The Modern Jeep
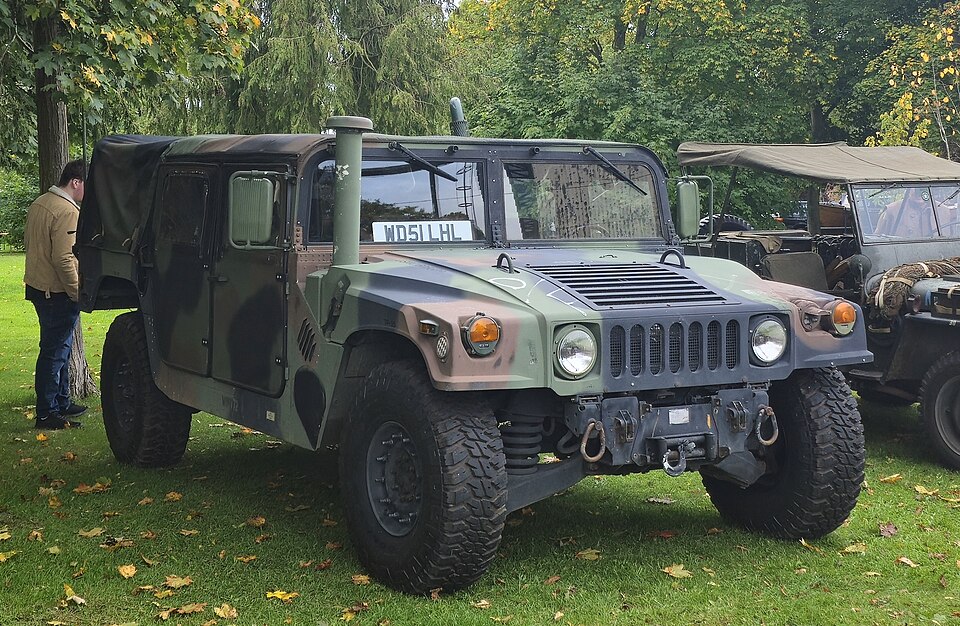
The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicles, HMMWV, or Humvee, was designed to replace the aging Jeep in the American military. The Jeep served U.S. troops well over its four decade tenure, but it desperately needed an update. The Humvee would become the modern day Jeep. Thus post is about the early and in general all softskin (non-armoured) versions.
As Armored Personnel Carriers (APC) go, the M113 was the most produced
tracked APC, at 88,000+. However, the most produced armored personal carrier is the Humvee. Unveiled in 1983, 280,000 vehicles have been built so far. It still comes in less than the iconic vehicle it replaced, the
Jeep, of which 650,000 were made. The Humvee was produced to be fully enclosed and Nuclear (Radiation), Biological, Chemical (NBC) proof. The Jeep was never considered to be "armored" as it was an open cab vehicle. Conversely, the Humvee, up armored, is considered an armored fighting vehicle.
 TOW version on fire trials in the late 1980s
TOW version on fire trials in the late 1980s
The utility and versatility of the vehicle was well proven after the end of the Cold War. A familiar sight in the Gulf wars and in Afghanistan, the Humvee was well-known and well-showcased by the world wide media, and became an iconic symbol of these conflicts, just as the Huey helicopter was to Vietnam. This is the quintessential modern U.S. "Battle Taxi", although this was not its primary objective or duty. The Humvee was largely exported and also inspired a wide range of civilian adaptations and applications.
Replacing and Improving a Legend
When the first studies started in the 1970s, the goal was simple: The Jeep was showing its age, despite modernization allowing this nimble vehicle to remain relatively up-to-date in the Vietnam War. The final Jeep iteration, the quarter-ton M151 Military Utility Tactical Truck or MUTT, had a number of failed innovations. Perhaps the worst was the tendency of the M151 to roll over at low speeds, causing a number of non-combat casualties. The Army also had a heavier truck, the half-ton M561 Gamma Goat, which also needed to be replaced due to a lack of reliability. The Army was not interested in designing two tactical vehicles at this point. They wanted to have one vehicle that could be used in the quarter-ton and half-ton truck roles.
The Jeep design had one overarching flaw from its inception in 1939. There was no protection for the passengers. As the Cold War progressed, there was no protection for the Jeep crew in case of an NBC threat or against shrapnel and small arms fire. The original Jeep was open where crew can literally jump in and out. However, during combat (not infrequent as it was used for reconnoitering in enemy territory), the driver had to react quickly and retreat swiftly before the enemy could effectively return fire. A completely armored, encased body would had the advantage of offering this supplementary protection without loosing the "fast descent" characteristic of the older model.
The idea of fitting an open back where soldiers can quickly embark and disembark without bothering with doors or hatches, was perhaps something related to the deeply popular and deeply rooted affection of civilians for pickup trucks. This trade-off with NBC protection was relative as the main 4-seats compartment was still fully enclosed. The Humvee was not a traditional APC due to its size and primary duties of reconnaissance and liaison. However its stiff construction and size allowed to adapt a large variety of weapons that the Jeep could never mount. So when the vehicle was eventually unveiled, it was praised as indeed the only true possible successor of the vehicle created originally by Bantam in 1939.
First appearance of the HMMWV program
Like many large scale military program, the Humvee gets its name from an unspeakable acronym, HMMWV for "High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle", reminiscent of the "General Purpose" of the previous Jeep. Already in the 1960s, knowing well the possible needs of the army for a replacement, several automotive manufacturers proposed various trucks or semi-trucks and utility vehicles with off-road capabilities. Many were tested by the Army was not interested.
The Cheetah
The most notable of these private ventures came from the famous Italian car maker than made a fortune selling their super cars to the wealthy throughout the world, Lamborghini. The brand was indeed better known for its classics like the gorgeous Miura and muscular, space-age Countach and surprised everyone in 1977 with the Cheetah. However it did not came out from the blue. Lamborghini actually approached Mobility Technology International (MTI) for a better access to military top brass, which in turn contracted the company for designing such vehicle. The cheetah was a copy by MTI of the former FMC's XR311 prototype of 1970, already rejected by the Military, which led to a legal action of FCM when the Cheetah was showcased at the Geneva Motor Show.
The Cheetah was very much in its appearance a progenitor of the Humvee. It was a powerful true 4x4, not with a Lamborghini V12 as some stated but a better suited engine for military specs, the Chrysler 5.9 liter (360 ci) V8. It was waterproofed and rear-mounted, with a 3-speed gearbox. The reinforced fiberglass prototype was built at MTI in San Jose, California and then sent to Sant'Agata near Bologna where it was completed by Lamborghini. At more than 2 tons (4,502 lb) and with a rear engine, top speed was not the primary objective. The prototype was only showed once unofficially, and stored as AM General was later awarded the contract for a very similar vehicle. Lamborghini however tried later the LM002 of its own design, which never got passed the prototype stage and did not profit the already dwindling finances of the company following the first petrol crisis in the 1970s.
AM General prototype
AM General (South Bend, Indiana) was not a known car maker but a heavy duty vehicle manufacturer, accustomed mostly to buses and trucks, but also Jeeps. The former company Standard Wheel Company expanded to off-road vehicles when absorbing Overland Automotive before the war, which became Willys-Overland, maker of the original jeep. After World War II, it was absorbed by Kaiser Motors, and itself became the Kaiser-Jeep Corporation in 1963. Then absorbed by American Motors and renamed AM General. It was a natural choice for making the next generation of US Jeep as the company linage did. Kaiser earned US$87 million Army truck contract in 1964, that really came to fruition in 1979, when the definitive program was launched.
The final specifications for a High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle were drafted in 1979, originally to replace the 1/4 to 1 1/4-ton range M151 MUTT and M565 Gamma Goat. Paramount was the off-road performance, but also a large payload capacity and extensive armor protection against indirect fire. Another demand for the width was to fit inside standard cargo planes as well as European tunnels, bridges, and roadways. At the end it was far larger than the jeep and twice as heavy, with improved suspensions and a 410 mm ground clearance. Field performances expected were climbing a 60% slope or stay stable on a 40% slope, ford 5 ft (1.5 m) of water unprepared thanks to a snorkel air intake and electronics waterproofed. In addition a radiator mounted high on the vehicle to prevent off-road damage. It was to be airlifted and air-dropped also, as well as lasting 12 years without revision in the most punishing conditions.
Over 61 companies were declared interested, but only three submitted their completed prototypes: AM General, Chrysler Defense, and Teledyne Continental. AM General prototype was ready in June 1980, and one year later, AM general was awarded the contract for several prototypes for tests, along with the two others, producing 11 prototypes that were tested in a 600,000 miles course including desert and arctic conditions. AM general prototypes were 2400 kg in curb weight, for a 6.2 L (380 cu in) V-8 diesel and a three speed gearbox. AM final production contract was awarded in 1983, for 2,334 vehicles. This was followed by a first batch of 55,000 vehicles to be delivered withing 5 years, and deliveries totaled 100,000 by 1995.
Design
Protection
The Humvee look is unmistakable, with only the vertical radiator grooves of the original jeep still showing on the hood, but the rest is unique. The Humvee is very wide at 7 feet (2.16 m), giving it stability on all terrains. It is also low in height at 6 feet (1.80 m), making it a difficult target to spot and hit, but was only a benefit of the specification about stability. Former Jeeps had tendencies to top over. The hull is made of rust-free, high-resistance heat-treated aluminum alloy. It is strong, but not able to stop 7.62 mm or 8 mm bullets.
It is resting on a narrow steel frame with boxed rails and five heavy duty cross members for extra rigidity. The chest-high transmission hump separated the crew but allowed the seats to be lowered, keeping the entire vehicle low profile and most components protected high up by a reinforced cage structure. The driver and co-driver had both large vertical windshields with bulletproof glass, as well as two other on the side walls. The roof is rigid, as the monocorps hull structure, providing overhead protection but no collective NBC system. Improvements were added to the bottom, as proven vulnerable to Improvised Explosive Devices (IED) and mines during Operation Afghan Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom.
Mobility
 Humvee prepped by Paras for deployment
Humvee prepped by Paras for deployment
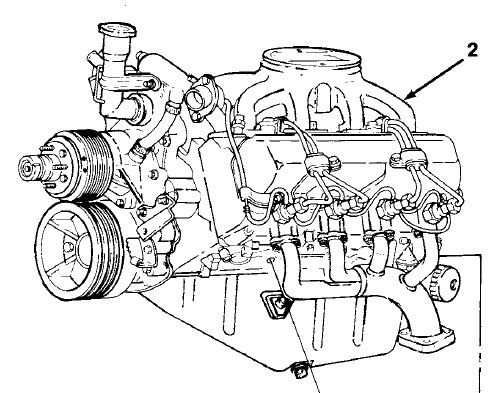 Chevy 62-65L engine
Chevy 62-65L engine
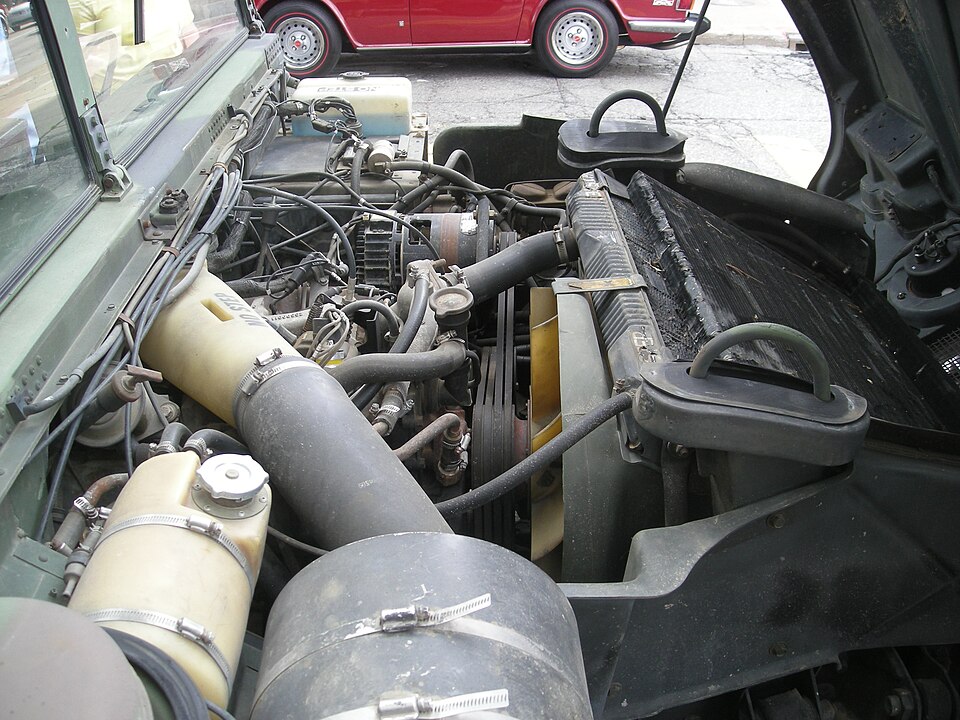 1984 AM General Engine
1984 AM General Engine
An all wheel drive was essential to the Humvee design, and an ingenious independent double-wishbone suspension units with heavy duty and helical gear-reduction hubs were installed for better ground clearance. There were disc brakes mounted high-up on all wheels outside of each differential (front-rear torsion, center locker type). The biased differentials allows forward motion as long there is one wheel in contact has traction. There is also an electronic traction system that engages when the vehicle is about to top over. Tires are 37 x 12.5 radial tires with run-flat cells. In addition there is an optional centralized tires inflation system (central tire inflation system or CTIS which was introduced on the DUKWs during World War II) helping to optimize ground pressure and contact surface performances on all terrains.
The standard interior of the Humvee is spacious, with two front seats separated by the massive transmission tunnel, two seats at the rear, and a large rear open storage area, large enough for four more personal or a 1,100 kg payload or a closed compartment with rear doors depending on the versions. Despite this they can be carried by most US transport helicopters and cargo planes. They are sturdy enough, and were tested to endure the Low Altitude Parachute Extraction System (LAPES).
 Humvee M1113 with a chassis-mounted XM1124 hybrid Electric diesel
Humvee M1113 with a chassis-mounted XM1124 hybrid Electric diesel
The engine was either the GM V8 diesel 6.2 L (380 cu in) or the V8 turbo diesel 6.5 L (400 cu in), both giving 190 hp (142 kW) @ 3,400 rpm or 380 lbf·ft (515 N·m) at 1,700 rpm, served by a 3-speed automatic or 4-speed automatic. Top speed was 55 mph (90 kph) at max payload, but up to 70 mph (113 kph) with a moderate payload. The average cross-country speed was over 40 mph. On its internal fuel of 25 U.S. gallons (95 L), it could travel up to 400 km. It also have a towing hook for a payload trailer of 9,000 pounds (4,100 tons).
Armament
There are 17 major variants of the Humvee, and many sub-variants with many weapons systems. Although the basic "battle taxi" is equipped with a central ring-mount for the "Ma Deuce" cal.50 M2HB heavy machine gun, the Hummer could be modified for numerous platforms including TOW and Stinger missiles, as mortar carrier, the M134 Minigun, Mk 19 grenade launcher, M240G/B machine gun and M249 LMG.
 Humvee with a Raytheon SAM
Humvee with a Raytheon SAM
Production
In 1983 AM general and its sub-contractors was given a $1.2 billion contract to produce 55,000 vehicles over a 5-year period, later expanded to 1.6 billion for 70,000. Financially AM general stocks were passed to LTV Aerospace and Defense Company on 24 July 1983 and is now its fully-owned subsidiary. Although the basic vehicle was ready this year, it was not until 1984 that other prototypes resumed testing with the first production vehicles reaching the military in March 1985. Additional contracts were obtained in 1989 and 1994. The A1 version was started in 1989, featuring technological, environmental, operational, and safety improvements. The A2 series was started in 1994, also called Expanded Capability Vehicle (ECV) series.
With the experience in Somalia (1993) and Bosnia (1994), better turbo-charged engines was adopted, and following the Afghan and Iraqi war experience, air conditioning became essential as well as extra protection features. The improved Expanded Capability Vehicle 2 (ECV 2) series came in 2008-2009. It was intended to regain mobility despite the increased weight of armor, and the TD engine was improved. As of 2011 an effort was made to try to balance the inventory fleet, both the active and reserve. Indeed, the Army National Guard ended with more HMMWVs than the active units.
Purchasing a Military Hummer
 M1038 H11 Demilitarized
M1038 H11 Demilitarized
As a matter of policy, old military hummers are not sold to the public directly. They are mostly sold as scrap. The only other option is to start looking for military surplus hummers. Officially, you can NEVER own a driveable military hummer. The Department of Defense states that these vehicles do not pass the DOT standards and are therefore not to be let loose on the highways. So, used military hummers are usually sold as scrap. But, every once in a while, production surpluses leak through the tight security and find their way to the common man. These can be legally owned. The Defense Reutilization and Marketing Service is the place where the military vehicle becomes available to civilians. The DRMS makes Military Surplus Hummers available to other branches of the Defense services, military bodies, and state and local governments. Some charitable organizations are also included in this list. Specific bodies with authorizations are also allowed into this elite group. Before the goods reach the DRMS, the cream of the surplus Hummers is purchased by other agencies. Sooner or later, these find their way to the public.
If you are wondering where to look, you may be able to spot various websites or companies that sell military surplus hummers. These may not be legal. Some companies that trade goods with the U.S. military get military surplus hummers in return. These are then procured by private individuals or companies and resold. Of course, all this increases the price tag of the military surplus hummer. Surplus military hummers start at U.S $ 19,000 and can go up to U.S $ 30,000 depending upon the model and the make. Due to increasing safety concerns, the government will not sell Humvees to the public directly. These have to be obtained through companies or intergovernmental agencies that have them. Many times, it is easier to get a reconstructed Military Surplus Hummer. Many private traders are remodeling the military surplus hummer with newer and better parts.
You must also make sure that you buy the vehicle with a SF97 form. This is the United States Government Certificate to obtain the title deeds of a surplus vehicle. Without possessing this form, you cannot show legal ownership of the military surplus hummer. Most people who are able to afford converting a military surplus hummer are in the super rich category. This is mostly because the Military version of the Hummer has been built to withstand the harsh conditions of the forest, jungle and military landscape. The Military surplus hummer leaks, and most people would not appreciate water dripping on them when it rains. The vehicle also makes harsh riding on smooth roads. There is little room or comfort within the military surplus hummer. The very size of the military surplus hummers makes it an intimidating buy for the common man who has to traverse busy, narrow interstate roads. The huge tires of the vehicles thud and crash over bumps. Acceleration in the Humvee is a long and tedious process, almost taking forever. The speed of the military surplus Hummer builds up very slowly to reach desirable limits.
It has to be understood that Military Hummers have been built primarily for off the road driving. That is why the vehicle is so rugged, noisy, creaky and strong. Rehashing a military surplus hummer can be very expensive. Many people have come to identify the military hummer as America - tough, rugged and strong. For most, it is the pride of ownership that instigates them to buy a military surplus hummer. For those who collect rare vehicles for fun of ownership and do not intend the vehicle to be seen on the highways, the military surplus hummer is a priceless possession, more so because it is so rare.
The Humvee in action
When first introduced in 1983, the Humvee replaced the M151 Jeeps (1/4-ton), M274 Mule (1/2-ton), M561 Gamma Goat (1 1/4-ton), and M718A1 ambulance (based on M151 1/4 ton truck), and M792 ambulance (based on M561 1 1/4 ton truck). There were 73,000 Humvees in service by the 1991 Gulf War. Among the earliest in service went to Ft. Lewis, Washington and the 9th Infantry Division. They were used to test the new concept of the motorized division. The Yakima Training Center (Washington) was the main testing ground for HMMWVs from 1985 through December 1991. Reports concluded negatively to the concept, which was abandoned and the unit disbanded.
Operation Desert Shield/Storm was the first theater-wide use of the Humvee. It was in the Iraqi desert that the Humvee made its mark and became famous. As the modern Jeep, the Humvee proved to be rugged and dependable. The Humvee handled the open desert easily. It more than kept up with the speed of the first Gulf War. Humvees were used by all parts of the military and were seen regularly on the news. It easily met the requirements of the American military in its various roles. By the end of the month long conflict, the Humvee had cemented itself into the U.S. military as the new tactical workhorse.
However, a decade later, the Humvee would be put back into battle in Afghanistan and Iraq in 2003. As an open terrain, off-road support vehicle, the Humvee performed above expectations. However, as an urban combat vehicle, the Humvee showed its weaknesses. The aluminum body and frame were designed for off-road performance, not for ballistic and explosive protection for soldiers. Although armored doors, windows, and plates gave the soldiers some protection, the overall structural integrity of the Humvee was not improved. Improvised Explosive Devices (IED) and Rocket Propelled Grenades (RPG) became the most effective weapons against the Humvee.
In an urban combat situation, the Humvee also proved to be a sitting duck, easily targeted by insurgents. The Humvee's top speed topped out at over 65 mph. However, when patrolling the streets, it usually kept the pace of the infantry on foot that were clearing buildings. This meant that the Humvee sat in the street, idle, while its infantry detachment cleared a building. Sitting still, they were easy targets for insurgents. Simply, the Humvee was not designed for urban combat. It was designed for off-road use during conventional warfare. Speeding through the desert or climbing mountain passes, the Humvee performed at its best. Unfortunately, it was the only vehicle available for wide-spread operations at the time.
Today, the Humvee is still in service, but it has taken a back seat to the new Joint Light Tactical Vehicle and the MRAP vehicle. The Humvee is still a viable platform for support roles such as ambulances, missile platforms, detection units, light cargo haulers, staff cars, and the like. Overall the Humvee has an excellent battle record in its intended role, and as an AFV. Unfortunately, the United States military tried to use it in an urban combat role, and many soldiers were wounded or killed because of it. The lessons learned from the Humvee have spurred new developments and requirements for the American military in the MRAP and JLTV.
The future
The replacement of the Humvee fleet appeared obvious with the rising losses due to IEDs and mines. This forced the DoD to develop another kind of vehicle. The HMMWV was created to meet the requirements of the potential Cold War, and to to engage the enemy on the large open Eastern European plains in a conventional war. As unconventional warfare progressed for the American military, new solutions were needed, and South African expertise was also requested. Apart foreign vehicles, the DoD mandated private companies to develop a domestic fleet of MRAPs, contracts that eventually conducted Oshkosh to provide a credible replacement for the Hummer, tailored for this kind of warfare. Nevertheless despite its age, and successive modernization campaigns, the Humvee will remain in the US arsenal for years to come, at least in the perspective of a conventional conflict, possibly as long as the original Jeep and more through the civilian market.
The civilian Hummer: A wolf in sheep's clothes
The Humvee was marketed as a civilian vehicle by AM General in 1992, as a standalone brand. Its first famous customer was Arnold Schwarzenegger. The first "Hummers" were directly taken off the regular military manufacturing line and were refined for civilian use. Acoustic insulation, more comfortable seats, internal garments and fixtures, and a comprehensive Hi-Fi sound system were but a few of the installed luxuries. Later on, the original model was re-branded as the H1, while the cheaper and more "civilized" H2 and H3 were revealed in turn. However, in December 2014 the DoD began to release 4,000 surplus vehicles to the civilian market (with the gradual introduction of MRAPs), and although used mostly by domestic law enforcement agencies, M998, M998A1, M1038, and M1038A1 were sold with bids starting at $10,000 for off-road use only, still with their original military gear (no modifications).
Humvee Iterations
Humvee A1 (1994)
In early 1994, AM General launched production of the A1 series (beginning with the M998). It was later standardized on all US Hummers in service and were incorporated into the M1097 Heavy Hummer Variant (HHV). It integrates upgraded components, new front seats, improved parking brake lever with safety release, metal hood grille, improved slave receptacle, solid state glow plug controller, modified rifle mounts, and upgraded rear half shafts. Standardization was widespread and still ongoing even when came the next A2 upgrade next year.
Humvee A2 (1995)
Already when the A1 was only beginning to be the next standard, AM general worked on a better version, which was the M998A2. It was using the M1097A1 HHV as a base and incorporated a 6.5 liter naturally aspirated diesel engine which developed 160hp coupled to a new electronically controlled four-speed automatic transmission. Together with a better output, it came in accordance to the redesigned emissions system meeting all of the 1995 US Government standards. This also came with an increased cargo capacity, better heating system, new rear seats (A1 standard) and self-canceling turn. This upgrade was standardized later, up to 2007.
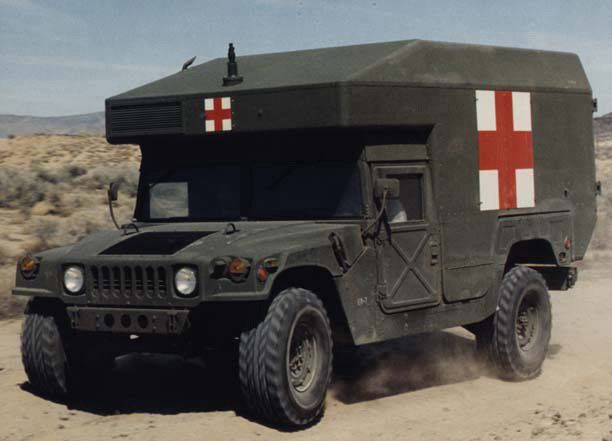 M997 Heavy Ambulance of the USMC
M997 Heavy Ambulance of the USMCVariants
The early base vehicle is the M1025 HMMWV (A1 chassis) replaced later by the A2 chassis known as the M1113. Along with the development of nearly twenty base variants (see later) generic options includes a winch with 6,000 lb (2,700 kg) capacity, and add-on armor, or several mounts for the weapons. This list includes the M56 Coyote Smoke Generator Carrier, M707 Knight HMMWV, M966 and M1036 HMMWV TOW M1045/46 up-armored tank hunters, M996/997 hard-top Ambulance and M1035 Soft-Top Ambulance, M998 and M1038 Cargo/Troop carrier, M998 HMMWV Avenger and M1097 Heavy Avenger (Stinger) SPAAMLs, M1025/1026, M1043/44 and M1109 up-armored Armament Carrier, M1037 and M1042 S-250/S-788 Shelter Carriers, M1069 Tractor for the M119 105-mm Gun, the Active Denial System ( directed-energy weapon), Ground Mobility Vehicle (special ops variant), IMETS (Integrated Meteorological System) and ZEUS-HLONS (Laser Ordnance Neutralization System) to neutralize explosive ordnance.
M707 HMMWV Striker
M966 HMMWV TOW Armored > Tank AFV
M996 Mini-Ambulance, Armored > Tank AFV
M997 Maxi-Ambulance, Armored > Tank AFV
M998 Cargo/Troop
M998 HMMWV Avenger
M1025 Armament Carrier, Armored > Tank AFV
M1026 Armament Carrier, Armored W/W > Tank AFV
M1035 Soft-Top Ambulance
M1036 TOW Armored W/W > Tank AFV
M1037 S-250 Shelter Carrier
M1038 Cargo/Troop Carrier W/W
M1042 S-250 Shelter Carrier W/W
M1043 Armament Carrier, Up-Armored > Tank AFV
M1044 Armament Carrier, Up-Armored W/W > Tank AFV
M1045 TOW Up-Armored Armor > Tank AFV
M1046 TOW Up-Armored Armor W/W > Tank AFV
M1069 Tractor for M119 105-mm Gun
M1097 Heavy HMMWV Avenger
M1109 Up-Armored Armament Carrier > Tank AFV
M1113 Expanded Capacity
M1114 Up-Armored Armament Carrier > Tank AFV
M1116 Up-Armored HMMWV > Tank AFV
M1123 Heavy Humvee carrier
M1121 TOW Armored
M1145 Up-Armored HMMWV > Tank AFV
Evolution
As shown the basic 1983 Hummer was already divided into six main versions and more than 20 sub-types. The basic versions included an Armament Carrier, TOW Missile Carrier, Ambulance Carrier, Shelter Carrier and a Prime Mover. The Prime Mover was designated M998, the Armament Carrier M1025. The Prime Mover was capable of towing the M119 light howitzer or M167 VADS system. The Shelter Carrier was also designed a heavy cargo capable of handling payloads up to 4,400 pounds (M1037).
Basic cargo/troop carrier:
-M998 and M1038 Basic Cargo Carrier: No roof, no side doors (or soft ones), rigidity bar and rear open bay with benches
The Cargo/Troop Carrier and its numerous derivatives were developed right at the beginning.
Depending on the climate and temperatures, Hummers of these "open air version" came with a diverse area of soft-top plastic and fabric enclosures.
-M1097 Heavier Cargo Carrier: Same configuration, but reinforced chassis.
In 1991 the Ml097 Heavy Hummer Variant (or HHV) featured an upgraded suspension, drive train, but with the same 15Ohp GM V8 6.2 Liter diesel fuel injected engine. Greater payload and more shelters.
Used for General transport they were Open or soft-top and capable of a payload of 1.25 tons, featuring troop seats in cargo bed, a basic electrical system. The M998 had the Standard payload but the M1038 was the Heavy payload version.
Armament carriers:
M1025 and M1026 were the unarmoured Armament Carrier, Weapons platform, open-top with turret ring; Typicallly armed with the M2 .50 cal, Mk 19, M60/M240. Later versions could accept kits in Iraq.
The M1025 was the Standard payload variant and the M1026 was the Heavy payload variant.
Specialized cargo carrier M1037/1042:
-M1037/1042 Specialized Cargo Carriers: Rear doors and rigid cargo bay at the rear. This version came out in 1995 as the Expanded Capacity Vehicle (ECV) or up-Armored XM 1109 with no loss in cargo-carrying ability and a payload which rises from 4,400lb to 5,300lb payload compared to the M1097A2. It was given a 6.5L turbo diesel engine generating 190 hp to cope with the supplementary weight. Uses also the AM General's Cap-Over Hummer Variant (COHHV) cargo truck components. These consists in a reinforced frame, modified differentials and steering system, improved half shafts, exhaust system, brakes, cooling system, suspension, and wheels. Starting in 1995, Central tire inflation systems and an air conditioning units were made standard.
Specialized troop/armament carriers (M1025)
Introduced in 1983, this version can be summarized as the "fully enclosed hummer". In fact its most distinctive aspect was the rear sloped tail over the cargo bay, which could carry cargo and troops in "descent" mode. This was the basic APC in widespread use by the US Military in the 1986 Panama operation, 1991 Gulf War, OAF, and OIF. The fully enclosed interior guaranteed collective NBC system and extra rigidity to mount a large variety of light to heavy armament; The basic version came with a 12.7 mm M2HB "Ma Deuce" HMG (cal .50). In fact the array comprised also the M249 5.56mm SAW, M60 and M240 7.62mm MGs, M60 7.62mm MG, MK 19 Mod 3 40mm Grenade Launcher. In the early 2010s, RWS systems became commonplace, especially in Iraq.
The M1025 is generally similar to the basic M998 HMMWV variant, but with a basic armor, and roof mounting base for a large array of weaponry being mounted. The M1026 receive a basic armor and winch, the M1043 receive with supplemental armor and the M1044 Supplemental Armor and Winch.
-M1043/M1044 Troop/armament carrier: 4 doors, open bay for rapid dismounting of troops, distinctive rigid rear.-M1045/M1046 heavier troop/cargo carrier: Same configuration but distinctive "x" rigidity bars on the doors and other details.
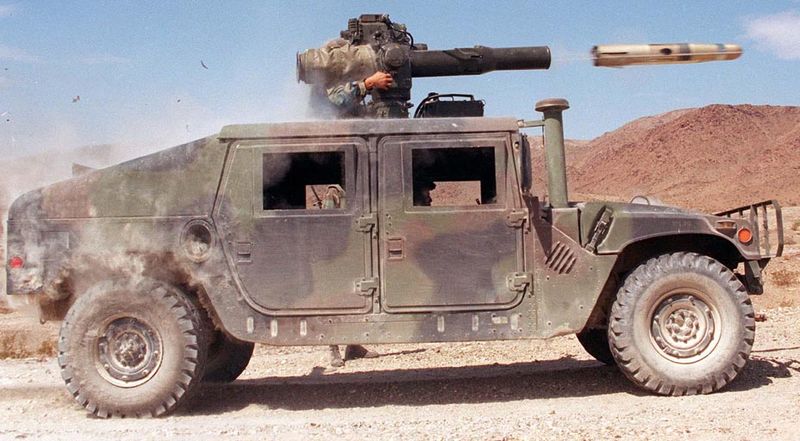 Humvee firing a TOW missile
Humvee firing a TOW missile
Others softskin variants:
-M997 Ambulance: Used for Casualty evacuation had an enclosed rear medical shelter, with Litter racks, climate control and medical equipment storage, unprotected in early versions.
-M1042/M1043 Shelter Carrier: Used for Communications, command, radar, electronics with a mounting platform Standard or heavy for TOC shelters, signal units, EW systems.
-M1035 Expanded Capacity Shelter Carrier with Extended wheelbase, Higher roofline as Mobile command posts, maintenance shelter.
-M998A1/M1038A1 (A1 Series) of the Early 1990s had a stronger suspension, a 6.5L diesel engine and 4-speed auto transmission but was still unarmored.
-M1151/M1165 in unarmored Configurations for training, rear-area logistics and some Allied forces, but optionally fitted with armor kits
-M1097 Heavy HMMWV: High payload utility (2.5 tons) for towing artillery, carrying shelters and logistics transport, optional kits only.
Prototypes
- Scorpion, a regular 2004 heavy chassis modified to carry the 2B9 Vasilek 82 mm automatic mortar.
- Composite Humvee. Regular aluminium hull replace by a new 450 kg cell made by TPI Composites of Rhode Island with AM General.
- XM1124 Hybrid-Electric Humvee, mobility prototype with an all-electric drive train from RDECOM/TARDEC, intended for Spec Ops.

Humvee STAR-T Telecom
Variants includes the M1114/16/23/24/25/65 up-armored carriers, M1115/21/67 TOW and improved TOW up-armored carriers, and the M1151/52 up-armored capable HMMWV which were designed for urban combat.
The Humvee in combat
(Chapter in Redaction)
Operators:

Slovenian Humvees
The USA now still operates without real replacement the Hummer and its versions and improvised versions, perhaps 150,000 in all (Formerly in total Army: 260,000, Marine Corps: 44,000), including some 1980s vehicles that had been completely overhauled. They are also in service with 71 countries.
Operators are:

Afghanistan: Operates some 4150 vehicle ordered and delivered from 2010.

Albania (20)

Algeria: More than 400 ordered.

Argentina: About 300 vehicles for the Army, Gendarmeria and IMARA.

Bahrein (unknown)

Bosnia-Herzegovina (a few used for de-mining operations in Iraq)

Bolivia: (50 vehicles only for the "Green Devils" anti-narcotic unit and Rangers)

Botswana (40)

Bulgaria (52)

Canada (A few used by y JTF-2 and CSOR in Afghanistan)

Chad (Some, Sold through the Foreign Military Sales program)

Chile: 250 army and 50 navy.

Croatia (85)

Colombia: 400+ vehicles

Czech Republic (601st Special Forces Group)

Denmark (30)

Djibouti

Dominican Republic

Egypt: 3,890+ vehicles

El Salvador (20)

Ecuador (130)

Ethiopia

Georgia (110+)

Greece (600+ license-built by ELBO).

Honduras

Hungary (27 ex-Afghanistan)

Iraq (New Iraqi Army and security Forces: 10,000+ Humvees)

Israel (2000+ assembled by AIL)

ISIS (Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant), some 2,300 captured (est.)

Kazakhstan

Kuwait

Jordan (130+)

Kenya

Latvia (60)

Lebanon (1300+)

Libya (200, donated 2013)

Lithuania (200)

Luxemburg (43)

Macedonia (80)

Mexico (3000)

Moldova (39)

Morocco (3500+)

Monaco (6)

Mongolia (30)

New Zealand

Norway (6)

Panama (7)

Oman

Peru (300)

Portugal (37)

Romania (122)

Russia (8, seized in Ossetia and evaluated)

Saudi Arabia

Serbia (21)

Slovakia

Spain (150+, Marines)

Sudan

Tanzania

Taiwan (7000+)

Thailand

Tunisia (52)

Ukraine (110)

UAE

Uganda (50)

Venezuela

Yemen (13).
IDF Humvees: Hamer Story
Hamer Memugan M1025:
Based on the M1025, modified by Plasan Sasa, and fully armored and wth a roof hatch behind the driver´s seat, spare wheel behind a new bumper at the rear of the vehicle. New wheels of the "aggressive pattern" type and large rectangular housing on the roof for the EW Counter Measure equipment to work on occupied territories and for border patrols.
Hamer Memugan M1113:
Almost the same as its predecessor but with a roof gun ring for a MAG-58 or a 40 mm grenade launcher and extended armoured grill. Air conditioning unit in the back and optional EW equipment with a cellular telephone jammer, anti-IED box plus two ammo stowage casings.
Hamer Memugan M1113 (with internal air conditioning):
Internally mounted air conditioning unit in the left rear stowage bin, absence of an external unit, mesh pattern in the lid of the left stowage.
Hamer Memugan M1114:
Standard M1114 wih extra screens over the windows, amber flashing light above the front windshield (wire mesh casing) and adaptors with brackets for ammo boxes on the roof.
Hamer Memugan M1114 Katlanit:
M1114 with a 12.7mm HMG with the Rafael Katlanit RCWS.
Hamer Siyur:
Based on M998 or M1025, roofless with roll cage, gun ring for a MAG-58, Mk 19 grenade launcher or others, rear bumper with rack for a spare wheel.
M998/M1025 Hamer Orev:
As above but with a BGM-71 TOW launcher system on the ring. Trunk for 12 TOW rounds, locally developed rack Kiveret, used dismounted and tripod stored.
M998/M1025 Hamer Machmat Hamer Siyur used as a tractor 120mm Makmat mortar. Grenades carried inside.
M998/M1025 Hamer Pikoud Ha’Orev:
Home Front Command vehicle, standard issue Siyur with decontamination unit for NBC warfare.
M998/M1025 Hamer Medical:
Siyur/Orev with a high sided stowage rack to store and transport medical equipment instead of the turret ring.
M998/M1025 Hamer Galit:
New prominent roll cage fitted with a tilt made of Shimshon sheeted canvas.
M998/M1025 Hamer Barkan:
Galit, with a large storage box in the trunk for FIM-92 Stinger missiles.
M998/M1025: Hamershit:
Same as Batashit/Abirshit used for desert patrol, hard top Galit with solid hard type, side and front panels made of Shimshon fabric, sideward facing search lights.
M998/M1025 Hamer Machmat
Galit based tractor for the 120mm mortar, grenades carried inside.
M998/M1025 Hamer Galit Pikoud:
Hamer Galit with a wide range of radios used as command platform.
M998/M1025 Hamer (mod):
Different types of arches, apparently used by field medical units.
M998/M1025 Hamer Gill:
Replacement for the Orev no mounted launching station in gun ring. The Gill aka. Spike missle could be used dismounted indeed to its launch position. 12 missiles are stored in the Kiveret rack.
M998/M1025 Hamer M998:
Standard M998 in cargo/troop configuration.
Hamer M1025:
Standard M1025 weapons carrier with a FN MAG-58, rear bumper with spare wheel mount, extra tail light.
M998/M1025 M-1025 Hamer Patrol:
Magav (Border Guard) units, with a MAG-58 LMG.
M998/M1025 Hamer Patrol (with air conditioning)
. The air conditioning unit is on the roof.
M998/M1025 Hamer police observation.
Deployed by the Magav for patrols with electronic system on top as a mobile observation post.
M998/M1025 Hamer driver training:
Trainer, with a stowage rack on roof top, box over each rear wheel well.
M1038 Hamer Tziyud:
M1038 with inward facing benches, rear, hard top, two door cab, and usual rear bumper with spare wheel. Four rearward facing seats in the front of the trunk, new roll bar welded to the roof for hauling goods and equipment. Shimshon tarp.
M-1037 S-250 Shelter Carrier:
M1037 Shelter Carrier with corrugated roof and IDF standards.
M1037 Hamer Lynx:
Stellite communications relay vehicle organically used by Tsahal with a container like the S-250 shelter but lower, large foldable satellite dish, like the M1113 Enhanced Capability Vehicle, detachable outriggers at the front for stability.
M1113 ECV Hamer Raccoon:
Also named Stalker II, used by Tsahal and the Magav for surveillance, reconnaissance and image acquisition with sensitive optical equipment.
M1113 ECV Hamer Communictions Relay:
Like the Raccoon but with wire reels on either side of the shelter and large array of antennae.
M1025 Hamer Raccoon Police:
Seen in 2011 in Jaffa, like the Raccoon.
M1113 ECV M-997 Hamer Ambulance:
On top of the hood, thin braces, shared with the Hamer Magen David, new type of vent.
M997 Hamer Nyedit Tazukaha Rekem:
Mobile Heavy Armor Maintenance Vehicle, with an oil filtration system, pump to change oil rapidly, onboard compressor for pneumatic tools, trunk, open rear seats, front seats with hard top and its stowage basket and tilt over it.
M998/M1025 OPFOR
Rare vehicle used by the unit at Ze’elim training grounds, part of the T-72M Simulator for manoeuvres as Opposing Forces (OPFOR) in several sub-versions. One to mimic the T-72 with a fake hull and makeshift turret and wide range of gear for war gaming purposes.
M998/M1025 Hamer Orev:
M966 TOW carrier with gas bottles or pressurized air to the right of the trunk, used by OPFOR.
M966 RDM simulator:
Used for OPFOR in several versions to mimic the BRDM-2.
M998/M1025 Hamer Tothanim:
OPFOR vehicle in several versions to mimic a 2s1 Gvodizka.
M998/M1025 Hamer Siyur Ze’elim:
OPFOR command vehicle with US roll cage with round bars.
M998/M1025 Hamer Ze’elim M1035:
OPFOR Ze’elim, standard M1035 soft top ambulance.
M998/M1025 Experimental Hamer Memugan M1114:
M1114 fitted with unknown RCWS, prototype.
M1114 Sparrow:
Made by EMIT with launching rail on top of a M1025 to launch the UAV Drone "Sparrow", proto.
M998/M1025 Hamer: Orev with IDF Gill anti tank missile.
M998/M1025 SPIKE NLOS (spike): Base platform (proto) for the "Spike" missile by Rafael (range 25 km).
M1037 Hamer 6x6 Yaalim:
One off version with 3 axles, made by Yaalim.
M998/M1025 Hamerim (mod):
Proto with ECM container on the roof of a Hamer Memugan, same stuff as Nakpadon NG.
Shalgonit: (Lagoon)
Cellular jammer for Incendiary Explosive Devices in a rectangular box (fitted to any Hamer).
Shalgon: (Popsicle)
Radio jammer equipment to disable IEDs and remotely activated Incendiary Explosive Devices, antenna with multiple rods. Fitted like above on the late Hamer Memugan or Early.
Optiona equipments
: David ULAV, Nag’mash Vayzata, Nagmachon, Nakpadon systems from Elisra. Air conditioning, Metashteshet kits to erase tracks.
Humvee specifications |
| Dimensions (L-w-H) | 8.43 x 3.51 x 3.18 m (331 in x 138 in x 125 in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 3,810 kg (84,00 lbs) |
| Crew | 2+4 (Commander, Driver, 4 infantry) |
| Propulsion | V8, 6.2-liter fuel injected diesel, 150 hp @ 3,600 rpm |
| Transmission | automatic with maximum input torque of 451 lb/ft. (612N-m) |
| Maximum speed | 65+ mph (48 km/h) on road |
| Suspension | Torsion bars |
| Range (Fuel) | (cc Liters/ cc.) |
| Armament | Standard cal.50 M2 (12.7 mm) -see notes |
| Armor | HT aluminium 8 mm - see notes |
| 280,000 |
The Humvee reaches concessions (2000)

General Motors Press Release January 9, 2000. Hummer H2 Vision Vehicle:
"A new chapter in the Hummer Legend. DETROIT - HUMMER, the world's most serious 4x4, stands alone atop the mountain of off-road vehicles. Until now. The new General Motors HUMMER H2 vision vehicle is an authentic evolution in a truly incomparable species. With its debut at the 2000 North American International Auto Show in Detroit, the H2 provides a look at what the future of the HUMMER sport/utility vehicle could be. The H2 draws reverently from the current HUMMER production vehicle and its tradition of strength, toughness and 4x4 leadership. The H2 echoes the roots of the HUMMER'S own heritage,
roots that trace back nearly a century to the 1903 Overland Runabout.
The first civilian HUMMER was delivered in 1992, after years of service to the U.S. military as AM General's "HUMVEE" multi-purpose vehicle. General Motors has acquired the exclusive ownership of the HUMMER brand
name and the right to retail the HUMMER utilities and pick-up. AM General was formed as a spin-off of the Kaiser Jeep Corp in 1964. The company traces its roots back to the Willys-Overland Co., creators of the original Jeep."
The designers made the H2 a clean and aggressive exterior with integrated winch, large brush bar moving in tandem with the hood for easy access to the engine. Multiple hooks on the front and rear, for pulling and hauling, along with high-intensity headlamps, fog lamps and auxiliary. Driving lights mounted on the brush bar. Thermostat-controlled articulating louvers for engine ventilation. Two exposed canister air cleaner filters are on the hood, one for providing cool air to the engine and another for clean air to the passenger compartment. The entire body has more of a clean, rounded shape. The wrapover windscreen and standout doors, less exposed rivets and bolts. It alsh had a full-across, power-operated canvas sunroof. It also had Rock-slider skid plates on the front and rear sides, approach and departure skid plates.

The H2 also comes with an all-new rear suspension, all-independent keeping one wheel from affecting the other on off-road tripes for a smoother ride, better handling, stability. Both front and rear suspensions are independent double wishbones with unequal-length A-arms, torsion bars, stabilizer bars, and long-travel, dual-rate coil over shocks with remote reservoirs. The 19 x 9.5-inch three-piece aluminum wheels have a rugged high-tech look with an integrated bead locking system and mounted with 35-inch off-road prototype Goodyear Wrangler All-Terrain tires.
Powering the H2 is GM's 6.0-liter, high-output VORTEC 6000 V-8 mounted longitudinally, mated to a heavy-duty four-speed automatic transmission with Autotrac four-wheel drive, which the driver engages via levers rather than the usual push-button. The interior features four leather bucket seats and center jump seat, second row. New instrument panel kept simple and straightforward, illuminated at night to glow oscilloscope green. The rear cargo area features a three-tier loading area with a floor lifting to reveal a secure, lighted sub-floor able to receive packages and equipment. The main floor can also be used for storage as the sides, featuring hammock-like netting holding more items and equipment.
The H2 has a new Central Information Center featuring a GPS navigation system, OnStarTM system, DVD video, CD player and MonsoonR audio with 10 speakers. Night Vision from Raytheon, Internet access, laptop docking station, cell-phone
docking station.
Legacy
Evolution and Upgrades (1990s–2000s) mostly consisted on Add-on armor kits (see tank-afv.com) for more. The main up-armored variant was the M1114. It had improved engines and transmissions, better communications and electronic upgrades. During the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, Humvees were increasingly modified to counter IEDs, Ambushes, Urban combat threats. But these modifications significantly increased weight, stressing the original design. Replacement and Legacy started when the vehicle, never designed as a mine-resistant vehicle was sidelined and then retired. MRAP filled heavy protection roles and the JLTV (Joint Light Tactical Vehicle) was developed as a long-term mass-built replacement. Despite this, enormous numbers means Humvees remain in service worldwide. Thjey are still used by U.S. allies, police forces, and civilian agencies (Over 280,000 produced, that needs to be recalled).