✙ German WW2 softskin vehicles & variants
Waffenamt trucks and special vehicles
 Three SdKfz 8 (a "zug") towing a disabled Tiger Tank on the eastern front. Only these prime movers were capable of this feat, and repeated as long as it was possible. These previous heavy tanks were too important to leave behind. Tracked vehicles were also used for the same task.
Three SdKfz 8 (a "zug") towing a disabled Tiger Tank on the eastern front. Only these prime movers were capable of this feat, and repeated as long as it was possible. These previous heavy tanks were too important to leave behind. Tracked vehicles were also used for the same task.
The German Army (all forces - (Wehrmacht)
see the prewar organigram - used a great variety of non-armoured vehicles during WW2.
They ranged from Zundapp Motorbikes and side-cars to mighty tank transport trucks, with a gazillon of vehicles of all sides, descriptions, age, and origin. As the German induustry was never capable to produce the required number of vehicles, the German made due with whatever material thay could find, and pressed into service a healthy number of non-German vehicles, that is, Austrian, French, Dutch, Czech, Polish, Hungarian, even Italian after the capitlation or in North Africa.
These countries had domestic production and manufacturers which were impressed in German service and under their supervision to proved the German logistic branch dependent of the OKW and in close coordination with the Waffenamt. Indeed, despite the budget of the Wehrmacht, 19 billion DM in 1939 rose several fold to €89 billion in 1944, it was mostly because the late setup of a true wartime economy and for the ground forces, costly tank developments which were arguably wasted, like the Tiger, King Tiger, Jagdtiger, or Maus, instead of improving existing chassis, like the amazing mass-produced STUG-III and Hetzer which had a still a much greater effient kill-to-weight/cost ratio.
Trucks and light vehicles were the poor parents, and probably the only rear effort consented was done for half-tracked or fully-tracked artillery tractors and supply vehicles on the eastern front, much in demand. The Raupenschlepper Ost was one of these.
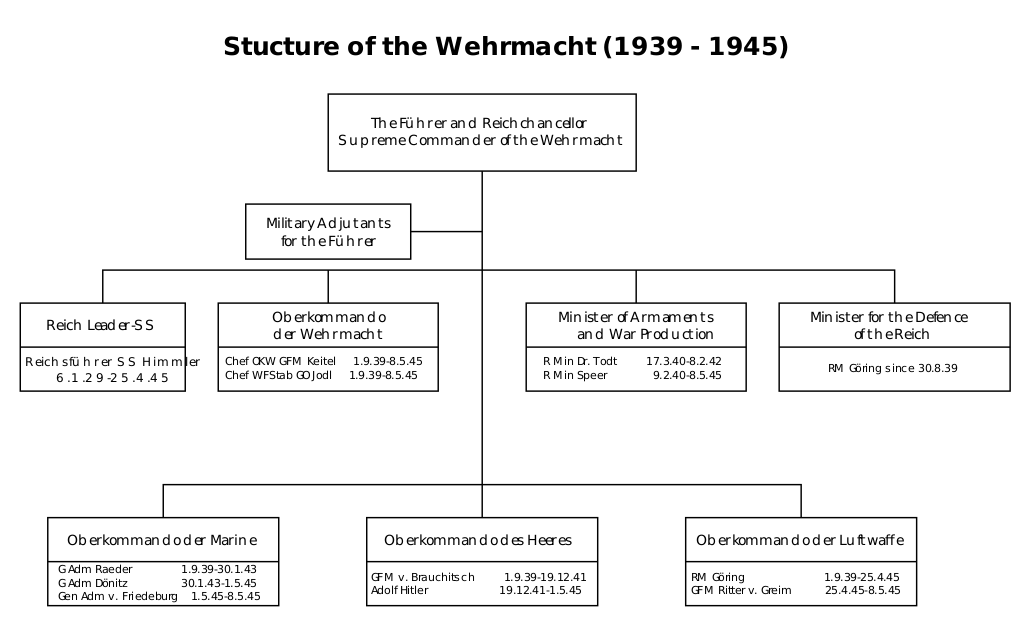 Structure of the Wehrmacht in wartime
Structure of the Wehrmacht in wartime
German mobility always had been criticized, not providing enough vehicles for the ground forces and indeed, the bulk of the German infantry went on foot, motorized infantry division being an exception. The "lightning war" only concerned this reduced motorized component spearheaded by Panzerdivisions (which needed their own sets of softskin vehicles). Only 40% to 60% of all units in the Eastern Front were motorized. Instead, willfully skipped by propaganda, baggage trains often relied on horse-drawn trailers and troops went on foot or by bicycle.
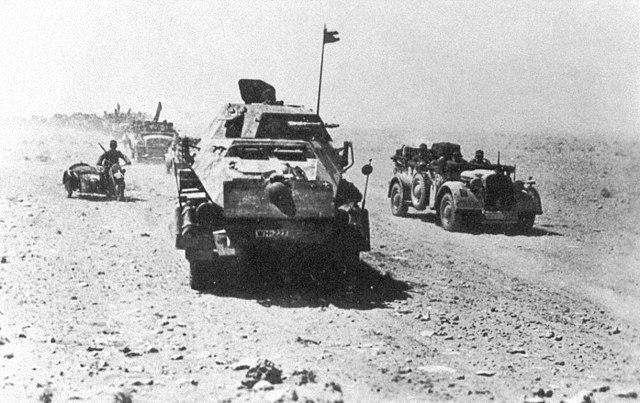 German mobility at its best: A small part of the Afrika Korps went on foot, while European horses could never had coped with the local conditions. Captured trucks and equipments made for this shortcoming, while the collaborating Italians were notoriously poorly equipped. However the desert proved to be blessed country for rapid wheeled columns using organically a large number of vehicles. Here, a Spähpanzer screening the 21 Panzer Division (DAK), with a side car and a variety of softskin vehicles behind.
German mobility at its best: A small part of the Afrika Korps went on foot, while European horses could never had coped with the local conditions. Captured trucks and equipments made for this shortcoming, while the collaborating Italians were notoriously poorly equipped. However the desert proved to be blessed country for rapid wheeled columns using organically a large number of vehicles. Here, a Spähpanzer screening the 21 Panzer Division (DAK), with a side car and a variety of softskin vehicles behind.
German Half-tracks
Probably the best-known German vehicles of the war, often seen as properly "military" were half-tracks. The compromised solution had just the traction needed for all-terrain warfare and were particularly in demand on the Eastern front from the summer of 1941, due to a notoriously bad network. A grand total of about 100,000 half-tracks were manufactured during the war, in eight main types and many derivatives and sub-types.
All were categorized as "special purpose vehicles" as shown by their waffenamt denomination, Sonderkraftfahrzeug, abbreviated as "Sd.Kfz." The ordnance had them classed into 99 different types, and sub-types. Any subtype was represented by a slash and number, like in Sd.Kfz 10/2, the second variant of the type 10 special purpose vehicle. In all on paper around 350 types were listed as such, but for more precision they were distinguished into four series and many types were only paper projects or just gaps with no entry at all:
- Sd.Kfz. 1 to 99: Unarmoured half-tracked vehicles
- Sd.Kfz. 100 to 199: Tanks and tank variants, such as tank destroyers and self-propelled artillery
- Sd.Kfz. 200 to 299: Reconnaissance vehicles, armoured cars, armored personnel carriers, and command tanks*
- Sd.Kfz. 300 and above: Mine-clearing and demolition charge laying vehicles
*including armored halftracks such as the types 250 and 251.
Here we are going to see most of the first and third series. Standard trucks, civilian models usedby the army or models produced for the army, were not listed into the waffenamt as "special vehicles" (see below).
German Trucks
Opel Blitz *
Opel Maultier *
Mercedes-Benz L3000 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.19 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.21 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.68 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.69 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.70 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.81 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.21 *
Krupp Protze Kfz.83 *
Borgward B 3000 *
Ford model BB *
Ford model V8-51 *
Tatra 111 *
Skoda Rad Schlepper Ost RSO Porsche 175 *
Steyr Type 2000A *
Einheits Lkw Kfz.62 *
Krupp LKW L3 *
Bussing-Nag 4500 *
Opel Blitz Omnibus *
Bussing-Nag L *
Mercedes-Benz L1500 *
Mercedes-Benz L4500 *
Magirus A 3000 *
Horch 81 *
Horch 108 *
Beute Studebaker *
Krupp L3H *
Hanomag SS-100 *
Ford B3000 S, V3000S, V3000A *
Beute Ford M1937 *
Beute Ford model V8-51 *
Beute Tatra 111 *
German Staff & Liaison Cars and side cars
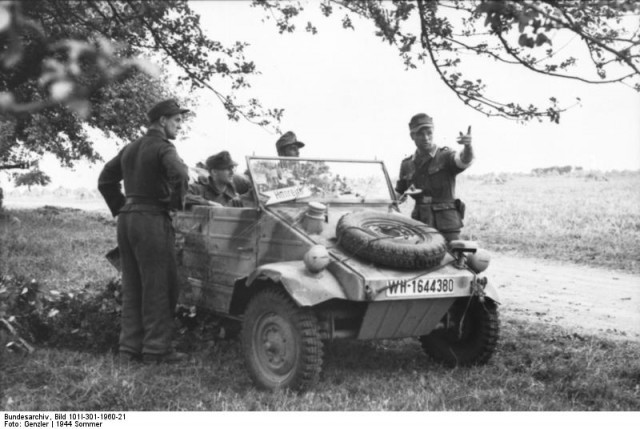
VW Type 82 Kübelwagen *
VW Type 166 Schwimmwagen *
BMW 325 *
Mercedes-Benz W 133 III *
Mercedes-Benz W 139 *
Mercedes-Benz W 152 *
Mercedes-Benz W31 *
Tatra V 809 *
Trippel SG6 amphibious car *
VW Type87 Kommandeurwagen *
Kfz.15 Horch 901 *
Beute Kfz.15 *
Type 952 Kubelwagen *
Kfz.31 Mannschaftswagen *
Kfz.70 Staff Car *
Mercedes 170 VK Kübelsitzwagen *
BMW R75 *
Wehrmachtsgespann *
Zündapp KS 750 *
BMW R 17 *
BMW R 71 *
Zündapp DB/ DBK *
Zündapp KS 600 *
Zündapp K 800 *
Beute Skoda Typ 903 Gelandewagen *
NSU *
DKW NZ 350 *
Nimbus
Degrees of Mechanization in the Wehrmacht
It is often believed the 1940-45 German Army highly mechanized. This is very far from the truth. Mechanization mostly reached the Panzerdivisions, but infantry divisions and their organic components (like artillery) were not. They depended on
horse-drawn carriages for the most and infantry was on foot.
There was nothing odd about it. Speed was the main factor within the so-called "Blitzkrieg" to reach objectives and secure a sector which was later exploited by more and more slower troops: Mechanized infantry, and then foot infantry. When piercing the front, surrounding a position and creating large pockets, the latter was often dealt with infantry and artillery which came as a second or third wave, while PZDs went on forward. This was true in Poland, France, the Balkans and in 1941 in Russia. Often unarmoured trucks were used for the second wave or in the "tail" behind the PZD wedge.
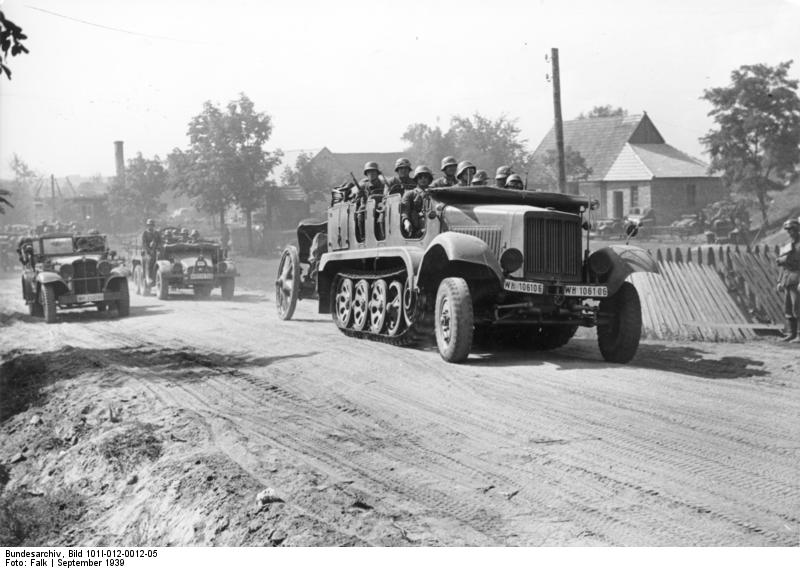

Mechanization in Panzerdivisions
PZD were highly mechanized as said above and depended on Frontline vehicles, armoured such as the
Sd.Kfz 250 and
SdKfz 251 half tracks, as each Panzerdivision needed an organic infantry, called the Panzergrenadiers, often placed in the center of the panzer wedge formation. It was well understood that Tanks could not operate alone, especially in forests and urban areas, where an enemy infantry could deal with ease with the lack of all around visibility. Panzergrenadiers amounted to
Mechanization in Infantry Divisions
Although German industry could produce score of trucks, there were never enough to carry troops, supply, fuel and ammunitions. They counted on thousands of trucks of local manufacture, and after the annexion of Austria, many more. Aside this, the Germans used 2.7 million horses during the war, and the myth of a highly motorized has been long debunked by contemporary historians. Only panzerdivisions were fully motorized, and only a small part of the following infantry was carried by trucks, often reserved to supplies and artillery. The immense majority went by foot. Trucks were however produced all around Europe, and were requisitioned whenever possible. Therefore models were used of all brands and from all Europe, which complicated often spare art management.
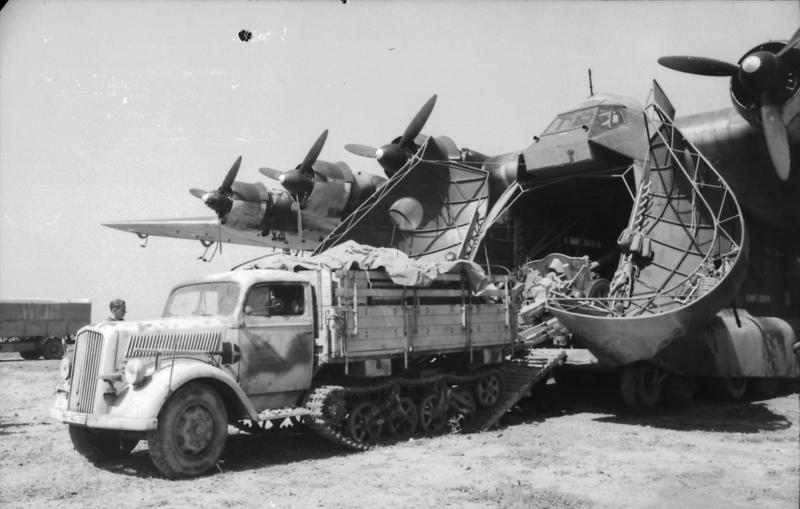

Therefore, like local captured tanks and armoured vehicles (Beute) local trucks were often used locally, especially if they came from small manufactures. The exceptions on the eastern front were Czech, Austrian and French trucks, that complemented the German supplies due to their great numbers and integration into the war effort: Manufacturer's production in occupied countries went on, and truck production in particular was less susceptible to be targeted by the resistance or partisans, due to its non-offensive role and a production often destined to a local civilian usage as well. Were concerned, Steyr and Tatra were probably the least risky, but Berlier, Latil, Peugeot and Renault in France, DAF in the Netherlands, MOL in belgium from 1944, Fiat and Lancia after November 1943 when northenr Italy was occupied, were more subject to disruptions.
Trucks in the German Army
German Trucks Main Models
-Opel Blitz and Maultier Sd.Kfz. 3 half-track variant
-Mercedes-Benz L3000
Krupp Protze
Kfz.19 - Telephone truck
Kfz.21 - Staff car
Kfz.68 - Radio mast carrier
Kfz.69 - Standard configuration for towing the 3,7 cm PaK 36
Kfz.70 - Standard configuration for personnel carrying
Kfz.81 - Ammo carrier conversion for 2 cm FlaK gun, usually towed
Kfz.83 - Generator carrier for anti-aircraft spotlight, usually towed
Borgward B 3000
Sd.Kfz. 4 half-track
Ford B3000 S, V3000S, V3000A, BB, V8-51
From other countries (see below for details)
Steyr-Werke AG (Austria) - Typ V, VI, XII, XVII, 40, 6x4
Steyr RSO Raupenschlepper Ost Half track (Austria)
Tatra 111 (Czechslovakia)
French trucks (Laffly, Citroën, Panhard, Peugeot, Renault, Unic, Matford, Willeme)
French halftracks (Citroën-Kégresse, Unic, Somua) - see later
German Trucks Manufacturers
Steyr-Daimler-Puch
During WWII in Austria, Generaldirektor Georg Meindl became one of the first German industrialists to suggest the use of slave labour from concentration camps to boost manpower in the company. This practice rapidly became common in German companies, such as Mercedes-Benz and MAN. There was no military range produced until the Steyr RSO Raupenschlepper Ost, equipped by an air-cooled 3.5 L V8 engine designed by Ferdinand Porsche. The company also went on producing its civilian range and also produced small arms, assault rifles, machine guns, and aircraft engines.
Opel
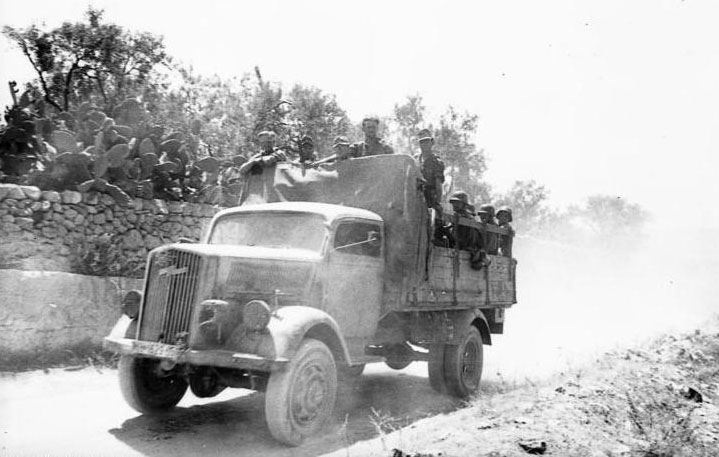 An Opel Blitz in southern Italy, carrying troops.
An Opel Blitz in southern Italy, carrying troops.
The 1930s saw a massive growth for Opel AG, funded by Adamn Open in Hesse in 1962. Since its first car in 1898 up to 1937, that year alone, the manufacturer produced 130,267 cars and its Rüsselsheim plant was Europe's largest in Europe, seventh worldwide. In 1938 was launched its flagship the Kapitän propelled by a 2.5 L six-cylinder engine, all-steel body, front independent suspension, hydraulic shock absorbers, hot-water heating (with electric blower), and central speedometer. World War II brought an end to this, and manufacturing was reaffected in the Autumn of 1940 by order of the government. The company was taske dinitally tto produced ammunitions but refused, and soon, it turned to truck production. Opelwerk Brandenburg (1936) became the main plant for this, and the model was the Opel Blitz (1938).
Opel automobile in 1942 Opel switched to aircraft parts and tanks but kept manufacturing trucks at the Brandenburg plant. The 3.6-liter Opel Blitz was already produced for the Heer since 1938 and under license by Daimler-Benz in Mannheim. It became its staple vehicle, the mainstay of German trucks during the war, including a half-track variant, the Maultier, for the eastern front. The Blitz was also declined in several versions, including a long wheelbase omnibus, used as troop transport.
Magirus
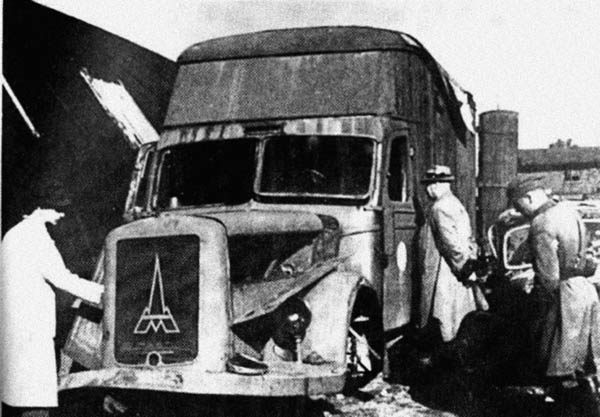

The company was well-placed to supply trucks to the Heer, as it was already manufacturing fire-fighting vehicles in 1866. It also later invented the turntable ladder. In the late 1910s, it started production of trucks and buses and grew steadily. It provided troop transports already during WW1, and in 1936 was fusioned with Humboldt-Deutz Motorenfabrik. Therefore from then on, trucks would be name Magirus-Deutz. The most common wartime truck became the
Magirus A3000, 3-ton, 4x4, Cargo. It was also declined in a Maultier version with half-track for the eastern front. In all, 16,000 were produced of both S (4x2) and A (4x4) type.

Mercedes

The famous company, immortalized in competition with its silver arrows, produced scores of vehicles during the war, but was not a standard provider for the wehrmacht. Mercedes-Benz however started to change with Germany's rearmament. From 1937, Daimler-Benz AG increased production of its LG 3000 truck and its aircraft engine division the DB 600 and DB 601. In the summer of 1941, the Daimler-Benz AG Board of Management was chaired by Wilhelm Kissel started to see there was no such thing as a "blitzkrieg" and that military production should be ramped up. Truck production now gained all the focus, whilst passenger-car manufacturing virtually came to a standstill by late 1942.
Three famous civilian models that contributed to the company's reputation:
 Mercedes SSKL, the epitome of a light, fast road car in 1935
Mercedes SSKL, the epitome of a light, fast road car in 1935
 Mercedes 540K, the pinnacle of sporty, luxury car in 1939
Mercedes 540K, the pinnacle of sporty, luxury car in 1939
 "Grösser Mercedes", the armored, massive show car of the nazi regime. Used until the end of WW2. Some technologuy in it was reused for wehrmacht staff cars.
"Grösser Mercedes", the armored, massive show car of the nazi regime. Used until the end of WW2. Some technologuy in it was reused for wehrmacht staff cars.
Alongside truck production, spare parts production and repair of chassis and engines grew in importance with new skilled staff to handle the increasing production and managed more automation or streamline in the process due to a lower workforce, enlisted in the army. Thus, the company recruited women to keep up with the volumes, and soon also in 1943, forced labourers, prisoners of war, but also abducted civilians and detainees from concentration camps. They were housed close to the plants or guest houses for those of western countries like France, Belgium and the low countries, in private accommodation or schools, and well treated.
Workers and POW from eastern Europe were interned in barrack camps monitored by the SS under inhumane conditions and “loaned out” to companies, so much that by 1944, almost 50% of the 63,610 Daimler Benz employees were "forced labour". This went hand in hand, and under Albert Speer's recommendation, with a simplification of design when possible on all models.

For trucks, these were:
-Mercedes G3a, 1.5-ton, 6x4, Radio Truck
-Mercedes L1500 A, 1.5-ton, 4x4, Personnel Carrier
-Mercedes L3000A, 3-ton, 4x4, Cargo
-Mercedes-Benz L4500A, 4.5-ton, 4x4, Cargo
-Mercedes-Benz L4500R Maultier, 4.5-ton, Halftrack, Cargo
-Mercedes Benz L6500 4x2, 13 tons very heavy road cargo.

Among most notable staff car models were the following:
-Mercedes-Benz W31
-Mercedes-Benz W133 III
-Mercedes-Benz W139
-Mercedes-Benz W152
-Mercedes-Benz 170 VK Kübelsitzwagen/W 136 K (Large staff car, a competitor to the Horch 901)
Faun
Faun is a German manufacturer of trucks, specializing in producing commercial and military vehicles. The company, founded in 1910, originally produced trucks and other vehicles for civilian use. Over the years, Faun became known for its robust trucks used in various sectors, including municipal services, construction, and waste management. In more recent years, Faun is primarily recognized for its range of specialized vehicles, such as refuse collection trucks and municipal waste management equipment. The company's focus is on developing vehicles that meet the specific demands of industries requiring heavy-duty, durable, and efficient vehicles. Faun is also known for its military vehicles, particularly during its earlier years, and has been involved in the production of various defense and off-road vehicles. Today, the Faun brand is part of the FAUN Umwelttechnik GmbH, a company that focuses on environmental and municipal technology, producing trucks for waste collection, street cleaning, and similar purposes.
Krupp
Borgward
Ford (Germany)
Volkswagen

The remarkable "bucket car", or Kübelwagen, VW Type 82 became the standard light laison and reconnaissance car of the German army.
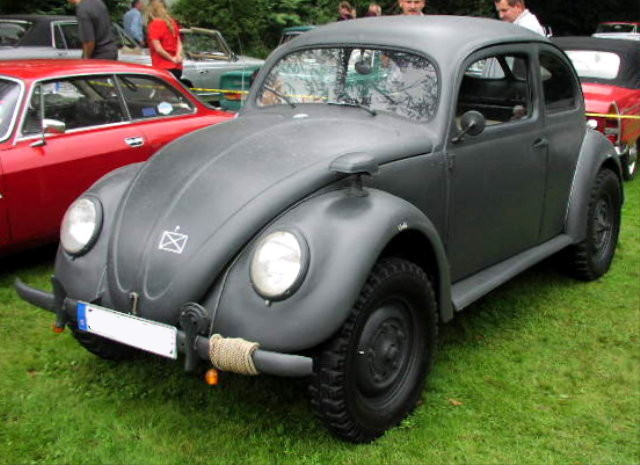

The "Käfer" VW Type 82E, short lived people's car here in military livery and used by military personal.
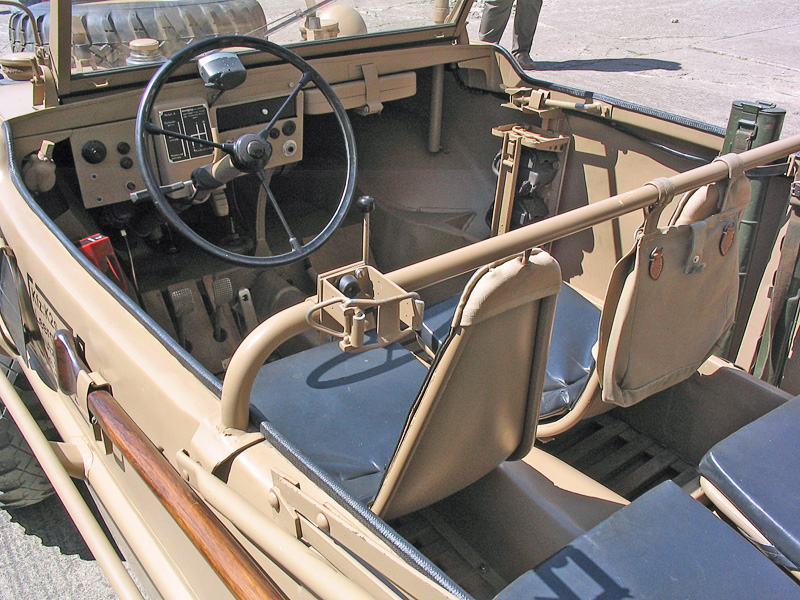

The "Schwimmwagen" VW Type 166, standard military light ampgibious car.
All vehicles according to their Waffenamt designations
No Sd.Kfz.1
-Sd.Kfz.2 (1940): The famous moto-half track (ketternkrad) see below.
-Sd.Kfz.3 (1941): Maultier variant of the Opel 3 tons truck (see below)
-Sd.Kfz.4 (1942): Maultier based 4.5 ton trucks and RL nebelwerfer variant
No Sd.Kfz.5
-Sd.Kfz.6 (1936): Medium 5 tons utility half track (see below)
-Sd.Kfz.7 (1937): Medium 8 tons utility half track (see below)
-Sd.Kfz.8 (1936): Heavy 12 tons utility half track (see below)
-Sd.Kfz.9 (1936): Heavy 18 tons utility half track (see below)
-Sd.Kfz.10 (1935): Light 1 ton utility half track (see below)
-Sd.Kfz.11 (1936): Light 3 ton utility half track (see below)
-Sd.Kfz. 100 to 199: Tanks and tracked AFVs
-Sd.Kfz. 221 (Leichter Panzerspähwagen with 7.92 mm machinegun)
-Sd.Kfz. 222 (Leichter Panzerspähwagen with 20 mm L/55 main gun)
-Sd.Kfz. 223 (Leichter Panzerspähwagen with radio gear)
-Sd.Kfz. 231 6-rad (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (6 wheel) with 20 mm L/55 main gun)
-Sd.Kfz. 231
-Sd.Kfz. 231 8-rad (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (8 wheel) with 20 mm L/55 main gun)
-Sd.Kfz. 232 6-rad (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (6 wheel) with radio gear)
-Sd.Kfz. 232 8-rad (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (8 wheel) with radio gear)
-Sd.Kfz. 233 (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen with 75 mm L/24 gun)
-Sd.Kfz. 234 (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen)
-Sd.Kfz. 247 (armored staff car)
-Sd.Kfz. 250 (armored light halftrack, 12 variants)
-Sd.Kfz. 251 (medium armored halftrack, 23 variants)
-Sd.Kfz. 252 (light halftrack ammunition carrier)
-Sd.Kfz. 253 (light halftrack observation post)
-Sd.Kfz. 254 (medium track or wheel observation post)
-Sd.Kfz. 260 (light armored radio car)
-Sd.Kfz. 261 (light armored radio car)
No Sd.Kfz. 261
-Sd.Kfz. 263 6-rad (heavy armored radio car - 6 wheel)
-Sd.Kfz. 263 8-rad (heavy armored radio car - 8 wheel)
-Sd.Kfz. 265 (Panzer I command tank)
-Sd.Kfz. 266 (Panzer III command tanks with FuG 6 and FuG 2 radios)
-Sd.Kfz. 267 (Panzer III, Panther tank, and Tiger I command tanks with FuG 6 and FuG 8 radios)
-Sd.Kfz. 268 (Panzer III, Panther tank, and Tiger I command tanks with FuG 6 and FuG 7 radios)
-Sd.Kfz. 300 (Minenräumwagen remote-control mine destroyer)
-Sd.Kfz. 301 (Borgward B IV heavy remote-control demolition layer)
-Sd.Kfz. 302 (Goliath vehicle light remote-control demolition vehicle)
-Sd.Kfz. 303 (Goliath vehicle light remote-control demolition vehicle)
-Sd.Kfz. 303 Goliath vehicle
-Sd.Kfz. 304 (Springer vehicle medium remote-control demolition vehicle)
-Sd.Kfz. 305 (Opel Blitz 3 ton 4x2 Truck)
Kfz designations
- Kfz.1: Leichter geländegängiger Personenkraftwagen - light cross-country passenger car
- Kfz.1/20 leichter geländegängiger wassergängiger Personenkraftwagen - light cross-country amphibious car
- Kfz.2 Nachrichtenkraftwagen (vormals als Fernsprechkraftwagen bezeichnet) - signals car (formerly designated telephone car)
- Kfz.2 Funkkraftwagen - radio car
- Kfz.2/1 Nachrichtenkraftwagen - signals car (designation deleten with AHM 196, 1938)
- Kfz.2/2 Funkkraftwagen - radio car (designation deleted with AHM 196, 1938)
- Kfz.2/40 kleiner Instandsetzungskraftwagen - small maintenance car
- Kfz.3 leichter Messtruppkraftwagen - light survey party car
- Kfz.4 Truppenluftschutzkraftwagen - anti aircraft staff carrier car
- Kfz.11 mittlerer geländegängiger Personenkraftwagen - middle cross-country passenger car
- Kfz.12 mittlerer geländegängiger Personenkraftwagen mit Zugvorrichtung - middle cross-country passenger car with towing hook
- Kfz.12 mittlerer geländegängiger Personenkraftwagen - middle cross-country passenger car
- Kfz.12 Filmaufnahmekraftwagen - film recording car
- Kfz.13 Maschinengewehrkraftwagen - machine gun car (armoured) - Made by Adler
- Kfz.14 Funkkraftwagen - radio car (armoured) - Made by Adler
- Kfz.15 Funkkraftwagen - radio car
- Kfz.15 Nachrichtenkraftwagen (vormals als Fernsprechkraftwagen bezeichnet) signals car (formerly designated telephone car)
- Kfz.15 Fernschreibkraftwagen (eingeführt vermutlich 1943) - telex car (introduced most probably in 1943)
- Kfz.15 Fernschreibanschlußkraftwagen (eingeführt vermutlich 1943) telex connection car (introduced most probably in 1943)
- Kfz.15 Fernsprechkraftwagen (eingeführt vermutlich 1943) telephone car (introduced most probably in 1943)
- Kfz.15/1 Nachrichtenkraftwagen - signals car (designation deleten with AHM 196, 1938)
- Kfz.15/2-7 Funkkraftwagen - radio car (designation deleten with AHM 196, 1938)
- Kfz.16 mittlerer Messtruppkraftwagen - middle survey party car
- Kfz.16/1 mittlerer Vorwarnerkraftwagen (middle early warning car)
- Kfz.17 Fernsprechbetriebskraftwagen (telephone operating car)
- Kfz.17 Funkkraftwagen (radio car)
- Kfz.17 Kabelmesskraftwagen (cable measuring car)
- Kfz.17 Rundfunkaufnahmekraftwagen (radio recording car)
- Kfz.17 kleiner Lautsprecherkraftwagen (small loudspeaker car)
- Kfz.17/1 Funkkraftwagen radio car
- Kfz.17/2 kleiner Fernsprechtruppkraftwagen (small telephone section car)
- Kfz.17/3 kleiner Funkkraftwagen (small radio car)
- Kfz.18 Gefechtskraftwagen (combat motor vehicle, later deleted)
- Kfz.19 Fernsprechbetriebskraftwagen (telephone operating car)
- Kfz.19 Funkkraftwagen (radio car)
- Kfz.21 schwerer geländegängiger Personenkraftwagen (6-seats heavy cross-country passenger car)
- Kfz.23 Fernsprechkraftwagen (telephone car)
- Kfz.24 Verstärkerkraftwagen (amplifier car)
- Kfz.31 Krankenkraftwagen (ambulance)
- Kfz.42 Sammlerkraftwagen (battery motor vehicle)
- Kfz.42 Nachrichtenwerkstattkraftwagen (signals workshop motor vehicle)
- Kfz.43 Flakauswertekraftwagen (AA evaluation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.44 Funkempfangskraftwagen (radio reception motor vehicle)
- Kfz.44 Sauerstoff- und Stickstoff-Erzeugungskraftwagen (oxygen- and nitrogen generation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.51 Werkstattkraftwagen (workshop motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 Fernschreibkraftwagen (telex motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 Fernsprechbetriebskraftwagen (telephone operating motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 (leichter)Funkkraftwagen (radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 Kabelmesskraftwagen (cable measuring motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 Kleinfunkkraftwagen (Small radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 Peilkraftwagen (radio direction finder motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61 Verstärkerkraftwagen (amplifier motor vehicle)
- Kfz.61/1 Funkkraftwagen (radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Druckereikraftwagen (print shop motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Lichtauswertekraftwagen (flash-light evaluation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Schallaufnahmekraftwagen (sound recording motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Schallauswertekraftwagen (sound evacuation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Stabsauswertekraftwagen (command staff evaluation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Vermessungsauswertekraftwagen (survey evaluation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.62 Wetterkraftwagen (meteorological motor vehicle)
- Kfz.63 Lichtmessgerätekraftwagen (flash-light measuring instruments motor vehicle)
- Kfz.63 Lichtmeßstellenkraftwagen (Flash-light measuring station motor vehicle)
- Kfz.63 Schallmessgerätekraftwagen (sound ranging instruments motor vehicle)
- Kfz.63 Schallmeßstellenkraftwagen (sound ranging station motor vehicle)
- Kfz.63 Meßstellen- und Gerätekraftwagen (measuring station and equipment motor vehicle)
- Kfz.63 Vorwarnerkraftwagen (early warning motor vehicle)
- Kfz.64 Vermessungsgerätekraftwagen (survey instruments motor vehicle)
- Kfz.67 Gepanzerter Kraftwagen (armoured motor vehicle, later Sd.Kfz.231)
- Kfz.67 gepanzerter Kraftwagen (Fu) (radio armoured motor vehicle, later Sd.Kfz.232)
- Kfz.67 gepanzerter Kraftwagen (Fu) later Sd. Kfz. 263 (6Rad)
- Kfz.68 Funkmastkraftwagen (radio mast motor vehicle)
- Kfz.68/1 Funkmastkraftwagen (radio mast motor vehicle)
- Kfz.69 Protzkraftwagen (limber motor vehicle)
- Kfz.70 Mannschaftskraftwagen (personnel carrier)
- Kfz.72 Befehlskraftwagen (command post motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Druckereikraftwagen (print shop motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Fernschreibkraftwagen (telex motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Fernsprechbetriebskraftwagen (telephone operating motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Funkbetriebskraftwagen (radio operating motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Funkhorchwagen a/b (radio interception motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Funkkraftwagen a/b (radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Funkschreibkraftwagen (radio recorder motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 Verstärkerkraftwagen (amplifier motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72 (mittlerer) Wetterkraftwagen (meteorological motor vehicle)
- Kfz.72/1 Fernschreibkraftwagen (telex motor vehicle)
- Kfz.73 Schwerer Vermessungstruppkraftwagen (heavy survey section motor vehicle)
- Kfz.74 Flakmesstruppkraftwagen I (AA survey party motor vehicle)
- Kfz.74 Flakmesstruppkraftwagen II same
- Kfz.75 Triebwerkkraftwagen (aircraft engine motor vehicle)
- Kfz.76 Beobachtungskraftwagen (observation motor vehicle)
- Kfz.77 Fernsprechkraftwagen (telephone motor vehicle)
- Kfz.79 Werkstattkraftwagen (workshop motor vehicle)
- Kfz.81 leichter Flakkraftwagen (light AA motor vehicle)
- Kfz.83 leichter Scheinwerferkraftwagen (light searchlight motor vehicle I/II)
- Kfz.91 Nebelkraftwagen (smoke mortar motor vehicle)
- Kfz.92 Mannschafts-Entgiftungskraftwagen (personnel decontamination motor vehicle)
- Kfz.93 Bekleidungs-Entgiftungskraftwagen (clothing decontamination motor vehicle)
- Kfz.94 Wasserkraftwagen (water motor vehicle)
- Kfz.95 Kammerkraftwagen (chamber motor vehicle)
- Kfz.100 Drehkrankraftwagen (Hebekraft 3t Revolving crane vehicle)
- Kfz.301 Funkmastkraftwagen (radio mast motor vehicle)
- Kfz.302 Funkkraftwagen (Kzw./Lgw.) radio vehicle
- Kfz.303 Horchfunkpeilkraftwagen (radio interception vehicle)
- Kfz.305 Mittl. Lastkraftwagen (o) mit geschlossenem Einheitsaufbau (Middle lorry standard body)
- Kfz.305/1 Fernschreibanschlusskraftwagen (KW) (telex termination vehicle)
- Kfz.305/2 Fernschreibanschlusskraftwagen G (telex termination vehicle)
- Kfz.305/3 Fernschreibvermittlungskraftwagen (telex relaying station vehicle)
- Kfz.305/4 Fernschreibwartungskraftwagen (telex maintenance vehicle)
- Kfz.305/8 Fernschreibvermittlungskraftwagen (telex relaying station vehicle)
- Kfz.305/10 Verstärkerkraftwagen (amplifier motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/11 Leitungsmesskraftwagen (cable measuring vehicle)
- Kfz.305/15 Funksendekraftwagen (radio broadcast motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/16 Funkkraftwagen (radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/17 Funkkraftwagen (radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/18 Funkkraftwagen (Kzw./Lgw.)(radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/19 Funkkraftwagen (Kzw. radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/20 Funkkraftwagen (radio motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/21 Funkbeschickungskraftwagen (radio feeding vehicle)
- Kfz.305/22 Funkpeilkraftwagen (radio bearing vehicle)
- Kfz.305/23 Funkempfangs Kw./Horchfunkempfangs Kw./Funkbetriebs Kw. (radio reception/interception/operation vehicle)
- Kfz.305/25 Funkmastkraftwagen (radio mast vehicle)
- Kfz.305/26 Radiosondekraftwagen (radiosonde motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/27 Radiosondepeilkraftwagen (radiosonde bearing motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/29 Ansteuerungssendekraftwagen (approaching signal sending vehicle)
- Kfz.305/30 Voreinflugzeichen- od. Haupteinflugzeichensendekraftwagen (marker transmitter vehicle)
- Kfz.305/32 Leuchtfeuerkraftwagen für schweren Leuchtfeuertrupp (mot.)(Beacon heavy vehicle)
- Kfz.305/33 Leuchtfeuerkraftwagen für leichten und mittlerer Leuchtfeuertrupp (Beacon light vehicle)
- Kfz.305/34-35 Richtverbindungskraftwagen für schweren Richtverbindungstrupp (radio relay heavy radio relaying)
- Kfz.305/36 Richtverbindungs-Tf-Betriebskraftwagen (radio relay Tf operating vehicle)
- Kfz.305/37 Richtverbindungs-WTZ-Betriebskraftwagen (radio relay WTZ vehicle)
- Kfz.305/38 Richtverbindungs-Antennengerät-Kraftwagen (radio relay aerial vehicle)
- Kfz.305/40 Richtverbindungsmesskraftwagen (radio relay measurement)
- Kfz.305/41 Geräteprüfkraftwagen 293 (instrument testing vehicle)
- Kfz.305/42 Bordfunkprüfkraftwagen (radio equipment testing vehicle)
- Kfz.305/43 Entstörkraftwagen (interference suppression vehicle)
- Kfz.305/44 Elektrischer Störsuchkraftwagen (electrical interference searching vehicle)
- Kfz.305/60 Bordgeräteprüfkraftwagen (On board devices testing motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/61-62 Zellen-Werkstattkraftwagen (air frame workshop vehicle)
- Kfz.305/63 Triebwerks-Wartungskraftwagen (Propulsion unit maintenance vehicle)
- Kfz.305/64 Bordgeräte-Werkstattkraftwagen (On board devices workshop vehicle)
- Kfz.305/65-66 Wetterkraftwagen A/B (Meteorological vehicle)
- Kfz.305/67-68 Triebwerk-Werkstattkraftwagen (propulsion unit workshop vehicle)
- Kfz.305/69 Steuerungsprüfkraftwagen (piloting testing vehicle)
- Kfz.305/70 Fallschirmlagerkraftwagen (parachute store vehicle)
- Kfz.305/73 Befehlsstellenkraftwagen (command post vehicle)
- Kfz.305/74 Geschäftszimmerkraftwagen (office vehicle)
- Kfz.305/75 Bekleidungskammerwagen (clothing chamber vehicle)
- Kfz.305/76 Sanitätsgerätekraftwagen (medical equipment vehicle)
- Kfz.305/77 Marketenderkraftwagen (canteen proprietor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/78 Elektroküchenkraftwagen (electrical kitchen vehicle)
- Kfz.305/79 Geschäftszimmerkraftwagen (office vehicle)
- Kfz.305/80 Waffenwartungskraftwagen (weapons maintenance vehicle)
- Kfz.305/83 Kfz-Werkstattkraftwagen (workshop vehicle)
- Kfz.305/84 Kfz-Ersatzteillagerkraftwagen (spare parts depot motor vehicle
- Kfz.305/85 Prüfkraftwagen für Drucköl- und Luftversorgungsanlage (testing vehicle for oil pressure and air supply)
- Kfz.305/86 Zahnklinikkraftwagen (dental clinic motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/87 Zahnlaborkraftwagen (dental laboratory motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/88 Röntgen-Schirmbild-Kraftwagen (roentgen screen photo vehicle)
- Kfz.305/89 Röntgen-Schirmbild-Dunkelkammer-Kraftwagen (roentgen screen photo darkroom vehicle)
- Kfz.305/90-91 Bildkraftwagen I-II (image motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/93-94-95 Wasseraufbereitungskraftwagen I/II/III (water preparation vehicle)
- Kfz.305/96 Wasserentsalzungskraftwagen (water desalination vehicle)
- Kfz.305/98 Sauerstoff-Instandsetzungskraftwagen (oxygen maintenance vehicle)
- Kfz.305/99 Sauerstoffumfüllkraftwagen (oxygen decantation vehicle)
- Kfz.305/100 Navigationskraftwagen (navigation vehicle)
- Kfz.305/101 Navigations-Vermessungskraftwagen (navigation survey vehicle)
- Kfz.305/102 Lagerkraftwagen (warehouse vehicle)
- Kfz.305/103 AF Messgerätekraftwagen (AF measurement instruments vehicle)
- Kfz.305/104 Lagerkraftwagen KTZ (warehouse vehicle)
- Kfz.305/105 Werkstattkraftwagen für Klempner und Schweißer (workshop, tinsmith and welder)
- Kfz.305/106 Werkstattkraftwagen für Hydraulik und Schlosser (workshop, hydraulics and locksmith)
- Kfz.305/107 Werkstattkraftwagen für mechanische Werkstatt (workshop, mechanical)
- Kfz.305/108 Werkstattkraftwagen für Waffen und Elektrik (workshop, weapons and electronics)
- Kfz.305/109-110 Werkstattkraftwagen für mechanische Werkstatt I/II (workshop, mechanical)
- Kfz.305/111 Werkstattkraftwagen für Schlosser und Schweißer (workshop, locksmith and welders)
- Kfz.305/112-113 Werkstattkraftwagen für Klempner I/II (workshop, tinsmith)
- Kfz.305/114 Werkstattkraftwagen für Hydraulik und Schlosser (workshop, hydraulics and locksmith)
- Kfz.305/115 Werkstattkraftwagen für Tischler, Maler, Sattler (workshop, cabinetmaker, painters, saddler)
- Kfz.305/117 Werkstattkraftwagen für Schweißer und Schmied (workshop, welders and blacksmith)
- Kfz.305/118 Kfz-Werkstattkraftwagen für Motor, Fahrgestelle und elektrische Anlagen (workshop, engine, chassis, electrical installation)
- Kfz.305/119 Kfz-Lagerkraftwagen (warehouse motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/120 Mannschaftskraftwagen für I-Dienst (personnel carrier, maintenance)
- Kfz.305/121 Gerätekraftwagen für I-Dienst (equipment vehicle, maintenance)
- Kfz.305/122 Entgiftungskraftwagen (decontamination vehicle)
- Kfz.305/123 Entgiftungsgerätekraftwagen (decontamination equipment vehicle)
- Kfz.305/124 Pressluftgerätkraftwagen (compressed air equipment vehicle)
- Kfz.305/125 Flugbetriebskraftwagen (air traffic vehicle)
- Kfz.305/126 Startkraftwagen (starting motor vehicle)
- Kfz.305/128 Kraftfahrspritze KS 8 (fire tank wagon)
- Kfz.305/130 Werkstattkraftwagen für Abwurfwaffen (workshop, bombs)
- Kfz.305/131 Werkstattkraftwagen für Schusswaffen (workshop, fire arms)
- Kfz.305/132 Waffenwerkstattkraftwagen (workshop, weapons)
- Kfz.305/135 Werkstattkraftwagen mechanische Werkstatt (workshop, mechanical)
- Kfz.305/136 Motorenwerkstattkraftwagen (engines workshop vehicle)
- Kfz.305/137 Werkstattkraftwagen für Flugzeugschlosser, Rüstschlosser (TMZ)(workshop, aircraft locksmith & equipment)
- Kfz.305 als Fledermauskraftwagen
- Kfz.305 as bat motor vehicle
- Kfz.309 Schlauchtender (hose tender)
- Kfz.311 Funkmastkraftwagen (radio mast vehicle)
- Kfz.317 Sauerstoff -Kesselkraftwagen (oxygen tank vehicle)
- Kfz.343 Tankspritze (fire tank-wagon)
- Kfz.344 Schlauchtender (hose tender)
- Kfz.345 Löschkraftwagen (fire engine)
- Kfz.346 Schlauchkraftwagen (hose motor vehicle)
- Kfz.353 Landebahnleuchtkraftwagen (runway lighting vehicle)
- Kfz.354 Bildkraftwagen (image motor vehicle)
- Kfz.384-85 Flugbetriebsstoffkesselkraftwagen (aircraft fuel tank vehicle)
- Kfz.410/1-2-3 mittlerer Flakkraftwagen (4,5t)(middle AA vehicle)
- Kfz.415 Flakmesstruppkraftwagen (AA survey party vehicle)
Sd.Kfz. vehicles
 An Afrika korps kettenkrad, Libya, october 1942.
An Afrika korps kettenkrad, Libya, october 1942.
The Kettenkrad (litterally "tracked cycle") was abbreviated from "Kleines Kettenkraftrad HK 101". This model was at first made fo paratroopers as required by the Luftwaffe's RLM - an airborne tractor for paratroopers and glider-borne infantry, which was to fit inside any of these planes in service (before the Me 323 Gigant that is). It could carry two infantrymen, had a 500 kgspayload and was able of towing a small multipurpose trailer. In service by 1940 it was manufactured to 8,345 vehicles total and served in way more roles as intended, including field reconnaissance.
Sd.Kfz. 3 Opel Maultier (1939)

The proverbial tracked truck of the German Army, tailored for the astern front and the Russian network made of bad to nonexistent roads. Indeed some 20,945 were manufactured from 1941, at Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz AG and the Ford factory at Asnière (France). The supply bureau ordered the conversion of the standard Opel, Daimler-Benz, Alfa-Romeo and Ford trucks. The tracked chassis was made of redundant Panzer I track assemblies. More were built to answer conversions to this new standard. The Opel Maultier ("Mule") also used standard Horstmann suspension components and based on the widespread Opel Blitz model S. A few were armored and became the
Sd.Kfz. 4/1 Panzerwerfer 42.
Sd.Kfz. 6 (1939) Büssing-NAG
Heavy utilitatian half tracks Made by Büssing-NAG, Daimler and Praga, about 3,500 in all until 1945.
 SdKfz-6
SdKfz-6
Sd.Kfz. 7 Krauss Maffei (1935)
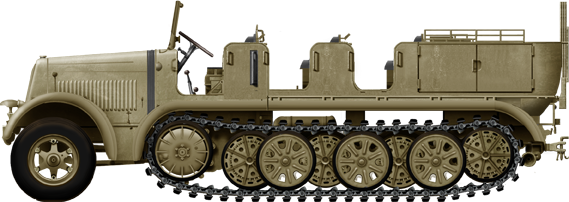 Basic Sd.Kfz-7 as they were painted in factory dunkelgelb
Basic Sd.Kfz-7 as they were painted in factory dunkelgelb
Medium utility half-tracks designed and made by Krauss-Maffei from 1934 and manufactured by Krauss-Maffei, Borgward, Österreichische Saurer-Werke AG, and Breda (Breda 61) in Italian service - about 12,187 delivered until 1945, many variants armoured and used as self propelled guns.
Sd.Kfz. 8 Daimler Benz 12 tons utility (1937)
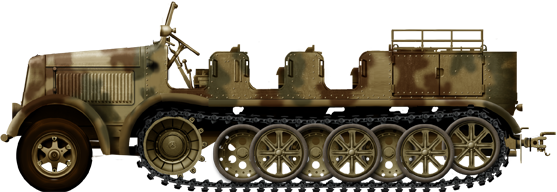 Basic camouflaged Sd.Kfz.8
Basic camouflaged Sd.Kfz.8
Medium utility half-tracks designed by Daimler-Benz and manufacturer by Daimler-Benz, Krupp, Krauss-Maffei, and Škoda to approx. 4,000 vehicles. Used in many variants, some armoured. One was a tank killer, the armoured variant of the 8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf Zugkraftwagen 12t (Sd.Kfz. 8). Just ten were made, making the Panzerjäger-Abteilung 8 which fought in Pola, France and Russia in 1941, but were all lost in action.
Sd.Kfz. 9 'FAMO' (1936)
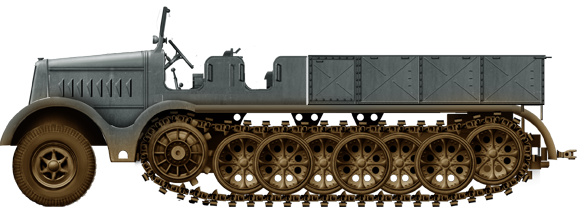
Heavy Utility half track designed by FAMO, hence the name. It was manufactured by FAMO, Vomag, Tatra to around 2,500 vehicles. It was declined into the Sd.Kfz. 9/1, Sd.Kfz. 9/2 and was often the only way to retrieve a disabled German heavy tank such as the Tiger on the battlefield.
Variant: 8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf schwere Zugkraftwagen 12t (Sd.Kfz 8) "BUFLA", 10 converted.
Sd.Kfz. 10 Demag (1936)
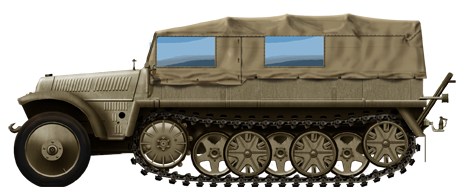
Light utility hald track designed by Demag and manufactured by the same as well as Adler-Werke, Büssing-NAG, MWC, MNH, MIAG, Saurerwerke to approx. 14,000 vehicles. It was one of the most prolific in the German inventory as 3.4 tons, and one of the more mobile. It was declined into the Sd.Kfz. 10/1, Sd.Kfz. 10/2, Sd.Kfz. 10/3, Sd.Kfz. 10/4, and Sd.Kfz. 10/5 variants. Some were armoured such as the Sd.Kfz. 10/4 and 10/5 20 mm FLAK30/38.
Sd.Kfz. 11 Hanomag (1935)

Prime mover half-track, used as a basis for the SdKfz 251. About 9,000 made by Hanomag, Adlerwerke, Horch, Škoda, Borgward from 1938. No armored versions known but possible ad hoc conversions of some variants.
Armored Sd.Kfz Vehicles
Sd.Kfz.221/22/223 (1939)
Called 221 Leichter Panzerspähwagen with 7.92 mm machinegun, 222 Leichter Panzerspähwagen with 20 mm L/55 main gun and 223 Leichter Panzerspähwagen with radio gear these were common armored four-wheeled vehicles of the Wehrmacht used for reconnaissance. There are treated
here in detail. We are not going to dwelve deep into it as it was armored and belongs to Tank Encyclopedia.
Sd.Kfz.231 (6-rad) (1934)
Called Sd.Kfz. 231 6-rad Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (6 wheel) with 8 mm MG.34. Main heavy recce vehicle of the Wehrmacht in 1936.
Read More
Sd.Kfz.231 (8-rad) (1939)
Called Sd.Kfz. 231 8-rad Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (6 wheel) with 20 mm L/55 main gun). Main heavy recce vehicle of the Wehrmacht in 1940.
Read More
Sd.Kfz.232 (6-rad) (1935)
Called 232 6-rad (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (6 wheel) FU (Funk) with radio gear, this was the 6-wheeled earlier vehicle designed from 1933, used a heavy recce vehicle and replaced until 1943 by the 231 8-rad model.
Sd.Kfz.232 8-rad (1939)
Called Sd.Kfz.232 Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (8 wheel) with radio gear
Sd.Kfz. 233
Called Sd.Kfz. 233 (Schwerer Panzerspähwagen with 75 mm L/24 gun)
Sd.Kfz. 234
Called Sd.Kfz. 234 schwerer Panzerspähwagen
Sd.Kfz. 264
Early Funk (radio) vehicle based on the Sd.Kfz 6-rad of 1934.
Read More
Sd.Kfz 250 (1939)
This small armoured half track was the second most prolific in service in the German Army (6628). It was developed to operation within the panzerdivisions, but not as an APC (see the following Sd.Kz.250), but like a multi-mission, small staff vehicle. The standard 250/1 and most variants were given to reconnaissance units (Panzer Aufklärungs), integrated into Panzer and Panzergrenadier divisions (28 and 18 issued respectively). They were used as small APCs carrying reconnaissance sections. 12 Variants were produced early on were added as organic support, and the Sd.Kfz.252 and 253 were derived from them. See the main article here:
Sd.Kfz.250
Sd.Kfz 251 (1939)

Most built by Hanomag, this model was the most promific armoured half-track of the axis, with over 12,000 manufactured and started as an armored version of the Sd.Kfz.11 half-tracked artillery tractor. It was at first used only by Panzergrenadiere, motorized infantry following the Panzerdivisions, but became the default APC of motorized infantry units during the war.
Since it's a hef-track armored and armed vehicles, with 12 main variants, its belong to the Tank section:
Sd.Kfz.251
Sd.Kfz 252 (1940)
Called Sd.Kfz.252 leichte Gepanzerte Munitionskraftwagen, derived from the Sd.Kfz.250 was to be the standard organic armoured ammunition carrier in Panerdivision for Panzergrenadiere units, with a lower storage superstructure at the rear, double doors, and trailer. Only 30 were built in June 1940, replaced by the Sd.Kfz.250/6. They were affected only to Sturmartillerie batteries and Sturmgeschütz vehicles.
Sd.Kfz 253 (1940)
The Sd.Kfz.253 Leichte Gepanzerte Beobachtungskraftwagen was a specialized artillery observation vehicle with a roof and circular hatch with binocular for the observer. 25 were built in March-June 1940, with a folding FuG 15 and FuG 16 aerial, base don the Sd.Kfz 250.
Sd.Kfz 254 (1938)
The Sd.Kfz. 254 was a German fully tracked armoured scout car planned in 1936 and developed under the designation RR-7 by Saurer in Austria as an artillery tractor for the Austrian army. Tests were successful in 1937, and order was placed, manufacturing starting in 1938. However only 12 vehicles were ready at the time of the Anschluss, but manufacture went on under German control afterwards. Records shows just 140 units built as RK-7 (Räder-Kettenfahrgestell). The waffenamt later gave them the designation Sd.Kfz. 254. It was particular in having a wheel-cum-track layout and diesel motor. Wheels were lowered on road, retracted when tracks where needed off-road. They saw action in the Afrika Korps as artillery observation vehicles, fitted with a radio and rail antenna.
The "freedom tank", became a famous vehicle after the war in 1950, when former mechanic Václav Uhlík from Líně in the Czech Republic repaired a derelict RK-7 artillery tractor, rebuilt as an armoured carrier. On 25 July 1953, he succesfully fled to the West, crossing three border zones by running over wire obstacles, thirty kilometres into West German territory. He applied for asylum and emigrated to the United States later, whereas his machine was exhibited as the "freedom tank", now owned by a private collector.
Sd.Kfz 260/261 (1939)
SdKfz 260, recoignisable to its single whip antenna. These vehicles were unarmed and apparently had no marking, no balkankreuz.
These derivatives of the SdKfz 222 were specialized radio vehicles (Funkraftwagen) more precisely called Kleiner Panzerfunkwagen Sd.Kfz.260/Sd.Kfz.261. Unarmed, they were fitted with a large bed-frame rod antenna and were used as signal vehicles. The 260 was given a medium range radio plus fixed antenna, the 261 was given long range radio, collapsible bed frame aerial antenna. Production was limited and over time they were upgraded with the antenna versions of the Sd.Kfz.250 half-tracks. Armoured, they belongs to the
Sdkfz.222 series page.
Non-Sd.Kfz vehicles
Schwerer Wehrmachtschlepper (SWS) (1942)

This non-Sd/Kfz designated vehicle was German's ultimate Heavy Military Tractor, half-track used in various roles between 1943 and 1945, unarmored used supply vehicle and tractor. There were sub-bariants, armored versions carrying FLAK or 10 barrel rocket launcher Nebelwerfer. 825 were built before 1945 by Büssing-NAG and Tatra, which resumed it after the war, with an improved model T809.
This was a 5 t (4.9 long tons; 5.5 short tons) tractor (Zgkw. 5t neuer Art), replacing nominally the earlier 5 tonne Sd.Kfz. 6/3 t (3.0 long tons; 3.3 short tons) Sd.Kfz. 11 half-track and other vehicles. Production started in December 1943 at Büssing-NAG and had all an unarmored cabin, similar to the earlier models. Later models had an armored cabin and armored engine compartment simialr to the Sd.Kfz. 251. Like Demag's Sd.Kfz. 10, its suspension system comprised five double roadwheels per side overlapping and interleaved (Schachtellaufwerk layout) on swing arms, sprung by torsion bars and rear idler wheel rear to control track tension. Tatra joined in production to icread numbers in 1943 but in vain.
In addition to cargo adnd artillery tractor role, the SWS carried the medium 3.7 cm FlaK 43 and 20mm flakvierling. Both were protected by large gun shields and sides had folded down armored panels.
-The Panzerwerfer 42 auf sWS was the 15 cm (5.9 in) Nebelwerfer 42 carried, fixed above an armored ammunition storage compartment like the SdKfz.4, more pecisely to replace the older Sd.Kfz. 4/1) based on the Maultier.
Tractors of the Wehrmacht
The Raupenschlepper Ost was developed in emergency as a fully-tracked tractor for the easter front, inspired by fully-tracked vehicles such as the STZ-5 "Stalingradets", U.S. M4 Tractor and overal Vickers universal carrier of the interwar, notably the "Ben Carrier". The RSO as abbreviated was an Austrian-built vehicle, powered by a Steyr V8 3.5l 8-cylinder Petrol developing 85 PS (RSO/01) or a 4-cylinder Deutz diesel which developed 66 PS on the RSO/03. It was unarmed and unarmoured, and tracked all German AT guns up to the gargantuan 88 mm. Only 80 to 90 were manufactured however. In 1944 it was envisioned to use its base as a very cheap tank hunter built in Austria which never came to fruition.
It was declined into the Raupenschlepper Ost Artillery SPG (four sIG-33 carriers) and the Raupenschlepper Ost 7.5 cm Pak 40 tank destroyer.
Foreign trucks in German service
Austrian Trucks and cars (detail)
 Steyr 1500A Kubelwagen
Steyr 1500A Kubelwagen
Austria had a dynamic industry in the interwar, with roots going back to the time of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, part of which was split between Austria and Chechloslovakia. Austrian brands responsible for trucks and cars were many, but of relatively small size, such as Austro-Daimler, Austro-Fiat (ÖAF), Fross-Büssing, Gräf & Stift, Perl, Puch, Saurer and Steyr. Austria satisfied its demands in trucks and staff cars already before World War I and even pioneered the armoured car with its Austro-Daimler Panzerautomobil. In the Interwar, industrial consolidation pushed forward a giant, the Steyr Daimler Puch AG group in 1934, responsible for the construction of most Austrian vmilitary vehicles prior to the Anchluss of March 1938 and to the Wehrmacht afterwards. Austrian models were produced generally under supervision until 1940-41 and production was reorganized for mass-production of lorries and staff cars or tractors depending of the needs.
Czech Trucks and cars (detail)
(To come)
French Trucks & Half Tracks in German service (detail)
France became rapidly the second-largest trucks and half-track provider of the German Army. In addition to the capture of more than 100,000 trucks, the local industrial network allowed under German supervision to produce many models of trucks, staff cars, and half-tracks already well developed for the needs of the French army since 1920. In addition these companies often produced spare parts and pairs of tracks for various German half-tracks. Some models such as the Sd.Kfz 9 and 10 were also locally produced or intended to in 1943-44. Allied bombardments and local resistance through internal sabotage and attacking transportation also played their part to disrupt this production.
Berliet:
Various models were used by the Wehrmacht such as the DGRA, GDC, GDM, VDCA and 30 Berliet tank carriers. In 1943-1944 1,262 more trucks (5t) were produced for the German army in occupied France.
Bernard:
A few Bernard trucks, mostly fuel carriers.
Citroën:
Trucks and halftracks: Citroën Kégresse P14, P17, P19. One of the most common halftrack was the Citroën-Kégresse P19 (Ci380(f) in Waffenamt nomenclature). They were used notably by Schnelle Brigade West. Many more were produced in 1941-1944:
- 3,700 type 23 trucks
- 6,000 type 32U trucks
- 15,300 type 45 trucks
Delahaye:
About 1,000 Delahaye (SdKfz-11) were produced for the Germans from 1942. Delahaye also produced spare parts for the Büssing-NAG 4500.
ELMAG (Alsace):
Provided 1,143 SdKfz-8 halftracks and spare parts for other German models in 1942-1944.
Ford:
At the beginning of WW2, French Ford factories (Poissy, Asnières) worked for Laffly, transforming 1,000 Ford trucks in halftracks with the Maultier system. Spare parts to maintain the park of Ford trucks throughout Europe as well.
Gnôme-Rhône:
Outside aircraft engines, the company produced motorcycles and side-cars for the Werhmacht.
Hotchkiss:
Produced spare parts, engines and chassis as well as models such as the Laffly R15R, S20TL, W15T and personal cars like the PKW Typ680, 686 and 686 PNA.
Isobloc:
French army buses and W843M medical buses, which could carry each 30 lying wounded soldiers or a full surgery antenna.
Laffly:
The models V15R, S15R, S20TL, and W15T. Armored SPW were derived from the W15T, used in the Schnelle Brigade West.
The company also converted R40 tanks for snow milling and as Luftwaffe towing vehicles with about 200 various German tracked vehicles as well as wheeled and tracked vehicles in snow ploughs.
Latil:
Latil trucks and utility vehicles were captured and pressed into service such as the heavy duty Latil TAR H2, produced during the war.
Lorraine:
Lorraine 37L and 38L tractors were captured and many modified and in addition the company produced some 500 SdKfz-9 in 1942.
Matford (Alsace):
A company which saw the fusion of Ford and Mathis, producing a few trucks but mostly spare parts for Matford trucks (common model, the F917).
Panhard & Levassor:
2,000 Panhard trucks were pressed into service whereas the company also produced 1,000 tracks pairs for the SdKfz-7.
Peugeot:
Controlled by KDFWagen (Volkswagen) it delivered staff and Gestapo cars such as the Peugeot 202 and 402, light trucks such as the Peugeot DMA and DK. Production went on between 1941 and 1944, delivering 12,500 Peugeot DK5, 15,300 Peugeot DMA, and 15,000 Peugeot 202 and 402 staff cars, but also parts for the Kübelwagen, Volkswagen type 82, 166. A local producion of the SdKfz-10, about 150 monthly, was planned from 1942. Delivery numbers is unknown.

The rare Trippel SG6, alternative model to the Schwimmvagen, also produced during the occupation by Bugatti.
Renault:
Archives disappeared during the allied bombings of 1944 but the figure generally accepted was 28,000 Renault trucks, produced for the Germans of the AHS, AHN, AHR, AGC, ADK, ADH models, added to the ones already captured. Prinz Von Urach managed the company and several factories which delivered notably some 23,000 Renault AHS trucks, when adding those captured. 4,000 Renault AHN and 2,000 Renault AHR, 704 AGC3 as well as spare parts for the SdKfz-7 and SdKfz-11 were manufactured.
Saurer:
Produced the Saurer type 3CT (1,800 3CT delivered), added to those captured (about 3,000). Also the Saurer RR-7
Simca:
Mostly personal cars for the German and the Italian Army such as 5,983 Simca 5, 3,960 Simca 8, 122 Simca 8, 19 Simca 5, 180 Simca 8, 23 Simca 5 all based on FIAT models. The Germans planned to deliver some 2,500 SdKfz-2 Kettenkraftrad but it never took place before 1944. However Simca produced tracks pairs for the SdKfz-7, SdKfz-10 and SdKfz-11 half-tracks
Somua:
The Wehrmacht captured the Somua MCL (S303(f)) and MCG (S307(f)) halftracks, armored for the most. Some were recycled into rocket launchers carriers.
Talbot:
The company was previously known for its personal cars. It was forced to produced tracks for the SdKfz-7, SdKfz-10 and SdKfz-11 and braces for the Büssing-NAG S4500, as well as spare steering for the Panzer 38(t).
Unic:
200
Unic TU1 U305(f) and 3,000 Unic P107 U304(f) halftracks were used by the German army.
Trippel (Alsace):
The factory was situated at Molsheim in the former Bugatti factory, producing a single model, the
Trippel SG6 amphibious car.
Willeme::
Willeme DU10 are 10t heavy trucks, used by the German army.
 Unit TU1 half track used as artillery tractor
Unit TU1 half track used as artillery tractor
 Renault AHR in service in the Werhmacht, Bundesarchiv circa 1942/43
Renault AHR in service in the Werhmacht, Bundesarchiv circa 1942/43
Read More/Src
Kfz list
forum.axishistory.com/
SdKfz list
Goliath
Henschel 33
Springer
Borgward IV
List ww2 german vehicles
kfz numbers
Schwerer_Wehrmachtschlepper
Pz.Sfl._II
kfz without numbers