BM-27 Uragan 9P140 (1975)
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
Truck (1975) - c1,500 built
The BM-27 Uragan ("Hurricane", GRAU index 9P140) is a self-propelled 220 mm multiple rocket launcher (SPRL) designed in the Soviet Union, specifically to deliver cluster munitions from large 220 mm rockets. It entered service from 1975. For the first time, a rocket launcher vehicle, long derivative of the famous WW2 Katiusha, is able to deliver a spin and fin stabilized rocket. The vehicle was designed and manufactured by Splav State Research and Production Enterprise on the base of the dependable ZIL-135 8x8 prime mover already made famous by carrying the SCUD across the world. Like many other versions of the ZIL-135, the BM-27 Uragan was exported to some 19 countries, was licence-built and derived and found a lot of action in a dozen of wars and conflicts, and this story is not over. The improved Uragan-1M commissioned in 2008 is its designed successor.
Development
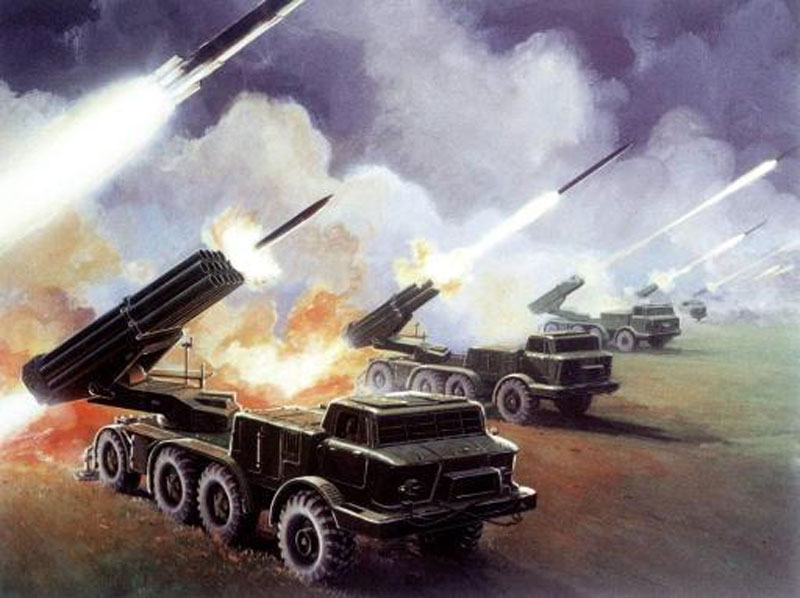 US DoD artist impression of the Uragan
US DoD artist impression of the Uragan
The ZIL-135 made famous as the primary 8x8 tractor for the SCUD missile around the world for its numerous operators, was declined into a large variety of specialized vehicles, including at least two main SPRL (rocker launcher vehicles): The 220mm BM-27 Uragan and the 300mm BM-30 Smerch, closely related but with much more powerful, long range and sophisticated rockets compared to the good old WW2 "Katiusha". The post here is about the BM-27 Uragan. It was specifically at first designed to replace the BM-21 122mm rocket launcher at brigade level of artillery division and regiments at army level.
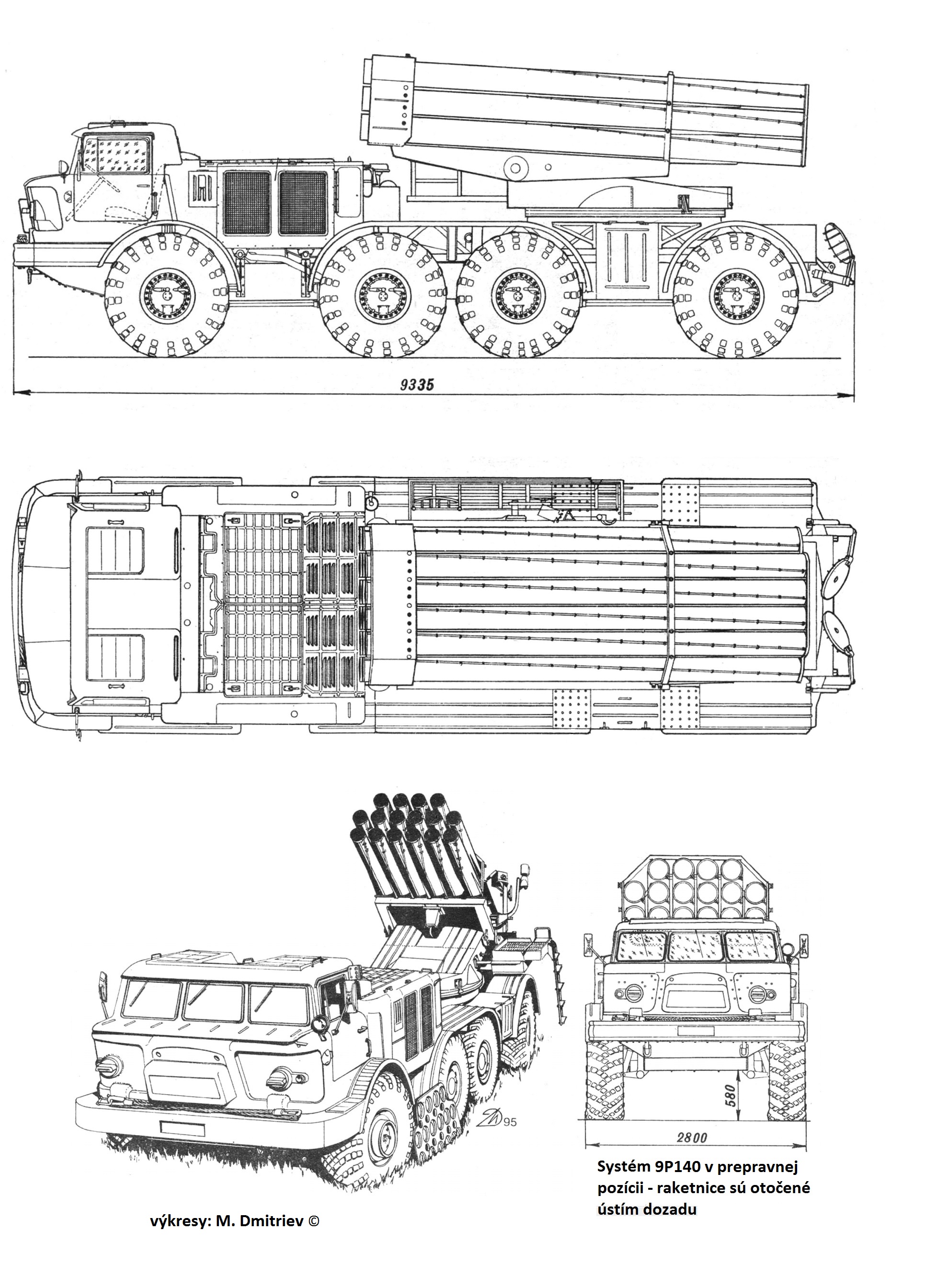 Tech drawing
Tech drawing
The complex, in service from 1975, publicly revealed in 1977, was in development since at least 1971. Chief designer was Alexander Nikitovich Ganichev and for the truck itself, Yu. N. Kalachnikov. The combat and transport-loading vehicle designed together were based on the same, but modernized chassis of the ZIL-135LM truck. It was designed to be able to fire sixteen of the brand new 220 mm rockets at 360° in one salvo of 20 seconds and to be reloaded in a minute or so. Initial specs noted a fully loaded combat vehicle no more than 20 tons for tactical airlift, whereas the rockets weights 280 kg alone, and to be served by a crew of no more than four. It was designed to replace older systems in rocket artillery regiments, districts based, as well as artillery divisions and in combined arms units for export.
 Vehicle of the 4th Tank Devisision
Vehicle of the 4th Tank Devisision
 Interior dashboard cab
Interior dashboard cab
It was designed to engage any type of group targets, vehicles as well as military and industrial facilities. It needed to be NBC proof, and operable from inside at any time, night aor day in all climatic conditions with temperatures ranging from -40° to +50°. The base truck but its launcher were to be not tall enough to be transported by railway, go under tunnels, and fit inside military transport aircraft.
Design of the BM-27

The 9k57 truck
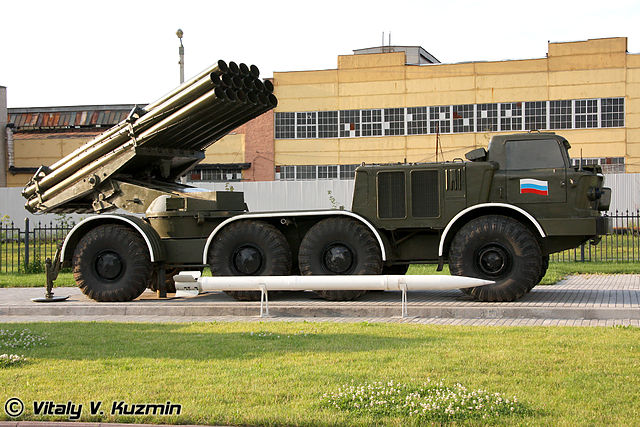
The main carrier is a 8x8 truck chassis ZIL-135LM. This truck is a modernized version of the 1959 ZIL-135 and is motorized by two diesels of 177 hp each, 350 hp total at 3,200 rpm driving all four wheels either side of the vehicle. Meaning if one of the engine fails, the truck cannot properly steer. The BM-27 system thanks to this powerplant could reach 65 km/h with a maximum cruising range of 570 km. It could negotiate gradients up to 57% and ford 1.2m without preparation. It can also climb up to 0.6m or gap a two meters trench.
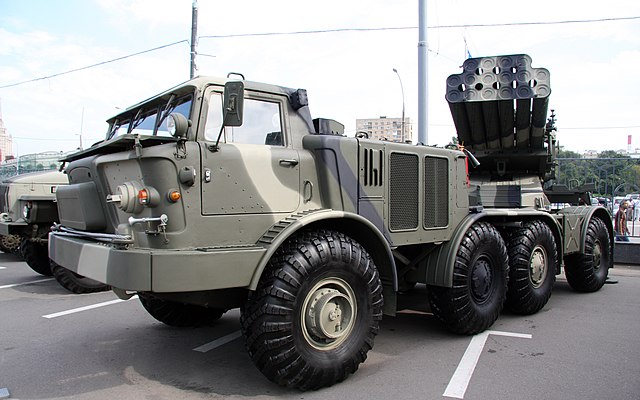
Launcher

BM-27 fully deployed and ready to fire, note the two hydraulic feet.
The launcher system of the BM-27 is mounted at the rear of a ZIL-135LM chassis wit the tubes arranged In three banks, the two lower with six tubes, the upper bank with four. The launcher is mounted in a way to present its front to the rear, for a powered elevation to +55º and a traverse of 30º left and right. There is a manual backlup in case, but to avoid overhang, and at the same time place the launcher as far as possible from the truck, the mount's arms extends in such a way, after a 90° turn, that the launcher is protruding from two meters at the rear of the chassis, largely clearing the cabin. The normal crew comprised four, a driver and three operators. The cab is identical to the ZIL-135 trus, fully enclosed but unarmoured. The two diesel engines powering the vehicle are immediately at its rear. The crew compartment was modified to house the preparation dashboard and displays as well as for the main operator to select single rockets or a salvo mode.
Features
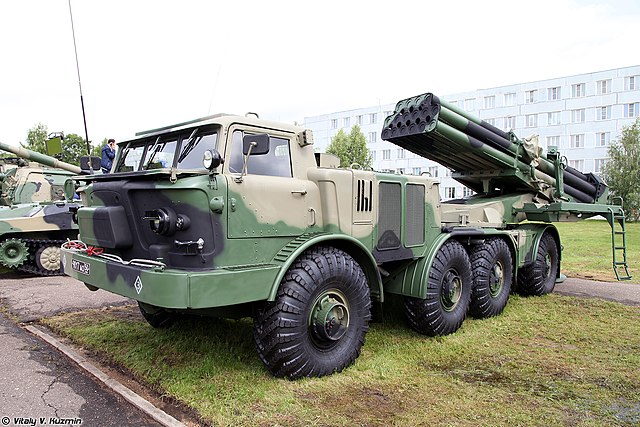
 BM-27 in parade
BM-27 in parade
The BM-27 comes with a dedicated sight, mounted on the left side of the launcher. It can be accessed via a folding ladder when the truck is stopped and prepared. While underway, the ladder is located on the other side and turned upwards 90°. In addition two sets of two manually lowered, hydraulic damped jacks, telescopic, acting as feet are lowered to the ground, fixing the chassis in place. The 9P140 cabin also posseses a blast shield raised during firing. The launcher electrical traverse had a backup. There is a protection for the tubes when travelling, with a light sheet metal cover over the muzzles to stop any froeign intrusion plus caps. When travelling also, the mount is locked in place. But there is no cover for the muzzle end of an unloaded launcher.
Support Trucks
9T452 transloader vehicle

A BM 9P140 unit is always assisted by one or two 9T452 transloader vehicle. The latter uses the very same ZIL-135LM chassis but with a flatbed designed to accomodate up to sixteen reloads arranged in two stacks on both sides, and at the extreme rear stands an hydraulic crane man-operated to perform the actual lifting, moving of the rocket, and it is capable of lifting 300 kg. The whole operation is usually performed in 15 minutes, by ideal conditions.
Kapustnik-B Fire Control Vehicle
1V152 (Kapustnik-B Fire Control Vehicle)
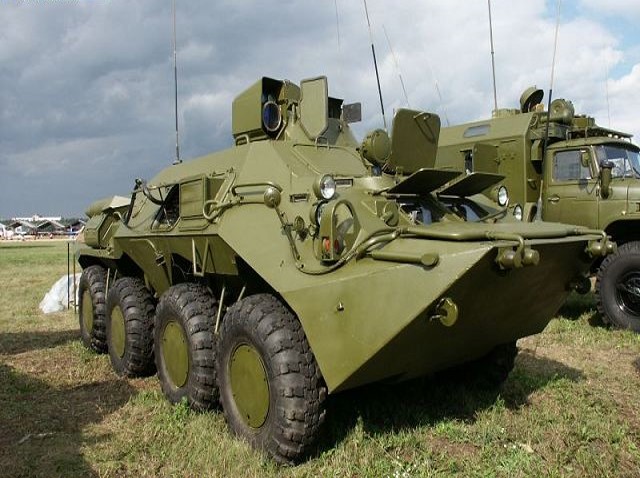 1V152 command vehicle (src odin)
1V152 command vehicle (src odin)
Any battalion is assisted by a an automated fire-control system carried inside the commander's vehicle 1V152. This is a variant, armoured, of the BTR-80 8×8 APC. There is also the Chief of Staff vehicle comprising housing, based on a Ural-4320 truck chassis. Also in the batallion are three Battery Commander's vehicles based on BTR-80 APC chassis plus three Battery Senior Officer's vehicles using the Ural-4320 truck. The Kapustnik-B is a complete suite geared for reconnaissance, initial orientation, location fixing as well as determining weather parameters and gathering firing data as well as inter-battalion and division communication as well as data link with other units and inside the bataillion. All the data is managed by a single data processing computer with displays for 2-3 operators.
 1V152 and Ural truck, part of the Uragan complex
1V152 and Ural truck, part of the Uragan complex
Base work of Rockets
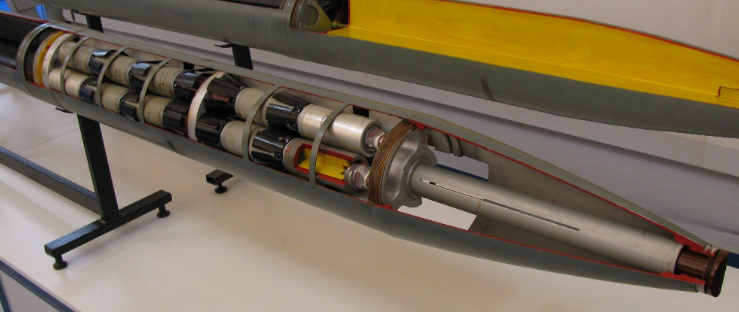 Rocket
Rocket
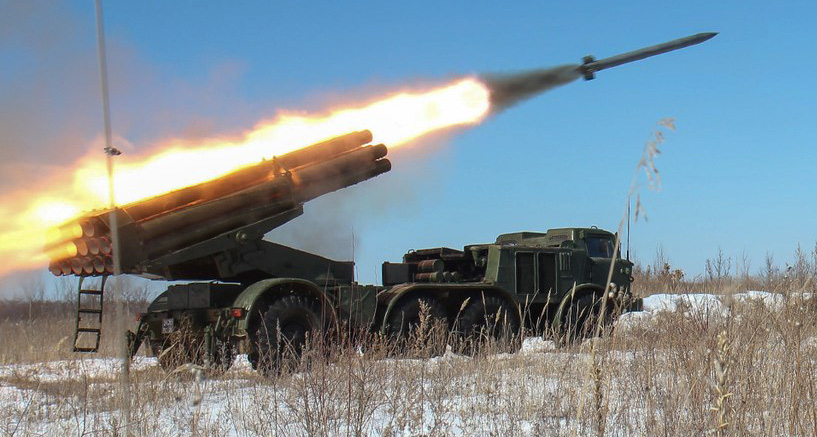
The BM-27 is setup and ready to fire in less than 3 min. It fires a volley in 90 seconds then moved away. When firing on short distances, a brake ring placed at the head of the rockets. The latter are Solid propellant rocket 9D159 (9D160 on the 9M51). They are given 9X164 or 9X963 wearheads, loaded with RNDSI-5KM gunpowder, or 9X258 igniter and the EVP-27M electric igniter (for the 9X317M) or the PP-9RS squib (on the 9X264). The fuel burning rate and thrust impulse depend on temperature, meteorology, in permissible ranges comprises between -50 °C to +50 °C.

The 9N128F warhead is equipped with a mechanical rocket fuse MRV-U (9E244) and the 9M27S with a remote fuse 9E261, whereas 9M27K3 is the expelling charge for 9X186 cassettes of cluster warheads. The tip is a 120-second tube TM-120 (9E245) with adjustable timeer from 4 to 120sec. and special expelling charge cocking fuses. It also reset the fairing and dispersed the warheads at the set time. Springs and centrifugal force due to the rotation also helps the scattering at up to 1150 rpm. The the initial rocket rotation is helped by the rifled tubes, with deep screw groove-guides, and after takeoff it is maintained by a deployable tail unit at a certain angle.

The Tail is auto-adjusted by taking in account side wind, and the tail acts like a weather vane to keep the course, fully stabilized even against the wind. The rockets are transported and stored in containers 9YA248/9YA248M. The standard 9M27F warhead contains 51.9 kg of explosives making on impact a 3 m deep, 8 m diameter crater on a soil of medium-density. The scattering commences at one to one kilometer and a half from 300 g of explosives of the hekfol type projecting striking elements. These are 9N235 hard rollers which can defeat a 6mm (0.3 inch) steel sheet on a 10 m radius or 2 mm thick at 100 m. It can kill anyone within a circle of 1150 m².
The 9N128K2 and 9N128KZ rockets carries mines with a self-destruction mechanism, staying inert to up to 40 hours, whereas RS 9M59 mines are set for 16-24 hours. Firing the 9N128KZ creates an anti-personnel minefield of low density over 150 hectares.
9BM27 Rockets

High explosive: 9M27F, warhead 9N128F, 280 kgs, 4832 mm long, 100 kg warhead, 51.9 kgs HE, 35 km range
Thermobaric: 9M51, warhead 9N515, 256 kgs, 5147 mm long, 143.5 kgs warhead, 30.2 kgs contact exploder, 13 km range
Cassette: 9M27K 9N128K WH, 270 kgs 5178 mm 90 kh HE fuse, 35 km
9M27K1: 9N516 WR, 270 kgs 5178mm 90 kgs HE fuse 35 km
9M27K2: 9N128K2 WH, 270 kgs, 5178mm, 89.5 kgs HE, 24 fuses charges, 35 km
9M27K3: 9N128K3 WH, 270 kgs, 5200mm, 90 khs HE 312×0.04 fuse charges 34 km
9М59: 9Н524 WH, 270 kgs, 5178mm, 90 kgs, 9× 1.85 fuse charges, 35 km
Incendiary: 9М27С (9Н128С warhead)
Chemical: 9M27 (9N519 warhead, 20x charges, fuse)
Propaganda: 9M27D, warhead 9N128D.
Variants
Uragan 1M
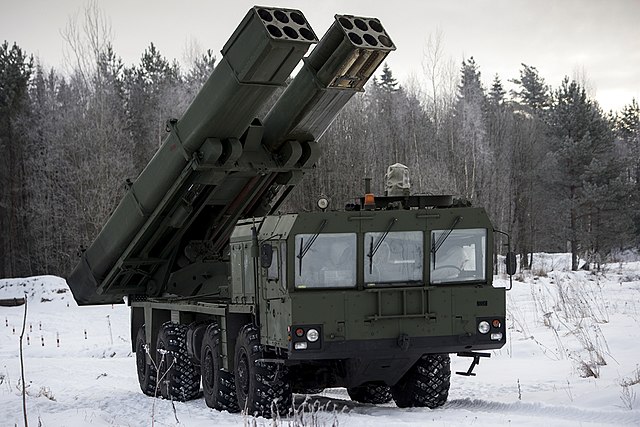

 Uragan 1M
Uragan 1M
The Uragan-1M presented to the public in 2007 is fully automated automated and is able to fire the 300 mm rockets of the BM-30 Smerch system as well, with a simplified reloading by just barrels, with two banks of six 300 mm launch tubes or fifteen 220 mm launch tubes fusing the Smerch/Uragan into a unified vehicle. Deliveries started by September 2016.
9A53 Uragan U
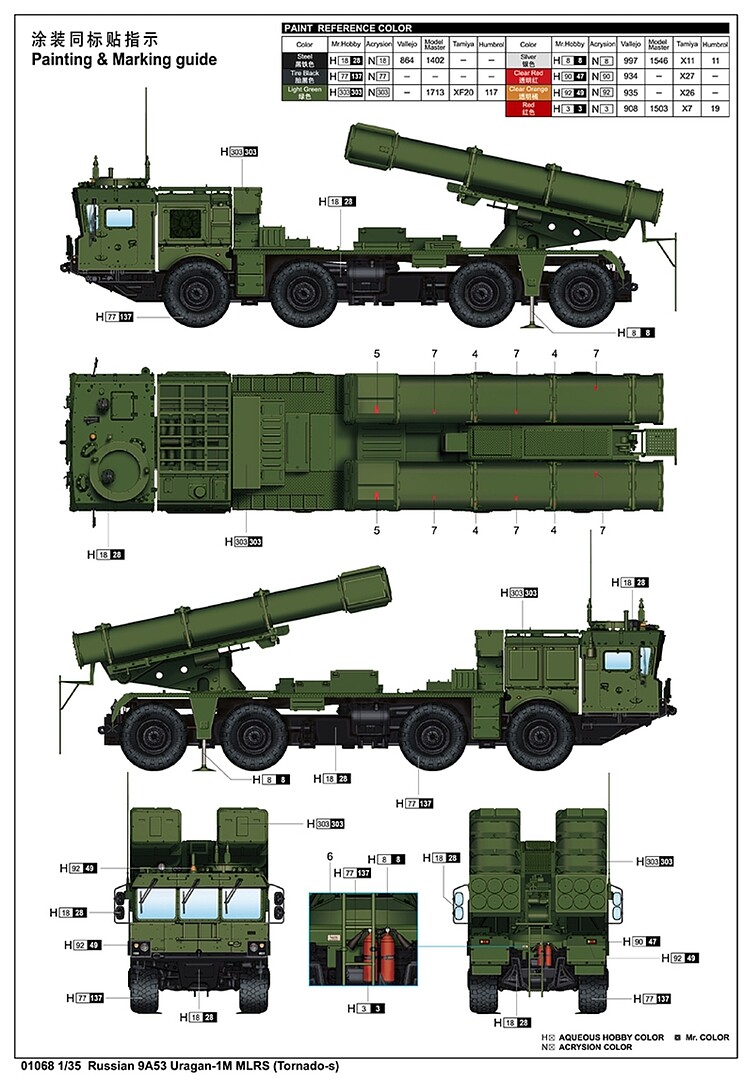 9A53
9A53
The system was also declined into the 9A53 Uragan-U presented by 2009 with two banks of fifteen launch tubes but on the more modern MZKT-7930 chassis. The modular assembly also using change of tubes allows to operate the BM-30 Smerch and BM-21 Grad rockets as well.
Bastion 03
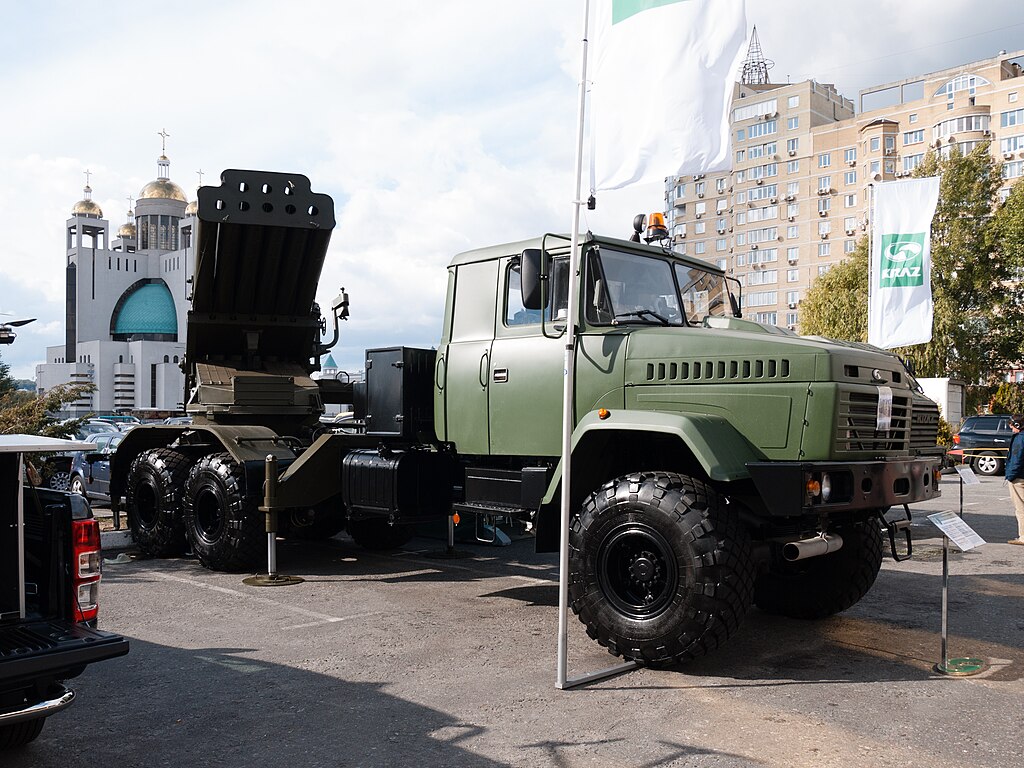

 KrAZ-63221RA 6x6 variant
KrAZ-63221RA 6x6 variant
There was also a 6x6 KrAZ-63221RA based variant, more compact, called the Bastion-03 made by AvtoKrAZ and presented in 2010. No production as yet.
Burevia

Prototype also called 'Shtorm' developed at the Ukrainian Shepetivka Repair Plant and featuring a brand new digital fire control system capable for target sharing between systems, with the old ZIL-135 replaced by a more moder, Western-sourced Tatra 8x8 T815-7T3RC1 chassis.
 The larger B-30 Smerch
The larger B-30 Smerch
Operators
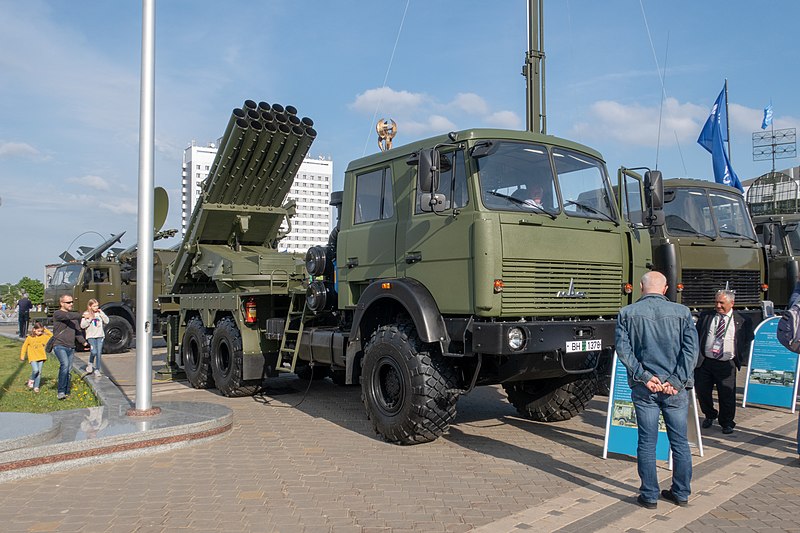 Belarusian upgraded 9P140B
Belarusian upgraded 9P140B
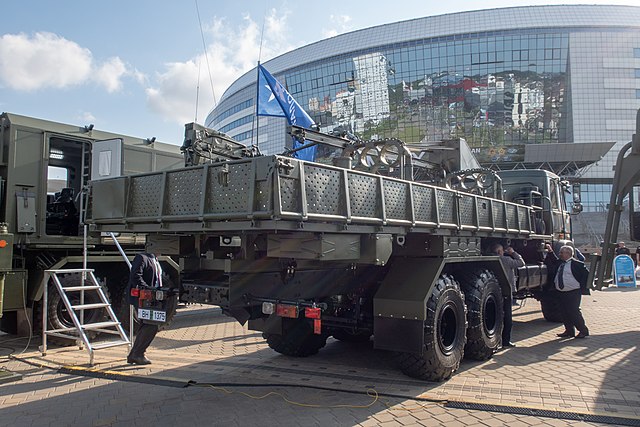 Belarusian 9T452
Belarusian 9T452
- Afghanistan: 18x 9P140 delivered, c15 as of 2010
- Angola: Unknown number Uragan-M, modernized Belarus 2023
- Belarus: 36x 9P140 as of 2023
- Eritrea: Nine 9P140 as of 2023, delivered 2007 from Belarus
- Guinea: Three 9P140 Uragan as of 2023 on 4 delivered
- Iraq: 24 Uragan delivered, no longer active
- Kazakhstan: 180 9P140 in storage by 2019
- Kyrgyzstan: Six 9P140 as of 2023
- Moldova: Eleven 9P140 as of 2023
- Russian Ground forces: 200 9P140 Uragan, 6 2K512 Uragan-M in service, 550 in storage
- Russian Coastal forces, Navy: 18 9P140 as of 2024
- Syria: About 6-8 9P140 Uragan as of 2023
- Turkmenistan: 60 9P140 as of 2023, allegedly 54 delivered
- Ukraine: 40x 9P140 as of 2023 over 139 delivered
- Uzbekista: 48x 9P140 as of 2023
- Yemen: 12 Uragan delivered from Moldova in 1994
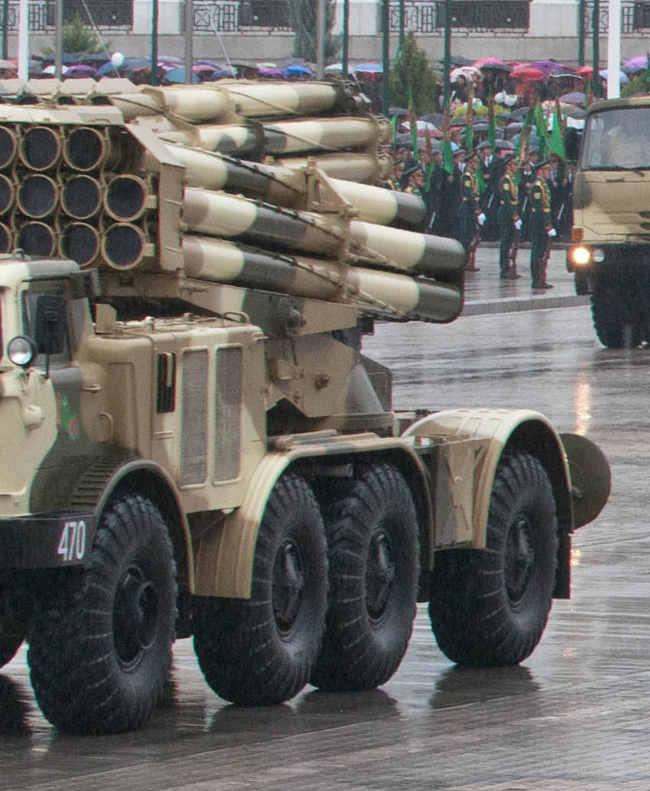 Turkmenistan Vehicle (9K57 Indep. Day Parade)
Turkmenistan Vehicle (9K57 Indep. Day Parade)
 9k57 winter Exercize
9k57 winter Exercize
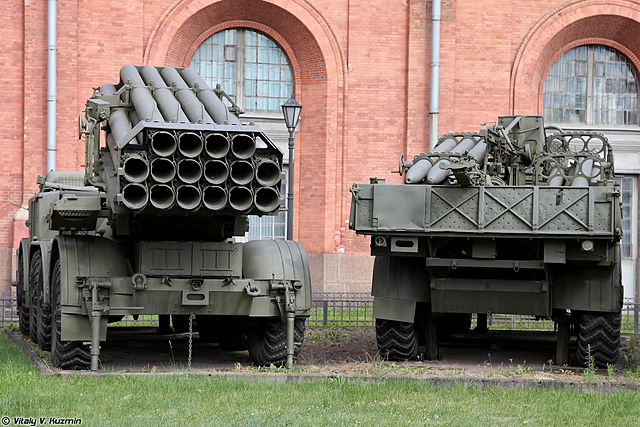 Both vehicle's rear
Both vehicle's rear
|
| Dimensions: | 9.63 x 2.8 x 3.23 m |
| Total weight, battle ready: | 15t empty, 22-24.3 tons FL, 48,590 ib |
| Tires: | 8x |
| Crew: | 4-6 |
| Propulsion: | 2x V8 Zil-135 Gasoline engines, c350 hp/3200 rpm |
| Speed: | 65 kph, 40 mph |
| Range (road/off road): | 768 tank, 570 km road, 311 miles |
| Armament: | 16x 220 mm rockets, see notes |
| Production: | c1400, or 900 based on exports. |
Tactical Deployment
 Vehicle of the 135th Arty Brigade
Vehicle of the 135th Arty Brigade
In the Russian Armed Forces, the Uragan are assigned to artillery regiments and brigades. Each of these regiments and brigades has a single rocket artillery battalion with eight batteries, each comprising six BM-27 (9P140) and 1 or 2 TZM 9T452 supply vehocle, a BTR-80, a modified Ural-4320 truck. Each division at HQ level also comprises three batteries, with one BTR-80, one Ural-4320 truck and a ZIL-130 repair shop truck, plus a "Zoo" radar truck for counter-battery and a Kapustnik system command vehicle. The whole unit was tailored to engage and suppress various objectives sich as open and covered infantry, unarmored, lightly armored and armored vehicles in motorized infantry and tank companies as well as enemy artillery units, tactical missiles, AA systems, ground concentrations of parked helicopters, command posts, communication centers, infrastructure and facilities.

So far, the 9K57 MLRS started to see its first combat use in Afghanistan. it was later deployed during the first and second wars in Chechnya, War in Georgia in 2008 and eventually the 2014 War in eastern Ukraine, by both sides, with Ukrainian forces using the 9M51 thermobaric rockets on pro-Russian separatists in Donetsk, Lugansk and Makeevka.
The vehicle was also deployed by non-Russian forces, such as the Syrian Arab Army during the Civil War, notably the siege of Palmyra and also directly by Russian armed forces.
 Ex-Russian destroyed 9P140
Ex-Russian destroyed 9P140
From 2022 onwards, the BM-27 had been extensively used by both sides after the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine. It was made infamous at Chasov Yar, killing 46 civilians and 2 Ukrainian army personnel and Human Rights Watch experts had started documenting such occurences, pointing out the use of 9M27K cluster munitions on Nikolaev, Chernigov, razing notably the children's hospital there as well as the Kharkov hospital among others.
 Monument in Tula
Monument in Tula
The Russian MoD compares the Uragan to the NATO
M270 MLRS, an armoured and tracked vehicle entering service with the US Army in 1983. The M270 featured at the time M26 unguided rockets with a cluster warhead M77 using cumulative fragmentation sub-elements, 32 km range. In the 1990s and later from 2009, the M270 received the M26A1 rockets for increased flight range (ER-MLRS using a frag warhead with 518 fragmentation sub-elements M85, 45 km range. After adoption of M30 guided missile on the M270/M142 in 2004, the M26 ordnance were gradually removed from 2009. The M142 MLRS of 5 inches or 227 mm caliber sports the M30 (FRAG) and M31 (HE) versus a dozen types in the Russian arsenal for the Uragan.
The Uragan was also compared to the NURS Mk-2 and Mk-4 rockers sported by the Israeli LAR-160 system. In 2010, IMI completed the 160-mm ACCULAR guided missile for the LAR-160, with guidance by adjusting the flight path thanks to microjets combined with a GPS and an inertial navigation system. For easy and fast reload, all rockets are pre-packed in transport launch containers (TPC) having the same caracteristic as a standard TEU shipping container. The Uragan was also compared to the Turkish MBRL launching both unguided and guided missiles of standard 122 mm, 230 mm, 300 mm, as well as the KHAN 610 mm tactical missiles .
Sources
en.topwar.ru/ The Uragan complex
issuu.com/avtokraz
navyrecognition.com uragan-1m-mlrs
armstrade.org
weaponsystems.net 1045-220mm+9M27
weaponsystems.net BM-27 Uragan
www.splav.org
weaponsystems.net 1044-9K57+Uragan
army-guide.com/
armedforces.eu
militaryfactory.com
armyrecognition.com bm-27_9p140_uragan
en.wikipedia.org
odin.tradoc.army.mil