OTR-21 Tochka (1973)
 USSR (1973)
USSR (1973)
GRAU 9K79, NATO SS-21 Scarab, c1,200 built*
The OTR-21 Tochka (Tactical Missile Complex "Point", GRAU 9K79, NATO SS-21 Scarab) is a missile and its transporter launcher erector, 9P129. Produced from 1973 it started to be replaced from 2020 by the 9K720 Iskander. It was a solid design, 6x6 amphibious truck capable of launching a conventional or nuclear-tipped 9M79K ballistic missile reaching from 70 km (43 mi) to 120 km (75 mi) depending on versions. It was also well exported and used in many conflicts, including Ukraine recently.
Development
 The previous 9K52 Luna-M
The previous 9K52 Luna-M
When the Tochka system was first planned, Soviet troops were armed with Luna-M missile systems, which accuracy and range left much to be desired. Development of the new complex was started by a resolution of the Council of Ministers, No. 148-56, on March 4, 1968. In charge was put the mechanical engineering design bureau (Kolomna) led by a weapons designer as main executor. The vehicle chassis was designed and manufactured by the Bryansk Automobile Plant (BAZ), whereas the control system was developed by the Central Research Institute of Automation and Hydraulics. The launcher was developed by the Barrikady production association. This initial phase went on in 1968-70.
Testing started in 1971, and after all fixes were done and the whole system was approved, serial production started in 1973. So great was the emergency that the systm had not yet entered service. It was tested on the field and improved back to the factory as production went on, by 1975. Soon were delivered for the 9M79 missiles two warhead versions: high-explosive fragmentation (HE-Frag) or nuclear. The initial variant had a flight range of 70 km (44 miles), with an initial accuracy radious of less than 250 meters (820 ft).
After entering service, engineers were asked to improve the missile, notably thanks to the prvision of new electronic components. The new missile had a passive radar homing head as “Tochka-R”, and entered service almost ten years later, in 1983. New requirements came in between, forcing to further improve performances, notably flight range and accuracy. From 1984, work started and ended with the “Tochka-U” (GRAU 9K79-1, NATO SS-21 Scarab B) tested from 1986 to 1988. It entered service in 1989 just as the USSR was about to collapse.
Production of missiles was definitely performed at the Votkinsk Plant and according to other sources, to Petropavlovsk Plant in Kazakhstan. Production of "special chassis", for the TEL needed the BAZ-5921 and BAZ-5922 at the Bryansk Special Automotive Plant. Final assembly was done at the Barricades Association. The missile system involved many sub-parts that came from all around USSR and beyond. Thus after the collapse, a reorganization was needed, until it was decided that a better system was needed as replacement.

 Related OTR-23 OKA 9K714 (NATO Code name SS-23 Spider)
Related OTR-23 OKA 9K714 (NATO Code name SS-23 Spider)
Design of the OTR-21 Tochka

The BAZ-5921/22
The name "OTR-21 Tochka" was in fact named 9K79 Tochka missile system. It comprised the missile itself, 9M79, for the initial version, and the TEL or Transporter Erector Launcher or "TEL", which was in that case the BAZ-5921 truck, later 5922. Both were very similar. This 3-axle amphibious chassis BAZ-5921/22 were a development of the initial BAZ 5937/5939, but made as TELs specifically. The vehicle itself received on its aft section the launcher 9P129 and loader 9T218. BAZ factory developed the amphibious chassis BAZ-5921 with a 4-seater cabin forward for the launcher while the BAZ-5922 was used for transport and loading, with a 2-seat cabin.
 BAZ 5921 supply truck
BAZ 5921 supply truck
They derived from the rear engined chassis 5937/5939 (Missile compex "Wasp"). In this case, the engine was moved to the center of the chassis for better balance. The unified BAZ 5921/5922 chassis shared the same same transmission, suspension, braking system as well as its water jets and the whole electrical equipment plus additional equipment. The 5D20K-300 diesel engine was very close and developed 300 hp but with a powerful cooling system, two radiators and a better starting preheater for winter operations. Mass production of the vehicle sarted by May 1974, whereas the missile was already in production since 1973.
The hull and general caracteristics
 Blueprint HD
Blueprint HD
The BAZ-5921 had a useful payload of 6.3 tonnes and a crew of four, one driver and three to operate the rocket launcher. The hull was very caracteristic, with a wedge-shaped front end, three wingdshields at the front, small, and narrow, triangular side windows with bulletproof glass. It seems this was the only protection. The vehicle, in all the sources i can found never was mentioned as armoured and no figure is ever given.
That's why it's on truck encyclopedia. It was essentially a futuristic looking amphibious TEL, NBC protected with sealing and overpressure. Two hatches were installed on the roof, one for the front seats to the left side, and on for the rear seats, on the right side. They could be used to fire on the move in the worst case scenarios, but at 70 km distance on the battlefield, these vehicle were not supposed to be engaged.
There was a built-in lifting ramp with rails at the rear as part of the launcher in the rear compartment. The rocket was placed horizontally during transportation and raised up for launching, with stabilization foots buried in the ground and deflectors to vent out the blast when firing. The payload of 6.8 tonnes was related to the loaded missile. The BAZ 5922 had a modified body, with a shorter control section, two seats forward, but an extended rear open compartment with a canopy to contain two horizontally placed 9M79 missiles. This was the reloader vehicle, fitted with a two-piece hydraulic crane at the rear for reloading missiles into the the TEL BAZ 5921. Overall dimensions were a bit different at 9,47 m in lenght, 2,89 in width and 2,44 in height.
Powerplant & Performances

The BAZ 5921 was powered by a centrally-mounted 5D20B-300 diesel engine rated for 300 hp, capable of bringing the 18 tonnes vehicles to a top speed of 60 km/h on road (degraded off-road) and its Amphibious speed was 8 km/h. Range was 650 km. The BAZ 5921 could climb a 60% gradient, 40% side slope, 0.5 m vertical obstacle and gap a 1.2 m trench. It was Amphibious without preparation and had enough buoyancy built-in its hull to cross any water obstacle, as long as it was not at sea.
The 9M79 Tochka (NATO Scarab)

The Scarab A missile was in development from 1968 until 1974, and entered service in 1975. The missile Missile weighted 2 000 kg for 6.4 x 0.65 m in dimensions, and carried a warhead of 480 kg which could be either conventional, chemical or nuclear, for a range of 70 km. This was a tactical ballistic missile which had poor accuracy, with 160m of radius error. Warheads were the following:
-9N123F HE (High Explosive) blast fragmentation warhead for any hardened objectives and infantry
-9N123K submunition warhead, very efficient against armor concentration or airfields
-9N39/9N64/9N65* nuclear warheads (yeld 100 kt)
*also 9M79 TRK 9K79 "Point"
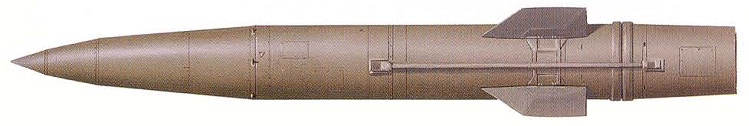
The Scarab B was developed in 1984-1988, entered service in 1989 with greater performances and accuracy across the board: The Scarab B Tochka-U was capable of hitting a target at 120 km and the Scarab C at 185 km with greater accuracy of 95 m and 70 m respectively. Given the heavy conventional payload, it ensure a blast powerful enough to flatten anything on a 200m radius. All had Inertial system for guidance. The Tochka-R uses passive radar to avoid radar detection.
The whole Complex was tailored to cross any obstacle and fired in all weather, day and night with temperatures ranging from -40 to +50°. Apart the 9T222(9T238) transport vehicle, the complex included a numbe rof specialized assistant vehicles such as the 9T218 transporter loader (BAZ 5922), 9V819 automated checkup and testing vehicle, 9V844 maintenance vehicle, 9F370 ammunition equipment set, and batteries of 9Ya234 missile plus their separated 9Ya warhead containers.
| BAZ-5921 specifications |
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 9.48 x 2.78 x 2.35 m |
| Total weight, battle ready | 18.15 t |
| Crew | 4 (driver, 3 operators) |
| Propulsion | 5D20B-300 diesel 300 hp |
| Top speed | 60 km/h on road, 8 km/h with waterjets |
| Suspensions | Torsion Bars |
| Range | 650 km |
| Armament | 9M79 Tochka (NATO SS-21 "Scarab") ball. tact. Missile |
| Armor | None but bulletproof glass |
| Production | Approx. 1,200* |
Deployment/Combat use

The Tochka complex was used for precise strikes on tactical targets: Control posts, bridges, facilities and depots, but also moving troop concentrations, or airfields. There were even alternatives of biological and chemical warheads developed. For safety, the missiles had a solid propellant, ideal for maintenance and deployment. These vehicles were musted in brigade with 18 launchers in a brigade, plus reload vehicles with two or three spare missiles, plus assistance vehicles seen above. Its amphibian capabalities and 60 km/h plus NBC-protection ensured great flexibility on the battlefield, notably it was envision to send them after the main push, safely 50 km behind the frontline in case of a counterattack.
The vehicle was well exported: During the cold war, it was used by USSR, but also Bulgaria (still 18 today), the Czech Republic, Hungary, East Germany and Poland. It became a vital part of the "second échelon" for long range strikes of the Warsaw Pact from 1975 to the end of the cold war and beyond.

BAZ 5921 reloading a BAZ 5922
Indeed after the collapse of the Soviet Union, small numbers were passed onto the ex-Soviet republics, and it was found in Armenia (3), Azerbaijan (4), Belarus (36, 465th Missile Brigade), Kazakhstan (12), Poland (4), Slovakia (Unknown, retired), and Ukraine (500 according to CSIS in 2022). It was also exported abroad, to Iran (Unconfirmed), Libya (Unconfirmed), North Korea (Licenced as the KN-02 Toksa), Syria (KN-02 Toksa), and Yemen (12, now Unknown). It is believed that Russia still currently possesses (they were not all operational) some 300 TEL vehicles and 310 nuclear warheads in all versions. In 1993 peak there were still 1,200 missiles estimated in park and in 1996 started a life extension program to prolongate the park for ten years of the Scarab B, with a first successful test by October 1999.
The missile itself was used rather recently, in the turbulent post-cold-war era: In the Yemeni Civil War (1994) First and second Chechen War, Syrian Civil War 2014 Russo-Ukrainian War and new 2015 Yemeni Civil War and intervention in Yemen as well as the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict.
Sources
alchetron.com
missiledefenseadvocacy.org
en.missilery.info
trucksplanet.com
ru.wikipedia.org
sixmania.fr
armedconflicts.com
armyrecognition.com
keymilitary.com 50-years-soviet-military-vehicle-testing
Related chassis, BAZ-5937, Osa (Wasp) complex
the-soviet-tank-thread-transversely-mounted-1000hp-engines/
militarytoday.com/
missilethreat.csis.org