GAZ-AAA Truck (1934)
 Soviet Light 6x4 Utility Truck (1934-43), 37,373 built
Soviet Light 6x4 Utility Truck (1934-43), 37,373 built
The "Polutorka" on six wheels

The 1932 GAZ AA, nicknamed "Polutorka" became the standard light truck in service with the Red army when Operation Barbarossa commenced in June 1941. Already 155,000 GAZ AA were in service, but there was a pool of one million total requisitioned. Production of the simplified GAZ MM started in wartime, while the 6x4 GAZ AAA followed suite with the Model 1940 and 1941. Production stopped in 1943 with just 37,000 vehicles delivered, a small fraction of its 4x4 cousin, but it found more specialized applications.
Development of the GAZ AAA
NAZ was created in 1926 with assembly line created to produce the Ford Model AA under knocked-on kits at first. In 1931 this NAZ-AA and the NAZ-A passenger cars were produced and from 1933 the factory was expanded, becoming GAZ ("Gorky Automobile Plant") in Nizhny Novgorod. From the successful 4x4, the company in 1934 created the GAZ-AAA, a 6x4 2t truck variant, from 1934. The army toyed around with the idea of better off-road versions such as the experimental GAZ-AAAA 8x8 (1936) or derivatives such as the GAZ-410 dump truck (1934-1947).
In the 1920s, the concept of three-axle or "six-wheeled" off-road vehicles with the 6×4 arrangement became popular in the global automotive industry. In Central Asia, the popular French medium-sized Renault MH utility vehicle proved it could do with difficult terrain, and some examples were purchased for civilian application, especially in the far east. meanwhile, the Red Army, pirchased the British heavy 7-ton Moreland TX6 truck. On the basis of the latter in 1931, a armored car D-9 was created. By the end of 1930, some 1,000 6×4 Ford-Timken trucks accepting 1.5–2.5 tons was purchased in the United States, as the basis for a standard two-axle (4×2) Ford AA, the ancestor of all "trihosok".
In 1931, the Ford-Timken was assmbled from knocked-down kits at the First Automobile Assembly Plant. On the basis of Ford-Timken already in 1931, armored vehicles such as the D-13, BAI and BA-3 were developed in 1931-1934 as well as the experimental BAD-1 and BAD-2.
Development of the Soviet 3-axle truck started at the
NAMI automotive research center, in 1929. Serial production started in Novgorod Nizhniy, in 1931 as the "Ford-Timken" improved on the base of small imported series of Ford AA. The experimental Ford-NATI-30K from the Gorkovsky complex in 1934 was the final prototype, and the GAZ-AAA was designed earlier than other Soviet 3-axle trucks. production only started by the end of 1934. In 1932, on the Ford AA chassis, NATI developed its own original three-axle version, a lorry with worm axle final drives and demultiplier. This was passed onto the design bureau of GAZ for special vehicles under the leadership of Vitaly Andreevich Grachev.
It's only in 1935 than it's rival the
ZIS-6 was presented by NATI Tractor Research Center as the Jag-10, with a reduction of the transmission, increase in transport capacities, higher weight and somewhat degraded performances. The GAZ-AAA still had better off-road capabilities than the ZIS-6. It was able to extricate itself from impassable terrain, and succeed when German trucks were usually bogged down.
Production
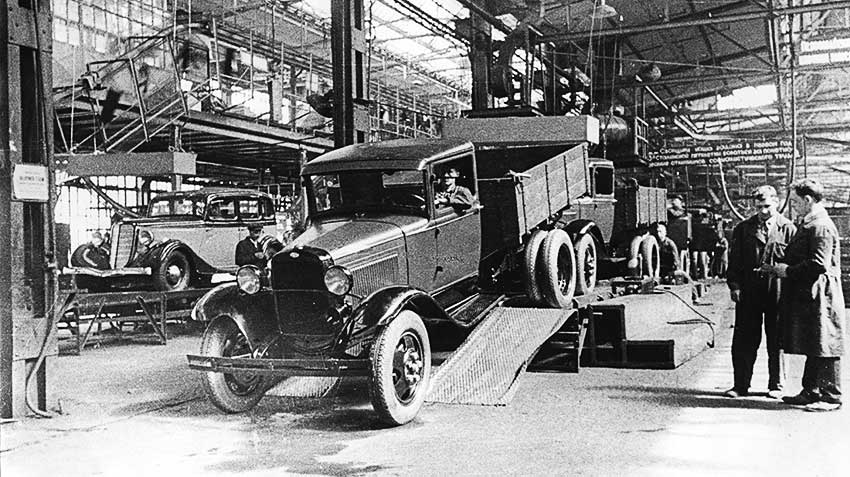
The total number of GAZ AAA is known for certain as 37,373 units built, unlike the roughly estimates of one million for the AA. Although the AAA on its experimental form was tested in 1934, production only started in 1936 with deliveries until 1943. Unlike the AA since it was a derivative, no licence applied, whereas the AA was firmly capped under 985,000 by contract. The AA was replaced by the MM later and was also off-licence. So only a small fraction of GAZ AAA existed alongside the AA. It was rarer to see on the battlefield, but presented some advantages. Two GAZ-AAA and three Ford-Tinken were comparatively tested during the Moskow-Karakum-Moskow rally of 10,000 kilometers, reports making the GAZ-AAA superior and thus, leading to authorize in 1934 it's operational status. The Ford Timken was sturdier though and declined into several armoured cars.
Serial production of GAZ-AAA was mastered in 1936 and went on until August 1943, stopped due to the destruction of GAZ Factory by the Luftwaffe. The last ones were assembled in 1944 from saved parts. Some 37,373 GAZ-AAA trucks were produced and this included 3,331 armored vehicles (BA-6/BA-10) and the 194 GAZ-05-193 buses.
From 1941 to 1943, the GAZ-AAA was massively simplified with right-angled mudguards, a simpler wooden driver's cabin and the other modifications made on the Gaz-MM. Some authors calls it the GAZ-MMM for this reason but seems never official. Spare wheels were now fixed on each side of the engine hood and the chassis was used to develop several armored or specialized vehicles. Nine years of production saw 37,373 GAZ-AAA delivered and some extra 273 or 194 GAZ-05-193 (command bus).
The successor: GAZ AAAA
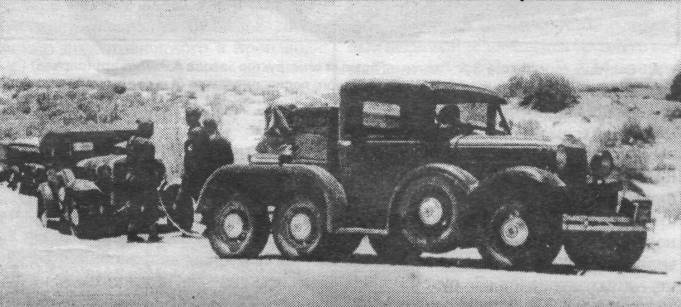
The first planned sucessor and improvement over the AAA was logically a 8x4 or 8x8 vehicle, the "four A", a prototype of three-axle transport vehicle based on the GAZ-A, never ported in serial production due mostly to complexity issues, and only two were manufactured in 1936. It looks like a 8x8 but with two extra spare roadwheels behind the forward axle, close to the cabin. The idea was to lower them in uneven terrains, but it proved too complex to use and costly to manufacture. They were created according to the idea of Vitaly Andreevich Grachev, and behind the front wheels, the two spare wheels could passively rotate and make it easier to move over bumps making for a 6×4 like the GAZ AAA. The two tested in 1936 used the GAZ-A chassis and components, but the closed cabin from the GAZ-4, and rear axles had a worm gear.
Design of the GAZ AAA
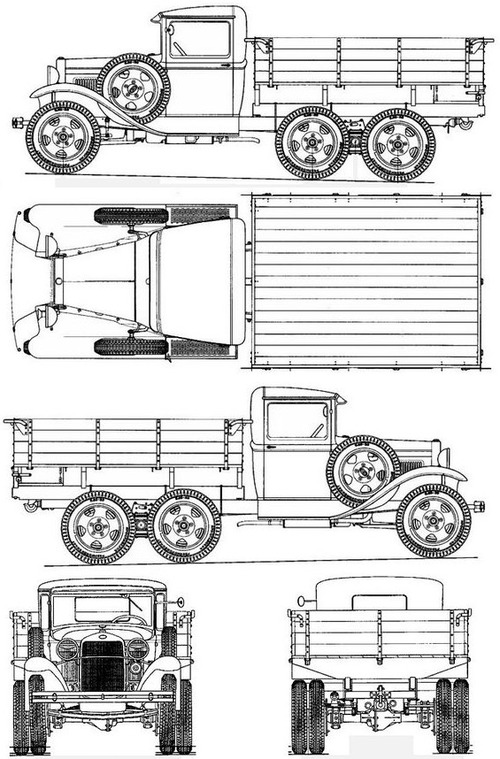
Chassis layout and bodywork
The GAZ AA was essentially the same AA, based on the Ford model AA/Ford BB with its FR layout or "Front engine, Rear drive", same chassis and body and where a single axle with two paired roadwheels were present, the ladder type chassis was just lenghtened to fit another axle with double wheels again, for a total of eight, ten when counting the front directional wheels. Dimensions were as follows:
Wheelbase 3,440 mm (135.4 in), Length 5,335 mm (210.0 in), Width 2,040 mm (80.3 in), Height 1,970 mm (77.6 in) for a Curb weight of 1,810 kg (3,990 lb).
Thus, the GAZ AAA was heavier than the AA with 2,475kg instead of 1,810 kg and slower with 63-65 km/h at best versus 70 km/h but the load jumped to 2 t, a 500 kgs improvement.
The cabin was a 2-3-seater with a simple bunk, manual folding glass windows, same profiled cabin roof with a forward sun and rain deflector with its removable cache. Aeration for ventilation was also manual. Just as the GAZ-AA, the AAA was not amphibious but can cross about 80 cm of water without preparation. The flatbed normal, max load was 2,000 kgs. The front wheels were covered by stamped fenders, whereas the rear axle had none, protected by the flatbed, and canvas mud deflectors forward and back when available.
The flatbed was surelevated on two sets of wooden framing, six supports and was made by two layers of wood surrounded by wooden panels affixed by using six riveted braces mounted on hinges to be lowered down as the back panel for easy access and removal. There were five sockets on each side also to mount a tarpaulin protecting the payload and troops from the weather. The cabin's back also had a small window. The vehicle was unarmour but sturdy, with 2 mm thock stamped road wheels hubs, a 5mm thick chassis framing, 15 mm woodedn flatbed, unarmoured radiator housing.
There were two headlights (electric network 6V) welded on a simple bar, running across and between fenders with a horn on the right fender. This was completed by tail lights plus a standard hook for towing the same payloads as the GAZ AA due to the same engine being used. The GAZ AAA could two trailers, and various pieces of ordnance no heavier than two tons.
Structurally, the GAZ-AAA was a three-axle modification of the two-axle GAZ-AA, where the rear drive axle was replaced by a two-axle bogie with a balancing axle suspension on 4 longitudinal semi-elliptical springs, worm final drives and a 2-stage reduction gear in the transmission. The associated increase in the number of wheels made it possible to reduce the specific pressure from each of them on the ground, which made it possible to increase the vehicle's patency on country and forest roads. The truck could climb 27° slopes.
Engine and performances
The GAZ engine was a derivative copy of the Ford 201 CID (3.3 L) 4-cylinder inline. It was a 3.3L GAZ-AA I4 coupled with a 4-speed manual manual geabox and reverse gear. This four-cylinder gasoline engine, which displaced 3.285 liters just like the AA, with an output of 29.5 kW (40-41 hp)@ 2,200 rpm. Tank capacity was also of 100 liters gasoline, for about 400 km by road despite the heavier weight and pyayload. The mechanical transmission had four forward gears, one reverse gear, for a top speed or around 63 km/h fully loaded. There was a dynamo with preheater to cope with winter conditions, plus the usual handcrank. The 3.3L GAZ-AA I4 Cylinder diameter was 98.43mm, piston stroke were 107.95mm. Compression ratio was 4.22/1. Maximum torque was 16.5 kGm (162 Nm). Average consumption was 20.5 liters for 100 km.
The GAZ AAA 6x4 meant only the forward rear axle was directional. The rearmost was fixed and only there to support the load. Off-road capabilities were still good and there was a spare tire strapped under the rear chassis. The 1938 GAZ MM received reinforced leaf springs and new military tyres, and this percolated into the GAZ AAA production from 1941, or retrofitted in the field.
Evolution
Model 1937
Basically the vehicle described above, refined in 1934-36 and approved for mass production in 1937.
Model 1938
In 1938, the truck underwent modernization, having received a more powerful (50 hp) engine and a number of other improvements similar to the base GAZ-MM model. With the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, the design of the GAZ-AAA was significantly simplified (like the GAZ-MM-V) in order to reduce labor intensity and production costs, which had practically no effect on performance characteristics. To increase the cross-country ability on the drive wheels of armored vehicles and special vehicles based on the GAZ-AAA, quick-detachable all-terrain chains of the "Overall" type were put on (they were included in the standard equipment of all medium-sized BAs).
Model 1940
The 1940 model received few changes: A new rear pintle, plus the two sparewheels were now mounted into the front fenders.
Model 1941
Final simplified version: A bit like the GAZ MM or ZIS-6T, straight front fenders, wooden cab, simplified roof or open one with tarpaulin and simple metal wings. Many other detailed simplifications between the dashboard and options. Produced 1941-43.
Variants of the GAZ AAA
RUS-2 early warning radio systems, radio stations and workshops of various types, gas and oil tankers M3-38, and so on, were mounted on the GAZ-AAA chassis. In addition, in 1941-1945, the GAZ-05-193 bus was produced on the GAZ-AAA chassis, which was used as a headquarters or ambulance, as well as hygienic and bacteriological auto laboratories of the AL.
At plant No. 92 in Gorky, on the basis of GAZ-AAA, with the installation of the ZiS-2 artillery gun behind the armored cabin, a prototype of the ZiS-31 self-propelled artillery gun was created, which was tested in July-August 1941, but the self-propelled guns were not launched into mass production.
The shortened chassis of the GAZ-AAA truck was used for the production of medium-class armored vehicles with a combat weight of 4.8-5.9 tons: BA-6 (1936-1938) and BA-10 (1938-1941). In addition, the BM-8-48 Katyusha multiple launch rocket system and the SU-1-12 self-propelled gun with a 76-mm regimental gun were installed on the GAZ-AAA chassis. Also, an AC 2 aircraft starter was created on the basis of the GAZ-AAA.
- Light Artillery tractor (with bunks for the gun crew and ammo on the flatbed)
- Troop Transport (Ten infantry on bunks)
- Cargo carrier (standard 2 ton payload)
- Ambulance
- Fire-fighting vehicle
- GAZ-AAA (4M): Light MG version, with
- GAZ-AAA (DshK): Medium MG version
- BA-6 armored car
- BA-10 armored car
- SU-12 self-propelled gun
- GAZ AAA Radio car (several types)
- RUS-2 EPIRB platform
- GAZ-05-193 command bus
- GAZ AAA Half-Track
About the GAZ-AAA (4M)
The GAZ-AAA (4M) was an improvized SPAAs fitted with a crude bolted set-up, the 4M quadruple Maxim MG mount, improvised. This was an expedient machine armed with the old stockpile of WWI Russian Imperial era Maxim machine guns, which thousands were available in various conditions. The quad 7.62 Maxim was only efficient against low-flying targets, thanks to its high fire-rate coming from four barrels and does not required skilful aiming. Thus mount also had a depression of -10 degrees, enabling ground support fire of needed. 4,000 rounds were generally carried stored on the flatbed's boxes and crates. These were organically delivered to units in the field during the later summer and winter 1941. Those which survived into 1942 were re-equipped with a single mounted DsHk, with thrice the range and much greater penetrating power. And naturally, some were fitted with a 37mm AA gun. In 1937, GAZ-AAA was used in the process of surveying the coast of the Taimyr Peninsula by hydrographers of the Chelyuskin polar station, who named an unnamed cape - Vezdekhod in honor of it. During the Great Patriotic War, GAZ-AAA vehicles were used mainly for towing artillery pieces, the AA reserved for troops.
About the GAZ-AAA Katyusha BM-13 (1942)
Since the GAZ AA was integrated into Katyusha units (as well as the more common ZIS-5, ZIS-6 and Studebaker trucks among others), they were fitted at first with the same BM-13-16 with launch rails for sixteen rockets, first tested in 1938. Over 10,000 systems would be mounted, and mong these a small proportion on GAZ-AAA chassis, which presented the advantage of better coping with the load. Almost nothing is known about such conversions, with only rare photos to come by.
About the SU-1-12 (1933)
Although attempts to produced SPGs were initiated by the RKKA back in 1933-34 it's the Leningrad Kirov Plant that was tasked of such design, asked for a simple and cheap vehicle. A few experimental vehicles were made, based on the GAZ-AA, leading to the SU-12, but it's carried armament was weak and a heavy gun needed a better chassis, so naturally a new one was developed from the GAZ-AAA chassis and more than 200 were converted and tested by installing a 1927 ACS SU-12 76mm howitzer, and after the initial SAU SU-12, unprotected, appeared the SU-1-12 with the gun fully masked and other modifications. 99 were built of the first in 1933-35 among which 51 SU-1-12 taking part in the Lake Hassan battle in the summer of 1938, Khalkhin-Gol next 1939 and the Finnish Winter War, but the remainder were destroyer in the summer of 1941. Better trackes SPGs were built afterwards.
The GAZ AAA in Military service
The truck had many applications
Just like the GAZ AA, the AAA soon became the other beast of burden of the red army, but it's small quantities meant it was used for specialized tasks. Organically, the GAZ AA and ZIS-5 reigned supreme. The AAA nevertheless was used mostly in organic specialized roles: The ambulance could carry more stretchers, material and personal, and assist medical units dispatched on the front. The radio vehicle could carry heavy receptor/receiver emitter stations and the power unit associated and take its place at batallion and divisional level for long range communications. Other "cabin" variants such as the RUS-2 EPIRB platform and PARM could be used as mobile workshops or power stations, chemical HQs, artilery HQs, ect. The specialized troop bus GAZ-05-193 could carry more troops, and in way better conditions than usual trucks on their flatbeds, also used as staff buses and command vehicles.
The greater towing capacity of the GAZ AA as tractor as its heavier payload allowed to carry the entire crew and ammunition of a gun and the latter in tow: From small antitank units equipped with the 45 mm model 1932 and 1937 standard AT guns, light and medium guns (such as the Divisional gun USV 76mm M1939), regimental gun M1927, or the 122mm M30 Howitzer, and the ZIS-2 and ZIS-3 field guns.
Specialied variants also brought many new applications to various forces:
On Soviet airfields for examples, three vehicles were useful:
-The SPAA versions with either the DsHk or the 37 mm AA,
-The starter variant for the taller bomber engines,
-The BZ-13 fuel truck, to bring gasoline to airplanes (The same were used to carry diesel for tanks in the army).
It should be said that a considerable number captured in 1941 by the Wehrmacht were resued, repainted with large balkankreuz. Not only their off-road caracteristic were much better than the moslty "urban" and heteroclitous panel of vehicle from West ern Europe used in adverse conditions, but they proved very sturdy and easy to maintain as well. The lack of parts was a problem, and many were cannibalized, by fault of capturing supply units. Production was delocalized in the Ural, out of reach.
Conversions and armed attempts
The GAZ AAA good off-road capabilities and heavier payload seduced the high command into ordering several derived variants, including armored ones. The earliest and most famous were the BA-6 and BA-10 armored cars, which 556 built, seeing action in the winter war against the Finns, Nomonanh against the Japanese, and Operation Barabarossa, until a planned replacement by the BA-10 that never came. They also led to the development of an armoured personal carrier, defined at first as am armored ambulance, the BA-20, although the latter was only experimental. It was used also to carry heavy ordnance in a self-propelled mode, notably the SU-1-12, in a small serie but still active in 1941.
Other experiments were more interesting such as the ZIS-31, designed to carry a single ZIS-3 high velocity field gun in portee style tank hunter. Never came out of it, or the more promising versions based on the half-track derivative, ZIS-42 and its ZIS-41, tank hunter version, armored with the same gun under mask. Another, confidental armored version that came to nowhere was the Chemical Batallion armored vehicle called the KS-18.
Succession
Although its technology was obsolete after 1942, the vehicle was still produced, still valid compared to the ZIS-6, but compaed less favourably to the lend-lease Studebaker US6 and GMC CCKW, larger, with better off-road performances and winches, or attachement for self-defensive armament. The question of its replacement was of course evident in 1942. Production focused on the simplified Model 1941 in between.
After the failure of the GAZ AAAA, deemed too complex for mass production, The GAZ-51 ("Gazon") was planned at its successor, but the first prototypes were only produced by 1945, strongly influenced by the Studebaker US6. Due to many issues, mass production only started in 1946. This 2.5 ton 4×2 standard was joined in 1947 by the 2 ton 4×4 GAZ-63, both powered by 70 PS (51 kW) 6-cylinder 3485 cc engine. Production of the latter went on until 1968 and the GAZ-51 until 2 April 1975, also produced in Poland, China and North Korea.
GAZ AAA survived until today in the Museum of Automotive Antiques (Vladivostok), the Gorky Automobile Plant (Nizhny Novgorod), the Russian Military History museum (Padikovo Village, Istra District, Moscow Region) and at UMMC (Verkhnyaya Pyshma).
Gallery
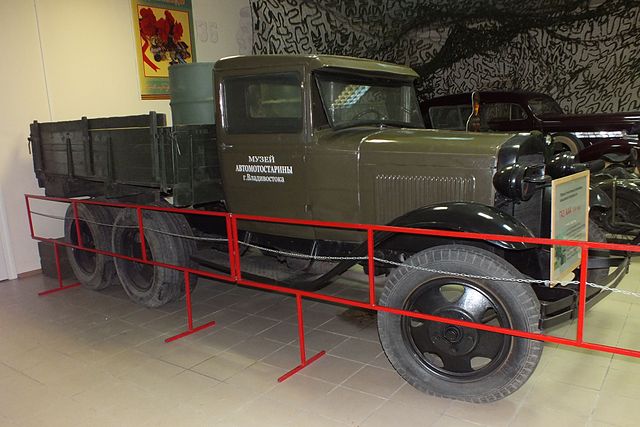


 In Vladisvostock
In Vladisvostock
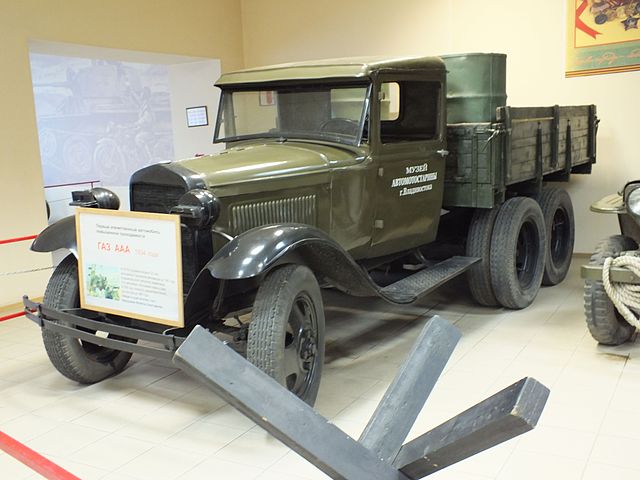
 In Ekaterinburg
In Ekaterinburg
 Another model preserved at Ekaterinburg
Another model preserved at Ekaterinburg
 Bundesarchiv - Captured GAZ AA
Bundesarchiv - Captured GAZ AA
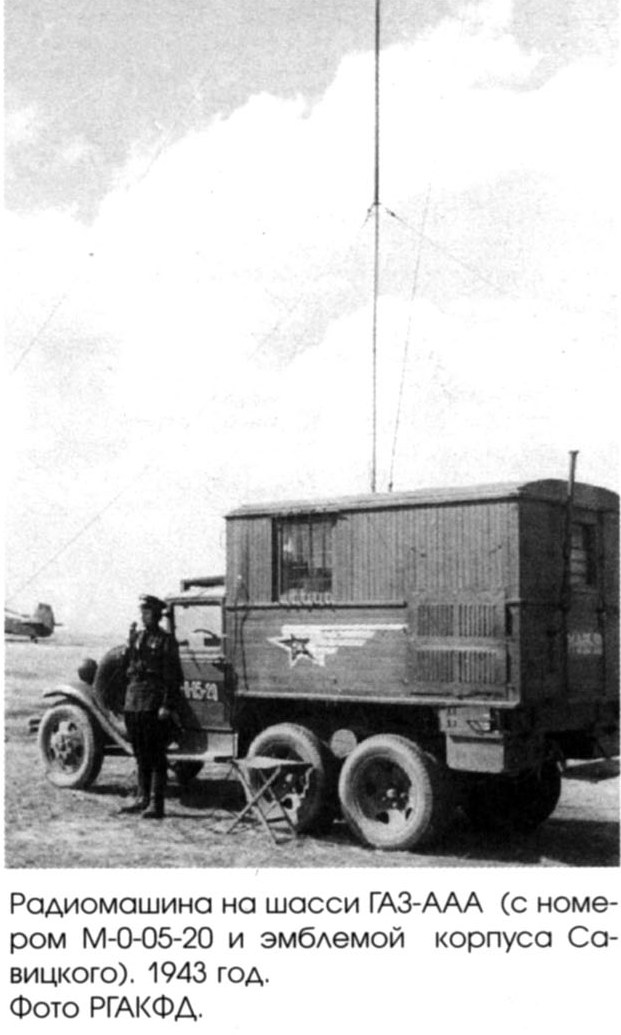 Radio station
Radio station
Sources/Read More
Trucks of the Soviet Union: The Definitive History, p.42.
GAZ-AAA (inaccessible link). Vladivostok: Museum of Automotive Antiques. Archived 2015.
Kolomiets M.V. Armor on wheels. History of the Soviet armored car 1925-1945. Eksmo, 2007.
Wheels of Victory: Rare military trucks ZIS-6 and GAZ-AAA. August 21, 2021.
Popov S. V., Troitsky V. A. Toponymy of the seas of the Soviet Arctic.
Andy Thompson: Trucks of the Soviet Union: The Definitive History
On automotomuseum.vl.ru
More photos (cc)
materielsterrestres39-45.fr
Vehicles based on the GAZ AA/MM/AAA Chassis
Trucks_buses.htm#GAZ on armchairgeneral.com
M1937 On o5m6.de
M1940 on o5m6.de
Various GAZ truck models
Kit review: the GAZ AAA model 1941
SPAA variants
Captured GAZ vehicles
Captured cabin and bus GAZ-AAA
About the SU-12
Model kit zvezda 1:35