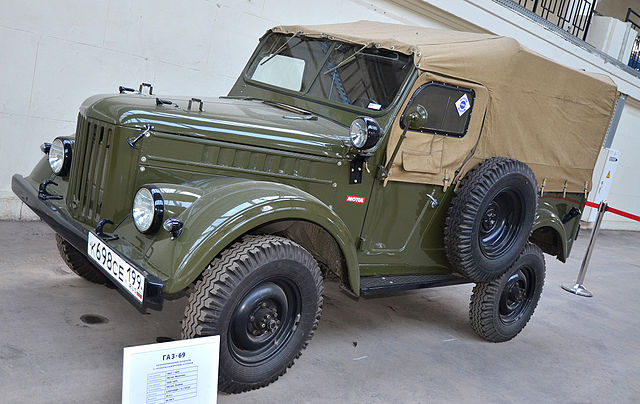
GAZ 69
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
Light 4x4 Car (1953-72) - 600,000 built
"Kozlik", the legendary soviet cold war jeep
The GAZ-69 and GAZ-69A were the main cold war Soviet off-road military utility cars, produced from 1952 to 1973. They had been created by a team of designers of the Gorky Automobile Plant (F.A. Lependin, G.K.Shneider, B.N. Pankratov, S.G. Zislin, V.F.Filyukov, V.I. Podolsky, V.S.Soloviev, under the leadership of G.M. Wasserman). The goal was to replace the
GAZ-67B. Development started already in 1946, and prototypes were produced from 1948 onwards, called "Workers". Serial production started from August 25, 1953 and went on at GAZ plant until 1956, transferred afterwards to the renamed Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant (UAZ). The GAZ-69 and its variants was popularly called "goat" or "gazik". It received hundreds of modifications either to its body (Pobeda monocoque) or equipments, taking numerous roles, including armed versions such as the 2P26 antitank version. After two decades more than 600,000 left both factories, exported to 56 countries and licenced produced by ARO in Romania and North Korea from 1962.
Design of GAZ-69
The previous GAZ-67, the "russian jeep" was design from 1942, much inspired by the lend-lease Jeep, by GAZ. It was related to the GAZ-64 (1940) of which only 840 were made, but also shared many components wit the scout armoured car
BA-64. The GAZ 64B succeed in 1944 and became the main production version until 1953, with a total of 92,843 vehicle. The next GAZ 69 was to adress many issues of the open F4 layout vehicle, more enclosed and sturdies, and possibly with amphibious characteristics, better engine and improved off-road capabilities.

The previous GAZ-67B
Engine & transmission
The GAZ-69 was given an in-line 6or inline 4 cylinder engine from Gorky Automobile Plant, having similarities with the GAZ-11. Its fundamentals were:
- Lubrication system's inertial oil air cleaner
- Two-section cardboard automobile super-filter-sump
- Full-flow slotted coarse filter with a sump
- Dry, single-plate clucth.
- 3 speed gearbox, 2 ways, synchromesh 2-3 gears
- floor gearshift lever spec. arrangement
- 1.15 and 2.78 gear ratios transfer case
- Three cardan shafts
- Conical main gear, two satellites
- Car tire sizes - 6.50-16
- Left Preheating boiler

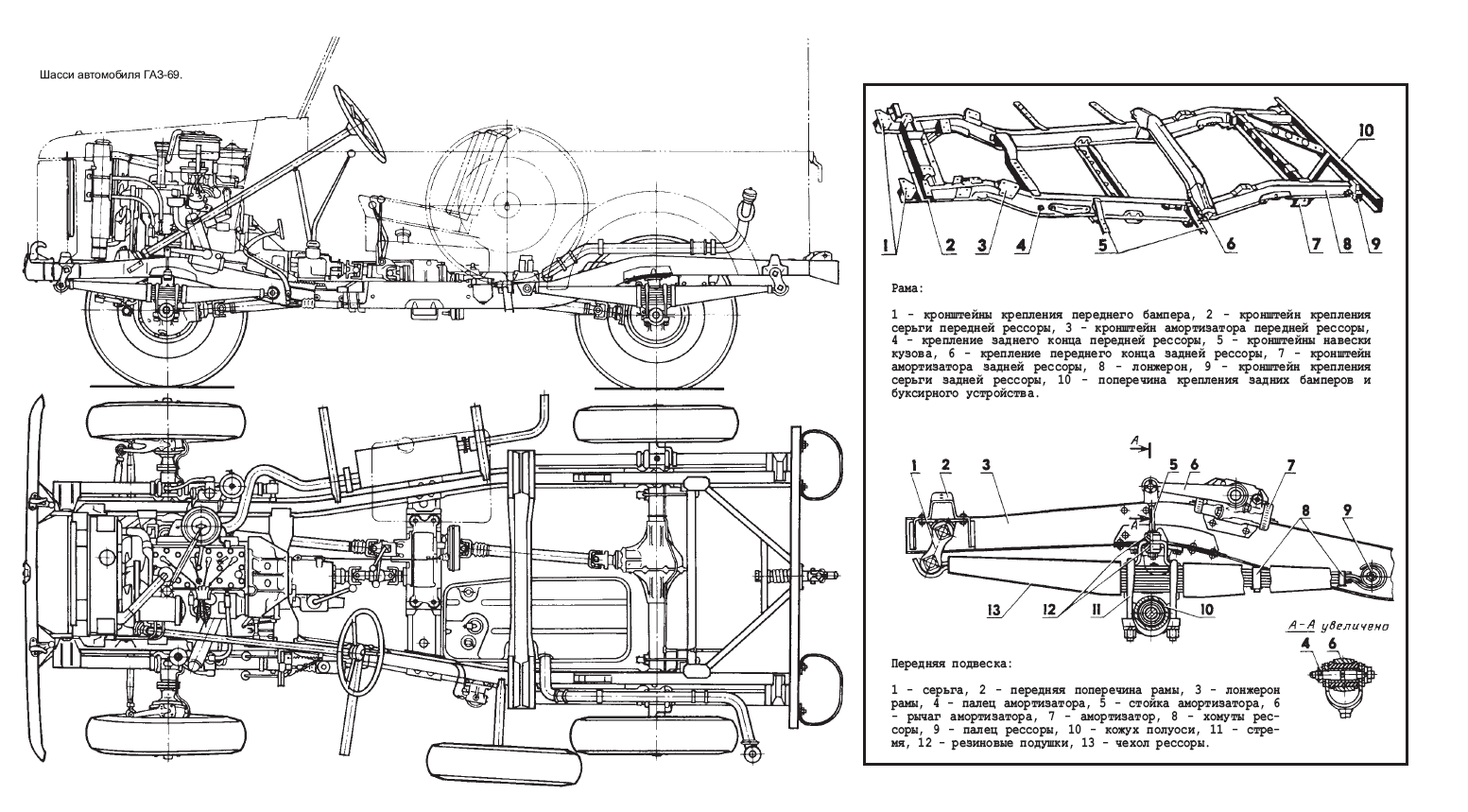
The gearbox was essentially similar to GAZ-M-20 Pobeda car but differed by its floor gear shifting mechanism; not on the steering column as for the Pobeda. For the transfer case, the low gear (2.78) can only be engaged after engaging the front axle. There were also three cardan shafts, intermediate rear and front and the main gear was a single conical model with spiral tooth. It was coupled with a differential with two satellites and the half-axles were completely unloaded. The front axle hubs could be disengaged for slightly reducing fuel consumption on well-paved roads. The driver had for this to unscrew the protective cap with a tubular socket wrench (same to adjust the hub bearings) and connect/disconnect the coupling. On early vehicles, the torque was transmitted to the hub via a tapered “cap”.
In winter, a preheating vessel mounted left, under the hood was procured, but it was still necessary to turn the steering wheel to the right for opening hatch in the fender, inserting a working blowtorch in the tube to ignite the vessel. The cooling system warmed up enough so that the engine oil was further warmed by hot gases. When the "dry" engine was heated, 5 liters of water were poured into the vessel, followed by gaz heating before starting the engine, and adding further water to the radiator. In maintenance, to retire the transfer case and gearbox the floor needed to be removed.
Body
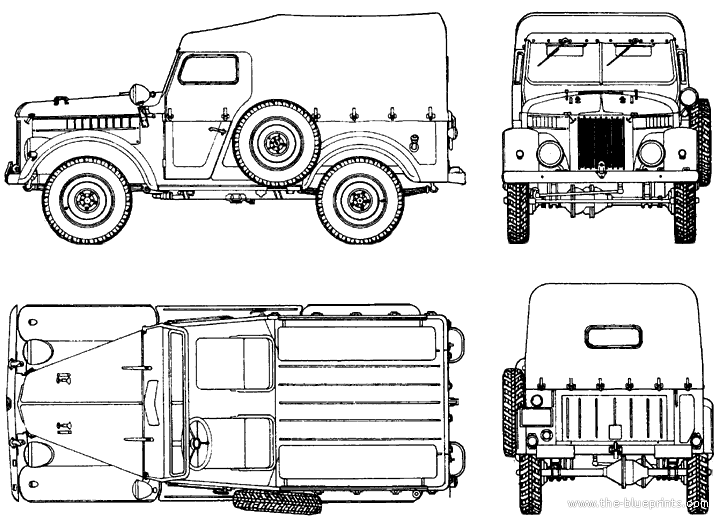
The body of the GAZ-69 and GAZ-69A was open with a folding windshield and removable metal frame. The upper sidewalls had fittings for a foldable tarpaulin on metal arches, with inserts of transparent glass. The body was referred to as "phaeton" on the grounds of removable, and not lifting side windows. The windshield frames cooled the interior but protected poorly against road dust. The windshield could be completely folded back onto the hood brackets, fixed with hooks when in fully open, hot climate configuration. A crew heater was located in the passenger compartment, which supplied warm air to the windshield via an electric fan. Warm air was also blow to the floor, warming the feet of the driver and passenger when moving through the air intake opening, behind the hood. The hood side panels were fully removable, facilitating engine cooling in summer.
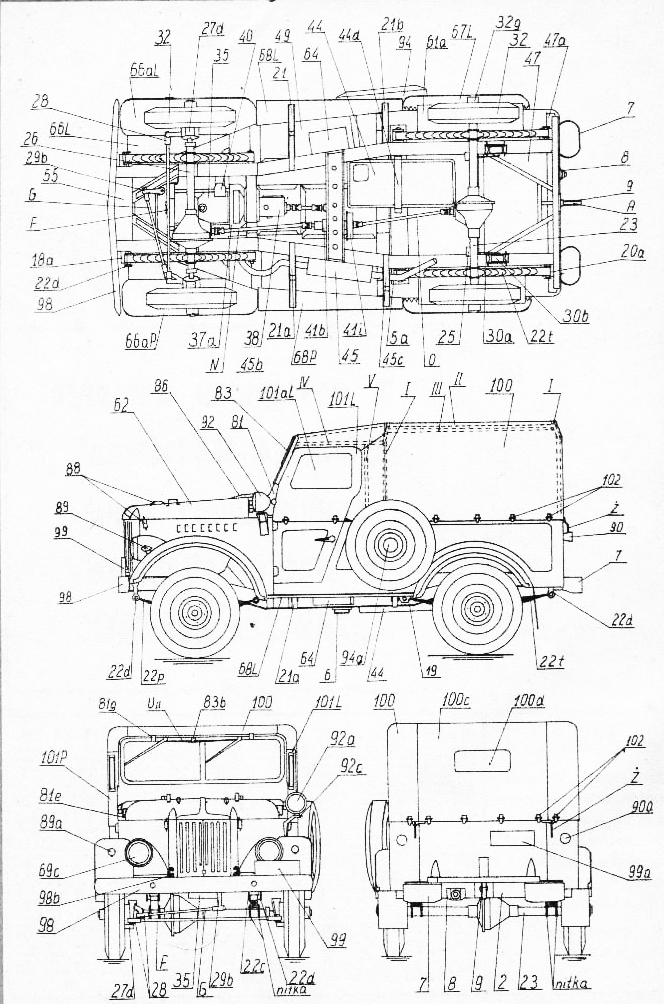
Technical schemes extracted from the original manual. Src:
smcars.net
The GAZ-69 basic layout was of an eight-seater body: The driver and one passenger sat in front, and six passengers sat on two three-seat benches. Tool boxes were managed under these benches. The GAZ-69 coild also transport wounded men on a sanitary stretcher: For this, the backrest of the front passenger reclined forward and the stretcher was mounted on the passenger handrail and back. The accompanying paramedic was seated on the left side bench. The left driver's door was narrower than the right passenger door, and shaped differently. The spare wheel was located behind the driver's door, on a bracket.
Differences on the GAZ-69A: It was a four-door, five-seater. From the passenger compartment, access to the engine was dfficult. The engine used a coarse fuel filter (with a sump) and fine fuel filter mounted over the fuel pump. The driver measured the gasoline level in the main fuel tank through a dipstick behind the transfer case levers. The base GAZ-69 additional fuel tank was placed under the passenger seat, eliminated on the A type. Ventilation of the additional fuel tank went under the body floor. Refueling was done only when the passenger door was open, which was problematic in confined spaces. The instrument panel had a sensor showing the amount of fuel, but only in the main tank. For the additional tank this was manual, by checking the filler neck. There was also a fuel tank switch on the floor of the driver's seat. The chassis was also slightly inclined forward, with a front overhang angle of - 45° and rear overhang angle of - 35°.
- Double, hinged tailgate
- Side internal storage for towing cable, stop sign, other equipments
- One gravity fuel tank (A), two for the GAZ-69
- Coarse fuel filter with sump
- Main gasoline tank sensor
Final design
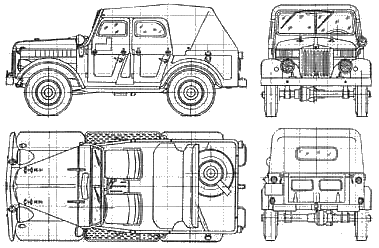
GAZ-69A - The blueprints
The GAZ-19 and GAZ-19A were very close as each had a rear-wheel drive with a carrying capacity of 600 kg, same dimensions and wheelbase. The first
Prototypes of both the GAZ-19 and GAZ-19A were built in Gorky, in 1955. They shared the exact same body, all-metal, with the same side doors, roof and double-leaf tailgate. The GAZ-19A however had glazing to carry extra personal at the rear. Instead of glass, the GAZ-19 stamped metal and plastic for the body panels. The GAZ-69 was more of a staff car for officers, but with possible use as urban delivery van. The GAZ-69A was more of a PC (Personal Carrier) (unarmoured).
So the base GAZ-69 featured two fuel tanks, one 47 litres (12 US gal; 10 imp gal) under the floor and one 28 litres (7 US gal; 6 imp gal) beneath the passenger's seat. All civilian models met Army requirements in case of wartime requisitions, making the hardtop version unavailable until 1993... The basic GAZ-69 only had two doors and and canvas top also covering the upper sides, plus plastic windows. In addition to the two seats in front there were two folding benches for three passengers each on the rear section, so six plus two, eight total. Much later the UAZ-69A was given four doors and a folding canvas top, plus two seats rows; It became the basis for the rear-wheel drive van GAZ-19, whih production was scheduled to start in 1955 but never passed the prototype stage. The off-road van/light truck UAZ-450 and UAZ-469 also derived from the GAZ-69.
 GAZ-69 Black Fold
GAZ-69 Black Fold
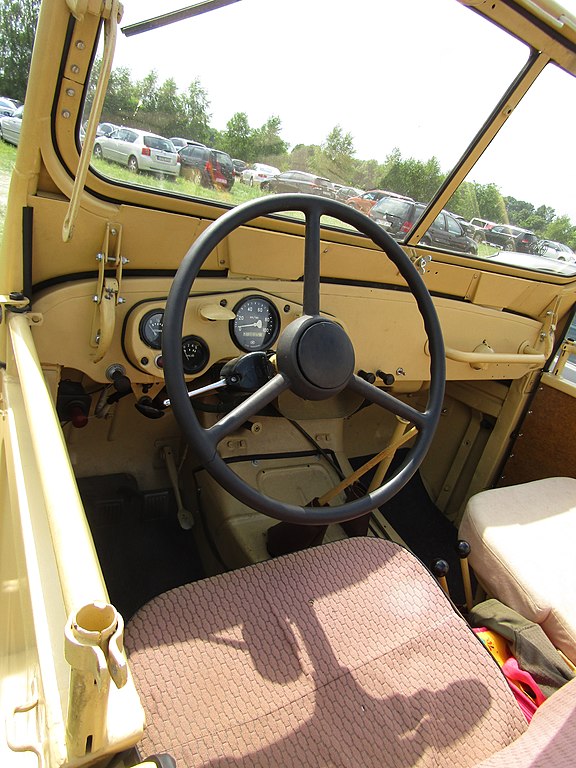 GAZ-69 Dahsboard
GAZ-69 Dahsboard
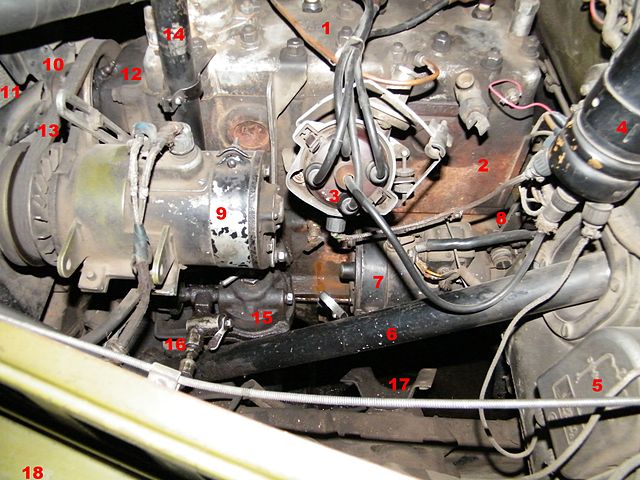 GAZ-69 engine
GAZ-69 engine
 Engine carburettor
Engine carburettor
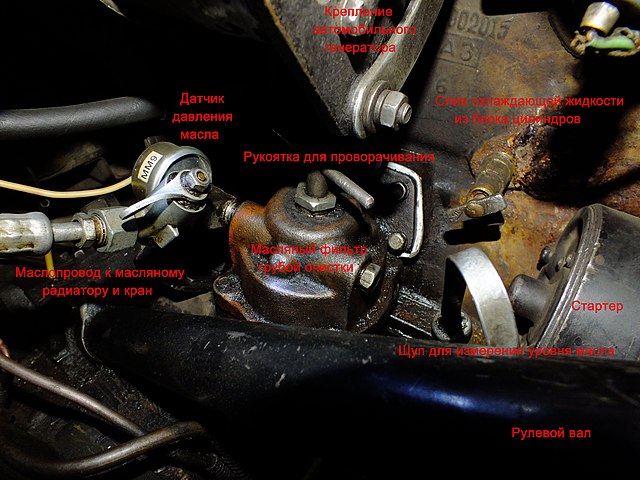 Engine detail
Engine detail
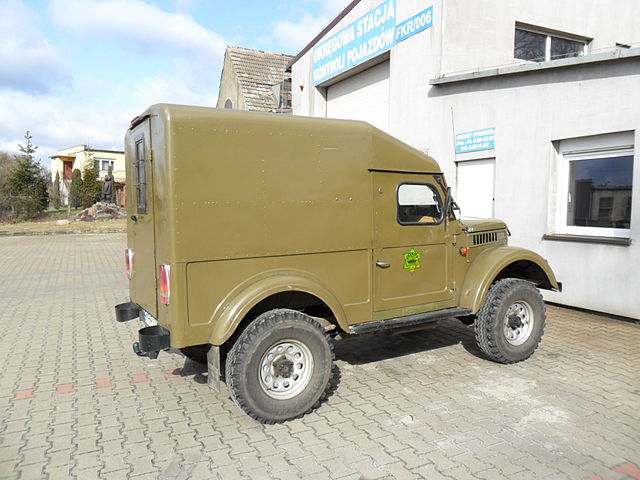 Hard Cabin
Hard Cabin
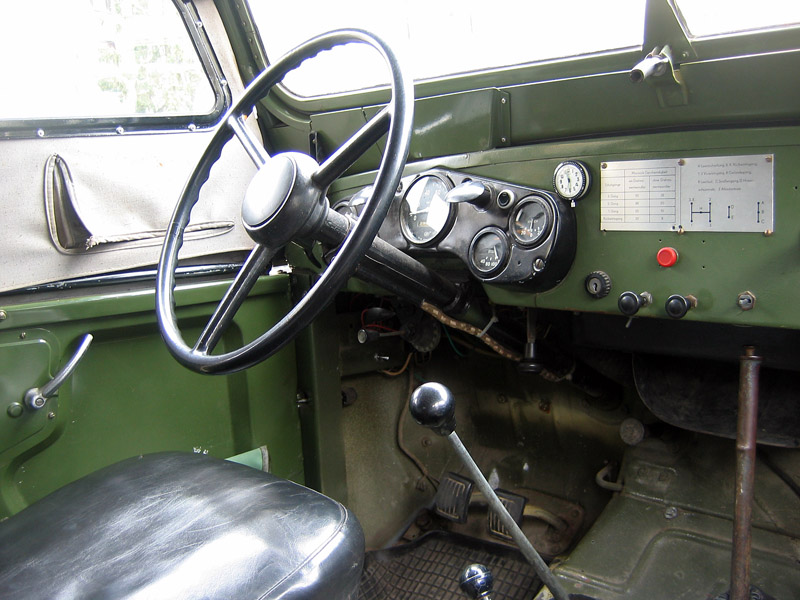 GAZ-69 Interior
GAZ-69 Interior
 Same
Same
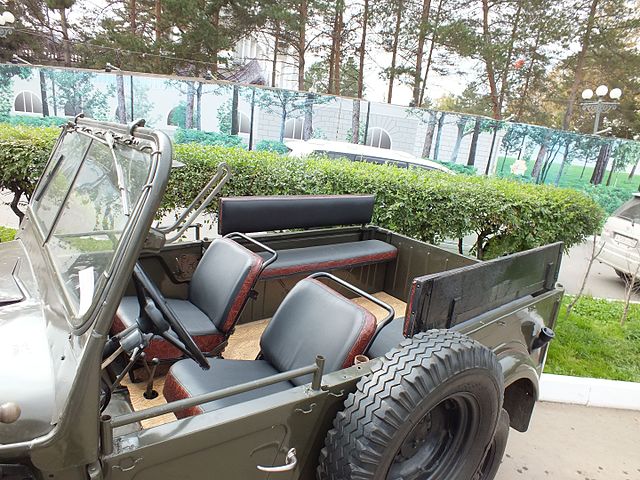 same, rear
same, rear
 Suspensions detail of the GAZ-69
Suspensions detail of the GAZ-69
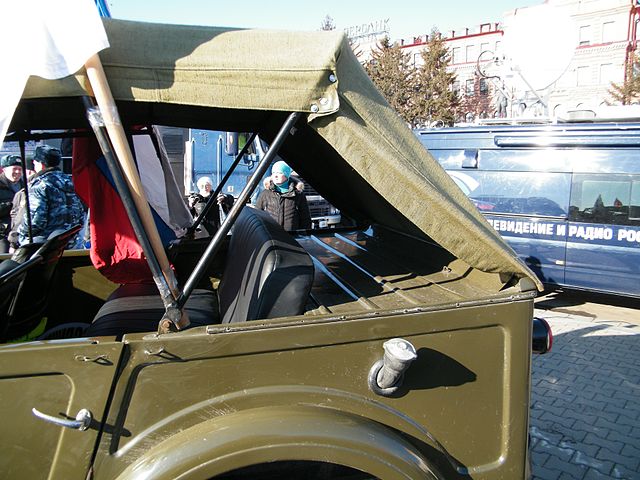 Rear details of the GAZ-69A
Rear details of the GAZ-69A
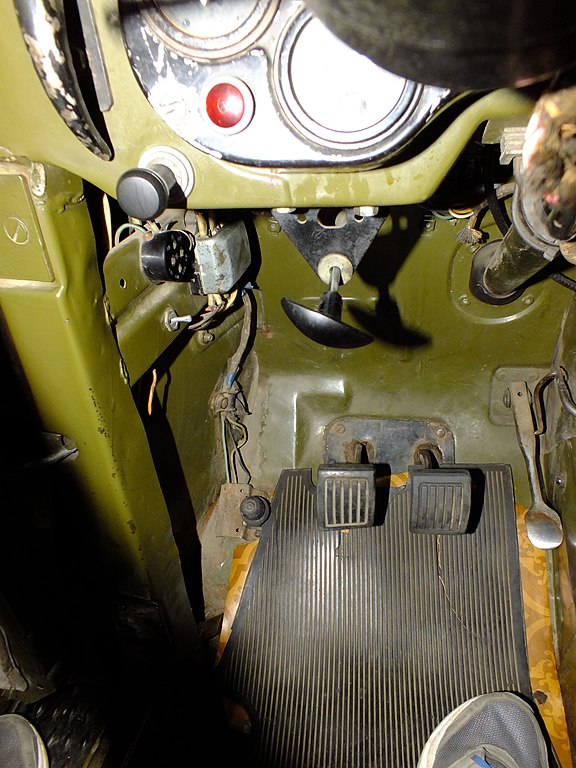 Interior of the GAZ-69
Interior of the GAZ-69
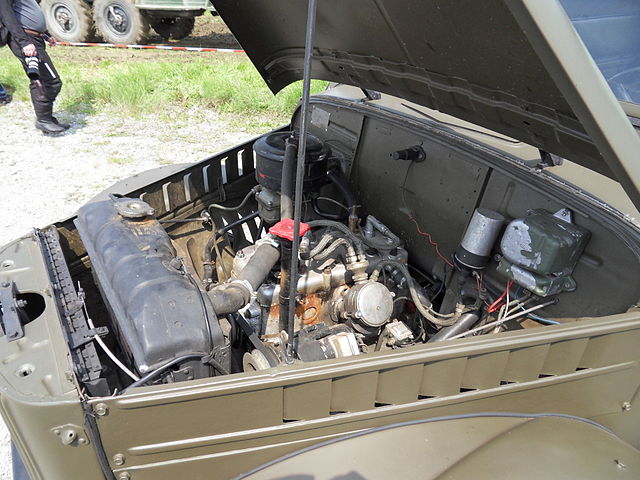 GAZ-69 Hood Open
GAZ-69 Hood Open
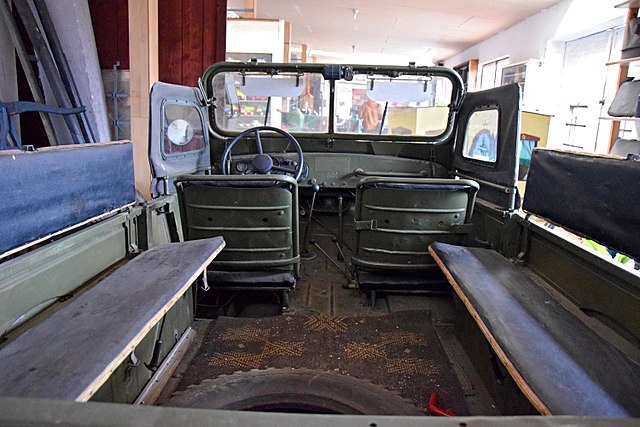 GAZ-69 aft interior at the Porezany museum
GAZ-69 aft interior at the Porezany museum
Serial Production
 GAZ-69 Park 1969
GAZ-69 Park 1969
Serial production was hampered as dies and molds of the Gorky plant were already fully used. A number of new models were in development. The relatively small need for a vehicle of this type also played against the GAZ-69 making the production setup economically relatively unprofitable. In addition, production of the GAZ-69 was already planned for transfer to the Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant, which made the development of modifications at the Gorky plant irrational. In Ulyanovsk plant, a more advanced design was developed, soon called the UAZ-450, with a wagon layout. It compared well with the GAZ-19, between the new engine hood layout and somewhat irrational body length which looked rather outdated. Subsequently, a small-scale production chassis was deployed.
The GAZ-69 in service
The GAZ-69 became the basic light off-road vehicle of the Soviet Army. In about ten years, it replaced the previous GAZ-67s and lend-lease WW2 Willys Jeep. They served bot as light transport and staff cars unti replaced by the UAZ-469 in the 1960s. The GAZ-69 was a softskin vehicle, unarmed (outside personal weaponry). Indeed, able to carry eight personal, so a half-section, armed with Kalashnikov and Manpads was still quite an ofensive proposition. However the GAZ-69 was also used as the basis for the 2P26 light tank destroyer (see below) and GAZ-46 MAV, a light 4x4 amphibious vehicle inspired by the WW2 Ford GPA 'Seep' also provided by lend-lease.
Variants of the GAZ-69
 GAZ-69
GAZ-69
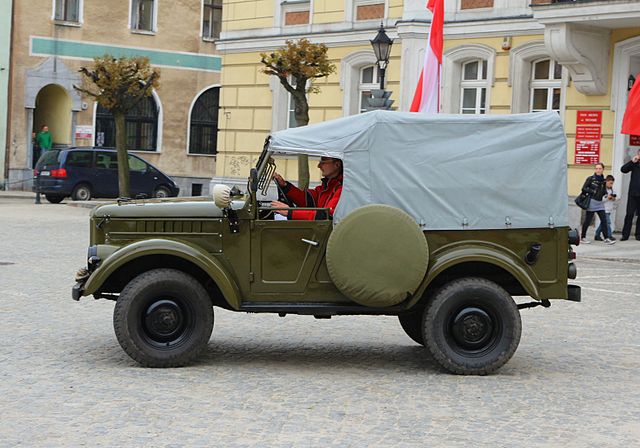 UAZ-69 in 1958
UAZ-69 in 1958
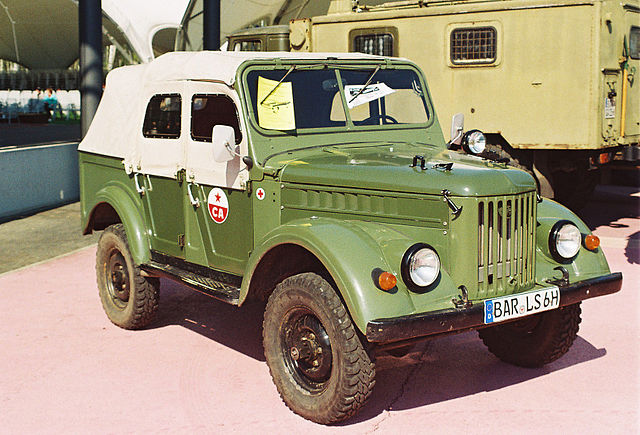 UAZ 69 A
UAZ 69 A
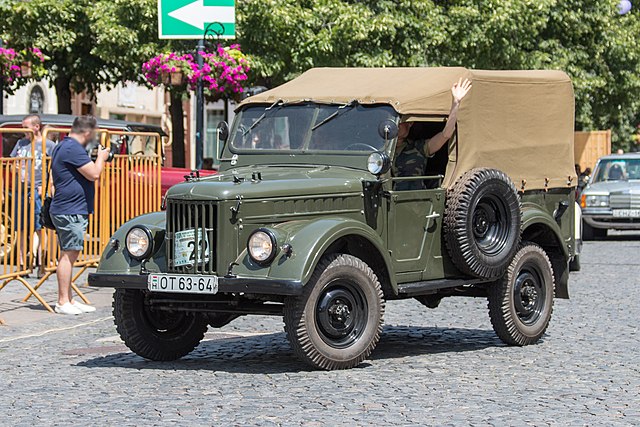 UAZ-69
UAZ-69
GAZ-69
Basic vehicle, 2 doors, 2+6 men (2 seats, 2 banks), 2 fuel tanks, canvas top, unarmed.
GAZ-69A
4 doors, folding canvas top, 2 rows of seats.
UAZ-69
Same as the 2-door GAZ-69 but made by UAZ.
2P26
Antitank version developed between 1957 and 1960, produced from 1961. Called 2P26 (GRAU), carrying the 3M6 Shmel ATGM (AT-1 Snapper ATGM). The aft part of the vehicle has a flatbed on which was installed up to six launching rails, mounted on a pivot allowing traverse and elevation. The mount culd be entirely covered by the tarpauling to disguise its true purpose. It offered an excellent mobility and antitank capability to Paratroopers. This version will be covered in detail in a dedicated post.
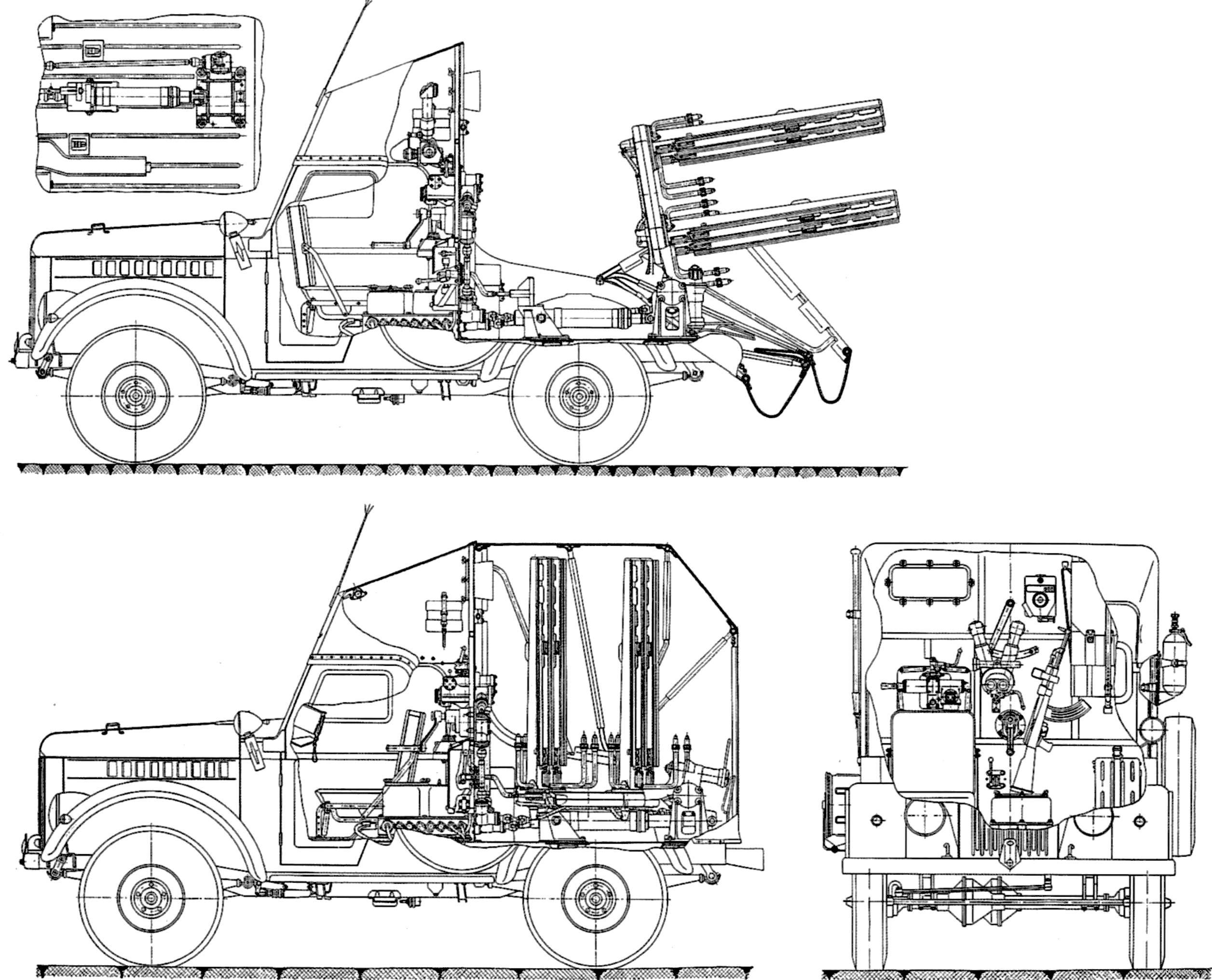 GAZ 2P26 Tank destroyer, armed with the 3M6 Shmel (AT-1 Snapper).
GAZ 2P26 Tank destroyer, armed with the 3M6 Shmel (AT-1 Snapper).
GAZ-46 MAV
The military amphibious car, which will be covered in detail in its own post. It was given a boat-like hull and sealing around the chassis, a4 cyl petrol, 2112cc GAZ-69 engine, vcoupled with the same 3-speed manual transmission with 2-speed transfer case, but of course was much heavier, with degraded performances as the base vehicle was already plagued by a low power-to-weight ratio with a weight of 1270 kg (GVW: 1770 kg). It was propelled in water with a PTO propeller drive. It shoud be noted that like the US, the Soviet army also wanted an amphibious truck, which became the BAV, copy of the DUKW.
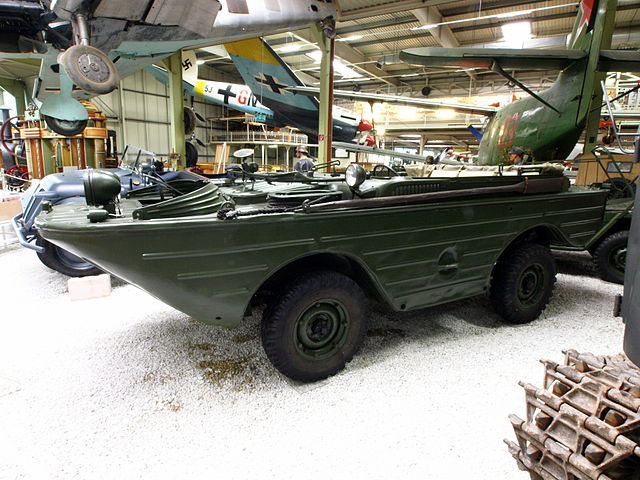 The GAZ-46 was the Soviet cold war equivalent to the WW2 US Ford GPA, the infamous "seep".
The GAZ-46 was the Soviet cold war equivalent to the WW2 US Ford GPA, the infamous "seep".
Export and military use
The simplicity and low cost of the vehicle allows exports to take place in the follwing countries (in addition to delivery to the Warsaw Pact countries): Bulgaria, Cambodia, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Egypt, Hungary, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel (Captured), Poland, Syria, Vietnam. They saw action in the two 1967 and 1973 middle east wars with Israel, in Cyprus, during the iran-Iraq war in the 1980s, Indonesian civil war, and Vietnam war. Some were even seen in action in the Syrian conflict recently, including with ad-hoc conversions. In Romania it was even produced under licence as the IMS-57, M59, ARO M461, and later in Indonesia as the Kaengsaeng 68 and Sungri 4.10/4.25.
Debunking the myth
(Translation and adaptation of
sovietauto.fr)
Nowadays, the GAZ-69 is experiencing a second peak in popularity: It is the star of classic car encounters or the guest of honor on off-road trips. A new version would be produced as announced in small series. Isn't that too much for old "Kozlik"?
The GAZ-69 has often been profoundly modified: Adapted to modern life, with manny amenities and features to facilitate maintenance and repairs. Why GAZ-69 owners are so proud of their 4x4 ? Why seven facts are still high among them ?. Debunk time !
N°1: The GAZ-69 is a true go-anywhere.
It seems true, even with its standard factory tires, offering an excellent all-terrain handling without adopting modern accessories. In a short range test, it is able to cross with confidence a 35 to 40 cm (2+ feets) deep marsh over a mile, and even pick up speed doing so. It is all possible due to the ingenious of transmission and the engine's very high torque at low speed. In addition to its front axle, the "Kozlik"'s two-speed transfer case shows short range gears having a ratio of 1.15 to 2.78. The vehicle was able to climb without hesitation a 8% snowy slope on the rear axle alone. After engaging the front axle the grip was even better an the vehicle was able to climb faster. The torque helped in this, with 123 Nm from 2,000 rpm. Fresh snow drive is smooth, whatever bumpy the terrain was, snowdrift is absent and the vehicle is able to keep the same pace while being straight. While shaking a lot in the process... Not only it coudld still run through 50 to 60 cm of snow but also water without preparation and when the fan belt was removed and gauge sealed tight, it could even ford a 80 cm deep river. The high ground clearance (211 mm at the lowest point) and angles of attack of 48° front, 37° rear also helped its off-road performances. By comparison the WW2 Jeep had 49° and 35° respectively. The main critic was its low power ratio of only 28.4 hp per tonne and limited tires choice (without central inflation system) were available. They proved unsuitable for compact snow, watery swamps and others. Both were detrimental in the 1970s when better, more mopdular vehicles were on offer.
N°2: The world's best 4x4 in 1960-70
Untrue, but granted, probably in the top two or three. It never was popular as some of its competition, but didn't need it, USSR being cutoff for said international (and western) competition. USSR indeed absorbed almost all of its production already and countries that adopted it could not afford that same competition. In the 1950s, it actually had few direct competitors other than the Willys CJ-3, Land Rover Series 1 and Toyota BJ. Indonesia, Iraq, Afghanistan, Algeria or Egypt alla dpted the vehicles and only saw its strengths, but they still carried out comparative tests with western or asian vehicles. In terms of comfort it might be surprising that the GAZ-69 outclassed the competition with its metal doors, heater. But still, it lacked door seals or a slot in the tarpaulin to adjust the search light from the interior in extreme cold.
N°3: The "goat" ("Kozlik") nickname
There was a reason behind this nickname of the "the goat". Main reason were some aspects of the suspension tuning and relatively short wheelbase. On small bumps and during hard braking, the vehicle was known to jerk back and forth a bit like a goat... Its primitive lever shocks were unable to dampen these movements while the short wheelbase brought no stabilization on the road. The UAZ-469 replacing the GAZ was unable to solve this peculiar caracteristic at the time common to all Soviet military light off-road vehicles, but also shared by early Land Rovers.
N°4: A pure military vehicle
Partially true. One one hand it was clearly designed for the armed forces. The humongus Soviet conventional ground forces of the 1960s could easily absorv all these. The tests and specs were all military-grade and between the factory and ministry, all were done under supervision of the Army and using military trailers like the GAZ-704 500 kg field canteen, light artillery and wheeled mortrars. The basic GAZ-69 was indeed used as a light towing vehicle and personnel carrier for eight total, a command vehicle and radio liaison vehicle as well. As a staff car it was perhaps too crude for upper officers... There was also an anti-tank missile carrier. The GAZ-69 was also extensively used in combat, during the Greek-Turkish was in Cyprus. It was also used a demining vehicle, mobile radio stations, guide vehicle on airfields and many other tasked adapted later. The "worker", nickname of the 1949 prototype, indicates its off-road capabilities were focused for the national economy and it was indeed used in civilian life, and beloved in deep countryside and in Siberia. Presidents of collective farms liked to use it, as well as agronomists and party workers. It was also a status symbol in a sense for these. Now it is retired in most militaries, more are found in private hands than the army.
N°5: A terrible canvas roof
True, and it's an understatement. However this critic should be recast while taking into account all of its peculiarities. Most GAZ-69 soft top were linked to its military service, and even all civilian versions were to be mobilized in case of war. Folding the windshield and the roof cover enable the vehicle became to be more conspicuous and a more difficult target to spot. It also allowed a rapid disembakation of the infantry. This tarpaulin was barely waterproof, and rapidly while driving under the rain the interior was soaked due to the absence of sealing around the canvas, while there were drafts inside the passenger compartment. Also, the loose fitting and air intakes made the interior particularly noisy above 40 kph to the point shouting was the only option. Specialized worked on these aspects recently, and notably hard roofs in small series were proposed for the police and medical services. The "hardtop" was not a military version, but a recent, civilian one. There was even a pilot GAZ-19 postal van designed for siberia but never produced. Instead, the UAZ “Bukhanka” was chosen.
N°6: The GAZ-69 could fly
True, as the GAZ-69 was designed for the military, including the Soviet forces habit ot "deep battle" paradrop tactics. Soon it was tested to be parachuted, helped by its low height, roof folded down. It was loaded into even light transport planes and helicopter, providing an excellent long range tactical mobility. Even the small MIL Mi-4 was designed to lift this vehicle. Paradropping preparations includd removing the spare wheel and bumper, installing the vehicle on a special wooden platform with many straps with rubber damper to land on any type of surface.
N°7: The GAZ-69 could swim
The base version could ford up to 80 cm (3 feets) but there was even a true amphibious version developed as the GAZ-46, or "MAV", to carry military engineers on all watery terrains, like the Pripet marshes. It was produced for only five years, 1953-1958, stopped when production of the GAZ-69 was transferred to Ulyanovsk, UAZ declining to assemble the amphibious version without serious retolling and new equipments.
N°8: Easy to maintain even under the worst climates
The GAZ-69 was designed to operate far away for repair facilities, out in the open on the most unforgiving terrain and under all climates, particularly sub-zero temparatures. And that included the north pole. The existing habit of Soviet engineers to simplify the design to its spartan core helped reduced the cost (production being always privileged above quality since Lenin said quantity was a quality). So the number of complex components and parts were kept to the strict minimum. Maintenance operations were all carried out on the field with limited support, in in agricultural machinery stations and private garages. This ease and simplicity was of course strong selling point. In addition to keep the price down, the GAZ-69 was composed of "off-the-shelf" readily available parts whenever possible. The engine, transmission, brakes, suspension all were developed from other vehicles. This reduced also the development time, avoided potential design flaws and teething probkems, but also greatly simplified the supply and maintenance chain. It was a good sample of the technical culture in USSR of that time. Read also the original source in Russian.
Read More
https://www.gaz69.org/
http://gvtm.ru/gaz-69
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%93%D0%90%D0%97-69
https://encyclopedie-des-armes.com/index.php/unites-mobiles/vehicule-leger-moderne/857-gaz-69
http://www.krasnayazvezda.com/terre/materiels/4x4/gaz69.php
https://autoclassics.us/e/gaz-69-history/
http://www.gaz69.org/gaz/HistoryEN.html
https://1cars.org/898-gaz-69-specifications-review-photo-video-price.html
https://www.curbsideclassic.com/blog/cohort-sighting-gaz-69-the-russian-jeep/
Ware, Pat. The World Encyclopedia of Military Vehicles (Lorenz Books, 2010), p. 177.
"ГАЗ 46". Retrieved 2 August 2021.
Thompson, Andy. Cars of the Soviet Union (Haynes Publishing, Somerset, UK, 2008), p. 70.
"The history of the development of the GAZ-69" (in Russian). www.off-road-drive.ru.
IMS M461, "Avtolegendy SSSR i Socstran" No. 168, DeAgostini 2015, ISSN 2071-095X (in Russian), p.3-6
Thompson, p. 176.
René Pohl: Mit dem Auto baden gehen. HEEL Verlag, Gut-Pottscheidt Konigswinter 1998
Andreev, Konstantin (in Russian). GAZ-46, "Avtolegendy SSSR" Nr 100, DeAgostini 2012