Land Rover Series
 4x4 light utility vehicle (1948-1985)
4x4 light utility vehicle (1948-1985)
The legendary British Jeep
The Land Rover series I, II, and III are compact British off-road vehicles. They were produced by the Rover Company since 1948, and after many postwar fusions, by British Leyland. Although clearly inspired by the US jeep of WW2 fame, the Land Rover had definitely its own style and soon ceame as well known and iconic in the realm of early 4x4 light vehicle. It was also the first mass-produced civilian four-wheel drive car with doors and hard roof. The design had many interesting ideas, notably the use of a sturdier, fully box-welded frame and non-rusting aluminium alloy bodies which explains their fantastic longevity. In 1992, Land Rover (now a brand), claimed 70% of all vehicles produced were still in use worldwide.
Evolutions
Early series had leaf-spring suspension, with selectable two or four-wheel drive (4WD). However the early serie I of 1948 up to mid-1951 still relied on a constant 4WD using a freewheel mechanism. At the other end of the spectrum, the initial V8 version, series III had also a permanent 4WD. The three series had an alternative starting system which was age-old, they could use a front hand crank with the option of front & rear power takeoffs to carry various accessories.
The long wheelbase model arrived in 1954, as well as the world's first four/five door 4WD off-road station wagon in 1956. These vehicles excelled in space utilization with three abreast seating with doors and aft troop seating, so seven seats in all for the SWB, and ten in the LWB models. This alone propelled ot to the category of 4x4 soft skin peronal carriers or UPC (Unprotected Personal carriers) appreciated by the military branch of dozens of countries around the world.
Development of the vehicle

The iconic Rover was conceived by the Rover Company in 1947, with fresh lessons of World War II in mind. Rover traditionally produced luxury cars, but the demand plumited in an empoverished country in the post-war period while there was still rationing on raw materials. Companies focused on building construction and industrial equipment, or those exported for exchange currencly were privileged. Rover's Coventry factory had been obliterated, like much of the city during the blitz, and move into a brand new "shadow factory" started even before the war in Solihull (Birmingham subburbs). It was used before to produce Bristol Hercules aircraft engines and was retooled and widened. The immense empty halls were setup for car manufacturing from scratch were a financial burden in case a reduced demand, so a new model promised to a very large production was targeted, a bit ike the 2VC in France and VW Beetle in Germany or the Topolino in Italy. The team was hard at work on a brand new, small and cheap car, which was only known by the time as "M Type". Drawings led to the manufacturing of a few prototypes, but still, production was deemed too expensive. Meanwhile, Maurice Wilks, Rover's chief designer, proposed to the direction a light agricultural and utility vehicle close to the Willys Jeep, which use became widespread after the war in the civilian market and was still in demand.
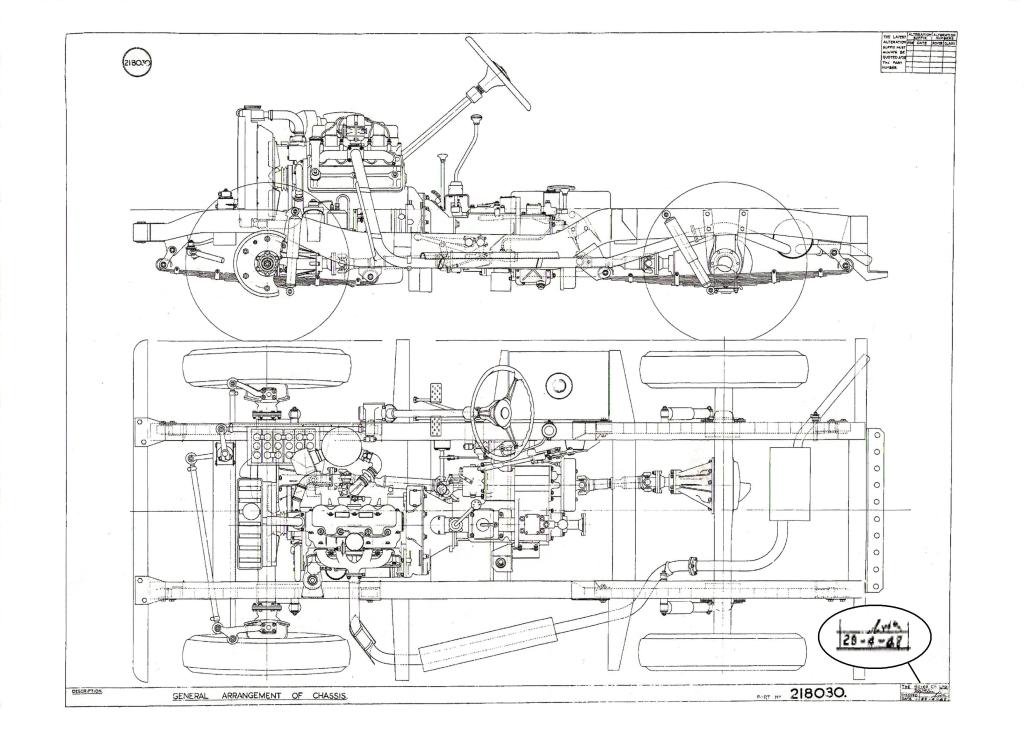
 Blueprint of the prototype
Blueprint of the prototype
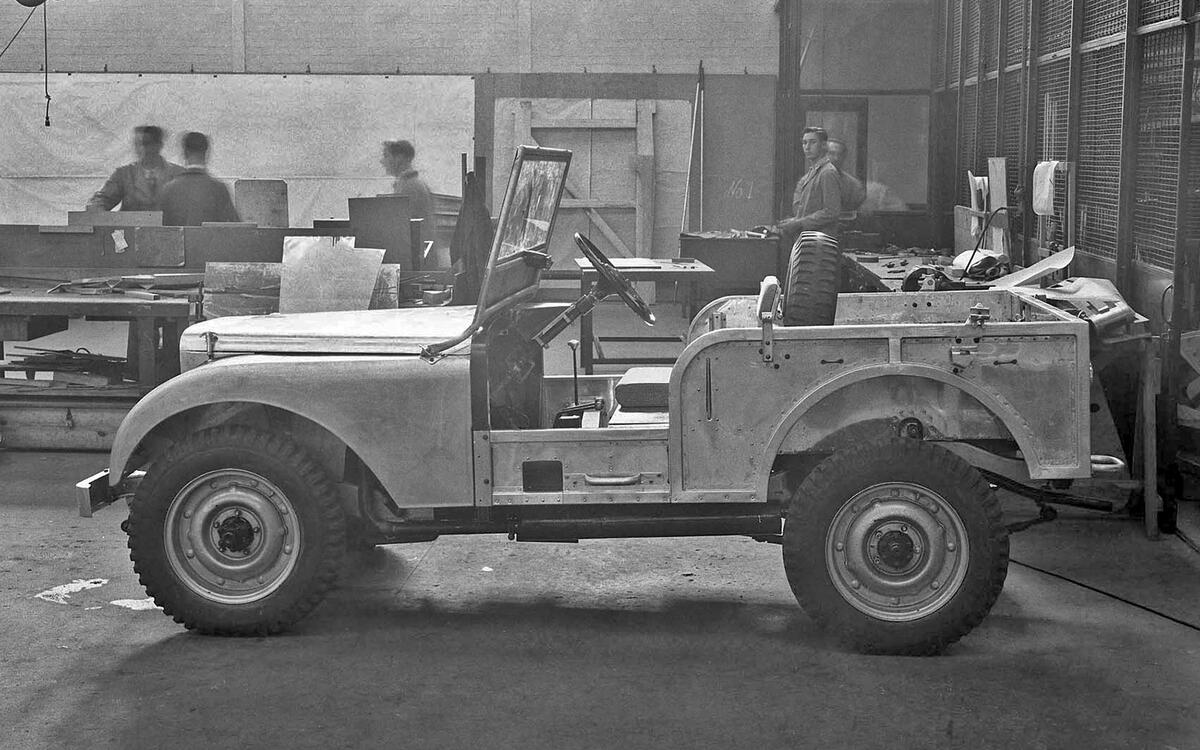 Land Rover Prototype (src autocar.uk)
Land Rover Prototype (src autocar.uk)
Wilks however emphasised an emphasis on agricultural use and therefore distinctive off-road capabilities. The Standard Motor Company at the time faced an identical situation and started earlier the Ferguson TE20 tractor in their own "shadow factory" in Coventry. The latter became an instant success and drew the factory profits up. Maurice Wilks himself made his tour of duty during the war as a driver of a Jeep and retained an army-surplus Jeep on his farm in Anglesey (North Wales). He only added a more modern power take-off (PTO) feature which was a novelty in the market by the time, an in-between jeeps and tractors. The first Land Rover early concept was indeed conceived as a cross between a light truck and a tractor, and had many features similar to the German Unimog developed at the same time. We know the success of the latter afterwards.
The first prototype resembled closely to the serie I, but differed in some details, notably its most distinctive feature, the steering wheel mounted in the middle of the vehicle. This 1947 model was therefore named the "centre steer". To gain time, it was built on a Jeep chassis while using and engine and gearbox from a Rover P3 saloon car. The bodywork was handmade, using a rather advanced alloy of aluminium and magnesium called "Birmabright" (from "birmingham"), created specially to save the rationed steel. The colours of the first models were limited at first to local surplus aircraft cockpit paint, so basically shades of light green, underlining their military aspect. The first pre-production Land Rovers arrived by late 1947, and were developed and tested by Engineer Arthur Goddard's team.
 1948 Land Rover pre-production number R04; at the National Motor Museum in Beaulieu, Hampshire, England.
1948 Land Rover pre-production number R04; at the National Motor Museum in Beaulieu, Hampshire, England.
 Land over prototype 1947 ‘Centre Steer’(cc)
Land over prototype 1947 ‘Centre Steer’(cc)
Tests showed the 1947 prototype to be a very capable and versatile vehicle, and its PTO drives fitted at the front of the engine, from the gearbox centre and rear was used to drive farm machinery like a tractor. It was used for ploughing and using other agricultural machinery in the field without problem, but somewhat lacked some torque in this matter, compared to s standard tractor. It was eventually setup for production, and as it happened, the emphasis on tractor usage became less important. In the end also, it was decided to drop the centre steering as impractical in a daily use, therefore the steering wheel was mounted off to the side. The bodywork also was simplified even more to ease mass production, some parts dropped, and unrelentless costs-saving measures helped to lower the unit price at a lowest point so far, without the benefits of lrge scale production still. In the end to gain torque, a larger engine was fitted with a dedicated transfer gearbox replacing the Jeep unit. The end result was completely rid of any Jeep component and ended even shorter and more compact than its American inspiration. It was however wider and heavier, but also faster while still retaining the original PTO drives.
 Land Rover serie I, initial serie.
Land Rover serie I, initial serie.
What is amazing about this project was that the Land Rover was designed as a short term, transitional product before the economical situation improves and the company could return, after making some cash for 2-3 years with it, to standard car production. Rover expected in particular much about export orders. As anticipated, car production restarted in 1950, but the team was surprised by the success of the off-road vehicle, which by far outperformed in sales all other models from Rover. With time, Land Rover became its own brand, still selling today with the same success. Its successful features were the result of simplifying tooling required for the vehicle and using little rationed materials. The aluminium alloy bodywork was retained throughout production despite being with time more expensive than steel, because it was light weight and resisted well to corrosion, ideal for an off-road vehicle. The flat body panels had a single, constant-radius curves defined by the original machine tooling limitations, made of hand-cut and hand-formed aluminium sheets on a basic jig at first. The sturdy box-section ladder chassis was made up from four strips of steel welded at each side to form a box, a simpler operation than for a conventional U- or I-section frame. All in all, this was a brillant combination of post-war scarcity ingenuity that defined the model, and despite it evolved to a more conventional set of technical solitions in recent years, the rugged classic of the 1960-70 still had a cult following worldwide. Naturally, he army sa immediately the advantage of such off-road vehicle to replace the Jeep in the 1950s, and the British Army became a naturak customer for the brand, as well as the average "gentleman farmer" that used to buy a station wagen before. Despite its rugged nature, the Land Rover became a status symbol as well and in the 1980s started to be "gentryfied", with powerful engines, luxurious interiors and more options in order to stay relevant. Of course the brand took the train of the urban 4x4 fad in the 1990s and adaptated itself as a trusted, classic marker of the
bourgeoisie, as far from its original agricultural roots as possible.
 Range Rover Chassis, original blueprints
Range Rover Chassis, original blueprints
 Range Rover Chassis
Range Rover Chassis
 serie II model 88 chassis
serie II model 88 chassis
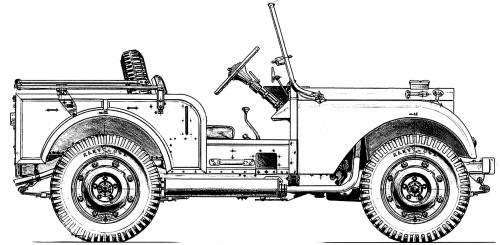
Land Rover serie I (1948-1958)
This was the first production version of the Land Rover, in 1948, also named Series I, or Mark I in the army. It was launched at the Amsterdam Motor Show, still equipped for farming and light industrial use, and with its original steel box-section chassis and aluminium body. Until 1951 it used an 80-inch (2.03 m) wheelbase, and 50 bhp (37 kW; 51 PS)1.6-litre petrol engine, and four-speed gearbox from the Rover P3 plus two-speed transfer box. Its four-wheel-drive system included an original freewheel unit disengaging the front axle from the manual transmission on the overrun, making a permanent 4WD. However it could be locked by using a ring-pull mechanism in the driver's footwell for a more conventional 4WD. To protect them from weather, they were given canvas tops for the doors and a roof, with a metal top in option. The Canvas were also optional, but cheaper, and requiped a folding frame similar to the Jeep, stored at the rear. It was like the Jeep, a two-doors only. In 1950, the lights were from moved behind the grille, to protruding through it. It was also clear that many customers complained about the very spartan interior and wanted a more cosy interior. In 1949, the body option "Station Wagon" was launched. It was made by Tickford, a coachbuilder working for Rolls-Royce and Lagonda. So its bodywork was wooden-framed, and had seating for seven people, which was quite unique at the time for such a small size. These Tickford serie I were also well equipped with leather seats, heater and one-piece laminated windscreen plus tin-plate spare wheel cover, interior trim many options. It was taxed as a private car, and fewer than 700 Tickfords were sold, nearly all exported. It did well to consolidate a more luxurious impage of the vehicle early on.
In 1952-1953, the serie I received a larger 2.0-litre petrol engine with Siamese bores while the unusual semi-permanent 4WD system was removed for a more conventional setup, front axle drive with a simpler dog clutch. It was by then classed as a commercial vehicle, free from purchase tax. But limited to 30 mph (48 km/h) on British roads, which of course rebuffed some customers for a daily use. A Law Lords appeal made it classed under a "multi-purpose vehicle" class, now only commercial if used for such purposes. The 1954 model had a longer, 86-inch (2.18 m) wheelbas and a pickup variant of 107-inch (2.72 m) wheelbase. This one was especially well used in many conflicts of the cold war, its rear platform rugged enough to carry all sorts of heavy weaponry, like heavy machine guns, bazookas, recoiless rifles and even light AA guns. The extra wheelbase provided additional load space also and the "spread bore" petrol engine was introduced with better cooling. This was appreciated in Africa where the vehicle became more widespread, gaining the image of the "safari car" by excellence. In 1955, the engine known as the 'later' spread bore appeared and by september that year, the first five-door model (LWB 107-inch chassis) appeared, known as the "station wagon", with seating for ten. The 86-inch version was still a three-door, seven-seater. They were cheap, using simple metal panels bolted together and intended for commercial use and transporting workmen to remote locations. They however had roof vents and interior lights.
The Station Wagons could be also fitted with a "Safari Roof", a second roof skin fitted on top to keep the interior cool in hot weather and reduce condensation in the cold. Ventilation was better. This version proved very popular and the Land Rover started to be used as a softskin APC by various armies around the world thanks to its great capacity. Ten men, this was basically an average infantry section. In mid-1956 the short wheelbase model became the "model 88" for 88 inches (2.24 m) and tle LWB the 109 inches (2.77 m) of model 109. The front chassis cross-member was moved an inch forward in order to make room for a new diesel engine optional in 1957. The 107 Station Wagon also received a diesel engine. These dimensions stayed standard on the serie II and III, for 25 years. The 1957 2.0-litre diesel engine used a modern overhead valve layout and was one of the world's first high-speed diesels for road use. It was rated for 52 hp (39 kW) at 4,000 rpm. It also of course gave much greater range to the vehicle, and consolidated even more foreign sales for the military.
 ancient ad, src autocar.co.uk
ancient ad, src autocar.co.uk
 Ad for the serie I
Ad for the serie I
 10th anniversary in 1958
10th anniversary in 1958
Land Rover serie II (1958-1961)
The series II (Mark 2) came in the previously developed 88 in (2.24 m) and 109 in (2.77 m) wheelbases, referred to as the 'SWB' and 'LWB'. It was the first to be overhauled by Rover's styling department, and chief Stylist David Bache. This model introduced the famous 'barrel side' waistline, of 5 inches (12.7 cm) greater width to cover wider tracks and reworked truck cab variant with curved side windows and rounded roof. The series II used a new 2.25-litre petrol engine producing 72 hp (54 kW), closely related to the 2.0-litre diesel. It became the standard until the mid-1980s when modern diesels too its place gradually. The 109-inch (2.77 m) series II station wagon had a twelve-seater option to take advantage of UK tax laws. Not only it was cheaper than the 10-seater version, but also the seven-seater SWB Station Wagon and remained a highly popular body style for decades, maintained until 2002. These vehicles were classed as minibuses and could use bus lanes if registered as such. On the military side, they became even more popular. having a 4WD vehicle of such size able to carry 12 men was appreciated. Africa was still, and remained, its first customer and the image of "Safari car" even reinforced. It even became the staple car in Kenya and most ex-British African colonies, rugged and easy to maintain and repair.
 A rare serie II LWB (model 109) with tractor wheels. Its agricultural DNA still there under the surface.
A rare serie II LWB (model 109) with tractor wheels. Its agricultural DNA still there under the surface.
Serie IIA (1961-71)
The SIIA only had minor cosmetic changes, with a SWB soft-top up to the five-door station wagon but avaliable with a new 2.25-litre diesel. From 1967, the 2.6-litre inline 6-cylinder petrol engine was available for the LWB Serie IIA with servo-assisted brakes. They were tailor-made for the American and Canadian markets. From February 1969 headlamps were moved into the wings on all models and panels were made shallower. The IIA was certanly the most sturdy of all these vehicles, and recoignised as the most classic Land Rover in the public's perception. By February 1968, the Rover Company was integrated into the Leyland Motor Corporationand its production total reached 600,000 vehicles, with 70% exported. The serie IIA proved also the most popular on the military market, and production did not even met the demand. 1969 was an excellent year, with 60,000 Land Rovers sold that year, more than any other production year of the brand. In Australia in the 1960s the Land Rover dominated at 90% the 4×4 market and this was also true in Africa and the Middle East. The vehicle naturally was featured constantly in many conflicts around the globe, the pickup LWB proving propular as a "weapon wagon" and the others as APCs.
 An army serie IIA FC model 101. It was used by the British Military (and others) as a prime mover, designed to tow the L118 Light Gun, with a ton of ammunition, retired by the late 1990s.
An army serie IIA FC model 101. It was used by the British Military (and others) as a prime mover, designed to tow the L118 Light Gun, with a ton of ammunition, retired by the late 1990s.
 An FC 110 troop carrier paraded in Jersey.
An FC 110 troop carrier paraded in Jersey.
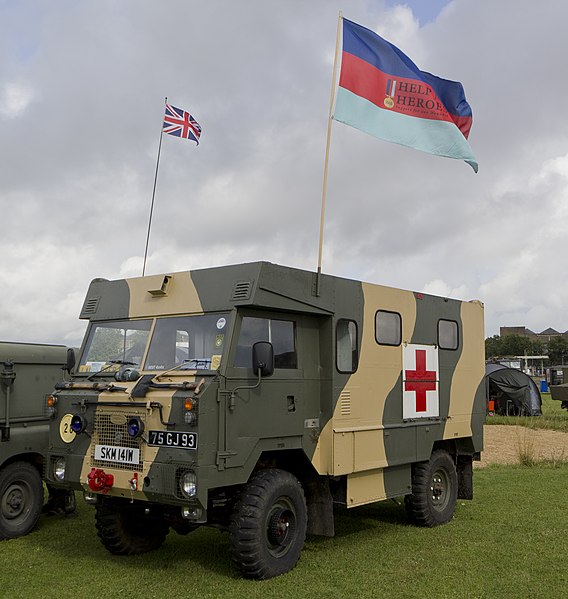 An ambulance version of the FC 110 used by the British Military.
An ambulance version of the FC 110 used by the British Military.
Series IIA FC (1962-1966)
The series IIA FC for "Forward Control" used the 2.25-litre petrol engine and the LWB 109 in (2,769 mm) chassis, while the cab was positioned over the engine to give more load space. This basically became truck in all appearance. Export vehicles had the more powerful 2.6-litre petrol engine and ENV (heavy duty) rear axle and later a matching front axle was introduced. Large tyres (900×16) were also fitted, with deep-dish wheel rims to spread ground weight as in trucks in general onrear axle. These FC remained however underpoweredfor their 1.5 long tons (1,500 kg) load. About 2,500 were made with an utility body and many were purchased by the military as a troop carrier.
Series IIB FC (1966-1974)
The Series IIB forward control was similar to the series IIA but fitted with the optional 2.25-litre diesel engine, which became a standard, but still wth the 2.6-litre engine for export. It was another Heavy duty wide-track axles truck, fitted with a front anti-roll bar and revised rear springs, mounted above the axle. This LWB was called model 110, because its wheelbase was increased to 110 inches (2,794 mm). Production ended when the vehicle range was rationalized, after the first ptrol crisis.
Land Rover serie III (1971-85)
 The RV serie III In action
The RV serie III In action
The series III used the body and engine of the IIa, with little or cosmetic changes, and the new serie III became by far most common with 440,000 built from 1971 to 1985. Headlights were moved to the wings on the late IIA models in 1969 to comply with Australian, American and Dutch lighting regulations. This became standard with the series III. The traditional metal grille was replaced with a plastic one and the compression was augmented for the 2.25-litre engine (8:1). In 1976 was celebrated the 1,000,000th Land Rover, from the same production line. The series III saw however its design upgraded to meet the 4x4 competition. It had synchromesh on all four gears, and interior design was revised as well as updated safety, plus the use of advanced materials. The dashboard became a moulded plastic dash and the central instrument cluster, moved to the driver's side. The LWB was fitted with the Salisbury rear axle, with the differential and axle case in one piece. Wheelbses remained the same as well as the chassis.
In 1980 however the old 2.25-litre petrol and diesels were updated with five main bearing crankshafts while the axles and wheel hubs were strengthened. This move was dictated by a tendency for commercial operators to overload their vehicles, and this had some consequences on the export market and pushed an unduring and undeserved reputation, despite 1982 fixes. New trim options modernized the interior, making it much more comfortable while the spartan interior was still optional for farmers and commercial users. In April 1982 the "County" spec. Station Wagon was introduced, on the 88 and 109 type wheelbases. They had new cloth seats from the Leyland T-45 Lorry, but also soundproofing kits, tinted glass and other leisurly options. At the same time appeared the high Capacity Pick Up (model 109 only). It offered 25% more cubic capacity and came with a heavy-duty suspension. It became very popular with public utility companies and building contractors, but also made its way in numerous insurrections and conflicts in alternative to the Toyotas. From 1979 was also introduced the V8 model, by Bruce McWilliams, then President of the Rover Motor Company of North America Limited, tailored for the American success, where it became a hit. Basically it used an alloy V8 from GM, 3.5 L 91 hp (68 kW) Petrol called "Stage One V8".
Land Rovers in the Army
 SWB LW model for the military
SWB LW model for the military
The British Army started to use series Land Rovers after testing the 80-inch (2.03 m) series-I in 1948. The Army wanted however a specially designed military utility 4×4 (developed by Austin, as the 'Champ'). But the Champ proved too complex, heavy and unreliable in battlefield conditions. The bacl up Land Rover thus became a favorite. The army also wanted standardisation its vehicles and equipment fleet. One of these plans was to fit Rolls-Royce petrol engines on all vehicles and a first batch of series-I was tested with Rolls-Royce B40 four-cylinder engines. This ended wth a 81-inch (2.06 m) wheelbase. The engine proved too heavy and harmed both the performances and torque which could be managed by the Rover gearbox. Rover therefore convinced the MOD that the Rover standard 1.6-litre engine was better, and eventually convinced the MOD order series I in testing batches from 1949. 50 were tested until the mid-1950s and 200 vehicles were ordered at times. By 1955, the Land Rover definitely gained traction, used in Korea as well as in the Suez Crisis, proving it was up to the task.
The 1960s saw the apparition of specialised versions:
-Standard 'GS' (General Service) vehicle
-'FFR' (Fitted For Radio), 24-volt electrics, large engine-powered generator and LR radios.
-Ambulance, 109-inch (2.77 m) series-II/series-III.
-LRDPV (Long-Range Desert Patrol Vehicle), the 'Pink Panther' (pink sand camo), 109-inch series II.
They were converted by Marshall's of Cambridge, stripped of doors and windscreens, fitted with grenade launchers, machine gun mounting ring, long-range fuel tanks, water tanks. They performed well with the SAS in desert patrol and special operations, ten years after the original LRDG. The tradition went on, and a modified Defender is now used by the same teams today.
 The LRDPV base don the serie II used by the SAS with their typical pink sand camouflage.
The LRDPV base don the serie II used by the SAS with their typical pink sand camouflage.
By the late 1970s, 9,000 series-III were used by the British Army, mainly as "heavy duty" versions, 109' chassis and soft top. They had improved suspension components and modfied cross-member chassis. They were declined with various electric power groups, 12-volt for the 'GS' and 24 for the radio version (FFR). A few actually had the 88-inch chassis, in GS/FFR variants later replaced by the air-portable 88-in "lightweight" version (SWB), successful in exports. Also this decade was launched two new models the 101-inch Forward Control truck and the 109-in FV18067 ambulance, both from Marshall Aerospace of Cambridge. The Royal Navy and Royal Air Force also used a small Land Rover fleet, the second using the 88-in model for staff transport, laisons and communications or airfield tractor duties. The Navy had a few GS-spec and Station Wagons for personnel/cargo transport. Typically they all used the 2.25-litre four-cylinder petrol engine, but the FC 101 truck had a more powerful 3.5 litre Rover V8.
The armoured Rover: The Shorland
In the 1970s the Short Brothers proposed an armoured version, the
Shorland Internal Security Patrol Vehicle, which saw extensive use in Ireland (dedicated post in preparation).
Other users
Netherlands & Denmark
The 88-in "lightweight" version (SWB) was adopted by the Royal Dutch Ground Forces and the Danish Army, but the latter used diesel engines and the Dutch had PVC tops. The Dutch also used the Forward Control Truck (FC 101), but used a 2.25-litre diesels instead of the Rover V8.
Australia & New Zealand
There was an Australian-made production, which concerned the series 1, 2, 2A and 3. They became the de facto utility vehicle for the Australian Army, Royal Australian Navy and Royal Australian Air Force, well adapted to local conditions. Aside the GS basic model used as Long Range Patrol Vehicles, there were also radio versions and ambulances, but also locally developed command reconnaissance cars, fire tenders and ceremonial vehicles. Production started as soob as 1948, replacing the Austin Champ and surplus Jeeps. The Australian series 2 came in 1958, 2a in 1963, series 3 in 1973. About 72 of the series 2 were converted as anti-tank "gunbuggy", armed with recoiless with a 106mm rifle. Special Forces also obtained the heavily modified Land Rover Perentie, a military variant of the Defender introduced in 1987, of which 2,500 4WD were delivered, but also 400 of the quite unique six wheel drive (6WD) versions in use today. The latter is used for special operations.
The New Zealand army was also quick to purchase 640 of the Australian-made series 1 in 1951-1953. 640 series 2 followed in 1959-1962 and a few serie 2A in 1965-1967 and in the 1970s, ex-series 2 and 2A vehicles, deployed notably by the ANZUK force in Singapore, re-manufactured by BLMC NZ Ltd in Wellington. The Land Rover "Skippy" is distinguished by differently cut guards. 566 Series 3 109" V8s were also purchased in 1982-1986. Land Rover V8s started to be phased out in 2006, when New Zealand opted for 321 Pinzgauer High-Mobility All-Terrain Vehicles.
Spanish Santana

"Santana" had become synonimous with 4x4 in Spain and beyond: Indeed Santana Motor S.A. was a former agricultural equipment manufacturer and spawned a car manufacturer unit in Linares (Jaén) financed by the Spanish government in 1954 to encourage development in Andalucia, Southern Spain. The company started talks with Rover in 1956 to get a licensing agreement for the series I like Minerva in Belgium or Tempo in Germany, Morattab in Iran. Agreement was signed in 1956 and production started two years later. The Santana Motor company made its vehicles in CKD form (Complete Knocked Down kits), shipped parts from Solihull, but assembled locally. From 1968 Santana created its own model with new engines. The old company "Metalúrgica de Santa Ana, SA" became "Land Rover Santana, SA". From 1964 onwards, the Santana was also promoted in the Central and South American Markets and Africa.
The company started to create its own CKD kits for Morocco and Costa Rica, and the models were modified from customer feedback. In fact it had better chances in exports due to lower prices, better local market knowledge and the financial position of British Leyland at the time. Santana engineered a gradually very different, more rugged version adnd its production diverged greatly from base Land Rover models until the late 1980s. The Santana range ios cheaper, but features anatomical seats, disc-brakes, turbo diesel engines, taper-leaf springs, coil springs, and reworked Forward Control versions and its own LWB called "Ligero". The agreement ended in 1983 but the company continued to develop its own range. However the company started to produce the Iveco Massif soon condemned because of the Fiat/Iveco merger with Chrysler, which owned Jeep at the time. The end result was that Santana went out of business in 2011.
Belgian Minerva

Minerva in Belgium was already famous for its
WW1 armoured car and produced a version of the Standard Vanguard under licence but when the army needed a lightweight 4×4 vehicle, Minerva's director van Roggen approached Rover in 1951 and by 21 June, they were preferred over Willys Jeep, with a contract signed in October 1951 for a sell starting in 1952, assembly granted to Minerva-Land Rover. The latter were manufactured under 80" and 86" chassis and production ended in 1956. Minerva later started to produce entire Land Rovers under licence. Arthur Goddard (Rover's Assistant Chief Engineer) validated changes by Minerva and helped setting up the factory for the assembly.
Src/Read More
Land Rover CC general
On classicsworld.co.uk
alchetron.com on Maurice Wilks
Land rover - dhrm4company.blogspot.com
Blueprint Land Rover 109 1962
expeditionlandrover.info
On petrodelicious Serie IIa
dunsfoldcollection.co.uk
On landroverlittlerock.com
On caradvice.com
The Range Rover On Wikipedia
The FC 101 On allisons.org