 Toyota FJ.45 (1960)
Toyota FJ.45 (1960)
Toyota disrupted the 4x4 maket internationally with the J2/J3, in the 1950s already, from a US Army demand to take part in the production of the mythical jeep. However a gradual redesign process resulted in an iconic and memorable look, defining the Land Cruiser for the next two decades. The J4 simply had a longer wheelbase, new cabin, new engine and innovated in many ways. By the end of its production run, there were four wheelbase lengths in the J4 family. It was amazingly popular in rural areas throughout Africa, Australia, Americas and Asia, for camping, public transportation and utility transport in inaccessible areas. The J45 was a development of that lineage.
The Toyota Land Cruiser Lineage

Toyota BJ/FJ (1951)
The BJ and FJ were also calledToyota Jeep BJ (1951–1954), produced at that time and assembled at Toyota City (Arakawa Auto Body) as 2-door softtop, Front-engine, four-wheel-drive vhzhicles powered by the 3.4 L B I6 or 3.9 L F I6 couplued with a 4-speed manual gearbox. pn a wheelbase 2,400 mm (94.5 in) long, it measured 3,793 mm (149.3 in) long for 1,575 mm (62.0 in) wide and 1,900 mm (74.8 in) tall, for a curb weight f 1,425 kg (3,141.6 lb).
They were a product of the Korea war, a contribution to the UN and US-led effort against the North Korean and Chinese. The United States government ordered 100 vehicles on the latest Willys specifications to Toyota. The "Jeep" BJ prototype was developed in January 1951 and went in high demand just like the Land Rover Series 1 developed in 1948. The BJ was larger than the original Jeep, more powerful with its Type B 3.4-litre 6-cylinder OHV 4-stroke petrol engine rated for 63 kW (84 hp; 85 PS) at 3,600 rpm plys 215 N/m (159 lb/ft) of torque at 1,600 rpm. It lacked a low-range transfer case. In July 1951, the prototype made history by reaching the sixth stage of Mount Fuji. The National Police Agency (NPA) placed an order for 289 and it became their official patrol car.
From 1953, regular production was spread between Arakawa Bankin Kogyu KK (body assembly, painting), and declined into the BJ-T (Touring), BJ-R (Radio) for the Japanese Japanese Army and BJ-J (Cowl-chassis for a fire-engine) By June 1954, the brand "Land Cruiser" was proposed by Hanji Umehara. Next the 92 kW (123 hp; 125 PS), 3.9 L Type F leading to the FJ-J type.
J20 (1955)

The second generation Land Cruiser called was introduced that year as a more civilian model, more refined than the BJ for export, with a new bodywork, better ride (longer four-plate leaf springs) and more powerful 99 kW (135 PS; 133 hp) 3.9 L six-cylinder Type F petrol engine for better road performances, but same 3-speed gearbox. The interior wad far less spartan, more comfortable notably by moving the engine a bit forward.
It introduced also a synchromesh on the 3d and 4th gears. In 1958 the FJ25 was licenced to Brazil and production of the "Toyota Bandeirante" started in January 1962 but with a Mercedes-Benz diesel, produced until August 1968 but confidential with just 961 vehicles. In 1959 Australia imported it through B&D Motors as the FJ25/28.
J30 (1960)
The J30 was produced only between February to October 1960 (FJ35-V) on the J20 chassis but as a 4-door wagon body by Gifu Auto Body Co. It measured 4,615m (181.8 in) for a wheel base of 2,65m (104.3 in), 5 seats, and with the Toyota F engine, 4 speed manual transmission and selectable 4 four wheel drive. The J40, or FJ45-V/LV with the same body had only 60 built.
J4 (J40) (1960)

In 1960 the 20 Series was upgraded to the now 40 Series with many production changes after the manufactirung included more moder steel presses. Mechanically it also had a new 93 kW (126 PS; 125 hp), 3.9 L F engine and low-range gearing on a three-speed main gearbox.
In 1965 production eached a historical milestone at 50,000 vehicles and it became eve the best selling Toyota in the United States.
In 1968 – The 100,000th Land Cruiser was manufactured. The Brazilian J40 Bandeirante started production from September, still with Mercedes-Benz diesels rated for 58 kW (79 PS; 78 hp).
In 1972 – The 200,000th Land Cruiser was sold and the next year, the 300,000th as well as the first diesel Land Cruiser with a longer wheelbase and six-cyli. H engine.

In 1974 it introduced a 4-cylinder 3.0 L B diesel which boosted sales in Japan thanks to a new lower tax compact freight-car category.
In 1975 The 3.9 L petrol engine was replaced by the 4.2 L 2F unit. The FJ55 received front disc brakes.
In 1976 the FJ40 Land Cruiser only existed for the US market, with front disc brakes from the FJ55.
In 1977 The Irish Army purchased 77 FJ45 Land Cruisers. They won praise as being fast, reliable with good off-road performance but they rusted easily as well in the wet Irish climate.
In 1978 – The first BJ/FJ40 and FJ55 models entered West Germany with diesels (BJ40) and petrol (FJ40/55) egines.
In 1979 the US merket only FJ40 was updated wit a new square bezel around the headlights, power steering and cooler. The Japanese market enjoyed the improved diesel engine 3.2 L 2B.
In 1980 the venerable H diesel (HJ45) was replaced by the 4.0 L 2H engine (HJ47).
In 1981 the Diesel version had new front disc brakes and 3.4 L 3B engine, and the LWB BJ45, the 3B engine.
In 1982 a 5-speed gearbox introduced.
In 1983 the last FJ40s were imported to the U.S., around 300.
In 1984 only Canada imported the BJ42, with a 5-speed overdrive transmission.
J45 Chassis

There was a “short” length chassis similar to the original and with a soft top.
The “medium” chassis was only for a short-lived station wagon, replaced after a couple of years.
The “long” wheelbase (LWB) also had a short life ass supplanted by the “super long” wheelbase.
The “super long” (SLWB) started to be a market-winner on export for military markets alonght e globe when used as a troop transport.
J45 1965-75
The J45 which is out main focus here was appreciated by various armies across the globe by combining its large capacity, ruggedness, ease of maintenance, speed and off-road qualities. When a pure armoured personel carrier was not needed, just as a taxi to the frontline, the J45 was quite appreciated. At its core it was as the J45/47 a long-wheelbase, four-wheel-drive vehicle, available in two-door hardtop, three-door hardtop, four-door station wagon, two-door pickup. The four-door station wagon FJ45-V/LV became rare and was replaced by the FJ55G/V in 1967.
In the 1980s especially, the J45 pickup body became widely used, especially in its military variant with a soft top cabin and windshield that can be folded down on the bonnet. This freed the forward arc of whatever armament can be installed on the flatbed, but with some limits. Indeed, the rear axle had only single wheels, not double unlike a common truck, so the load needed to be moderated in order not to break th axle. However it was so though that much heavier armaments than anticipated were routinely installed. The J45 started to ba a common "technical" used in a lot of civil wars and local conflicts, especially in Africa, the middle east and Asia.
 Half-Track variant
Half-Track variant
J45 1975-84

Layout
The vehicle was completed with a cabin, and body that was either "Estate" (6+ seats) or pickup (2 seats, flatbed). It measured 499 cm long for 166 cm wide, 196 cm high, and a ground clearance of 225 mm. It weighted 1,800 kg, the pickup was a bit lighter around 1,600 kgs.
Propulsion

The J45 sported a 6-cylinders in line, gazoline, longitudinal forward, and fed by twin-cam carburettors Side-mounted camshaft, 2 valves per cylinder, the latter being 94.0 x 101.6 mm. This engine displaced 4,230 cc for a compression ratio of 7.8 and an output of 135 hp at 3,600 rpm, a torque of 31.7 mkg at 1,800 rpm. It had a 4-speed gearbox with standard reduction, 4x4 suspension, free rear differential but no traction control. The steering used Ball joint. The Front and rear suspensions used Leaf springs. It had front and rear drum brakes. The tires were 7.50 x 16 frong and rear. With a Power-to-weight ratio of 13.3, top speed was 135 kph. It carried a 83 liters fuel tank for c800 km range on road.
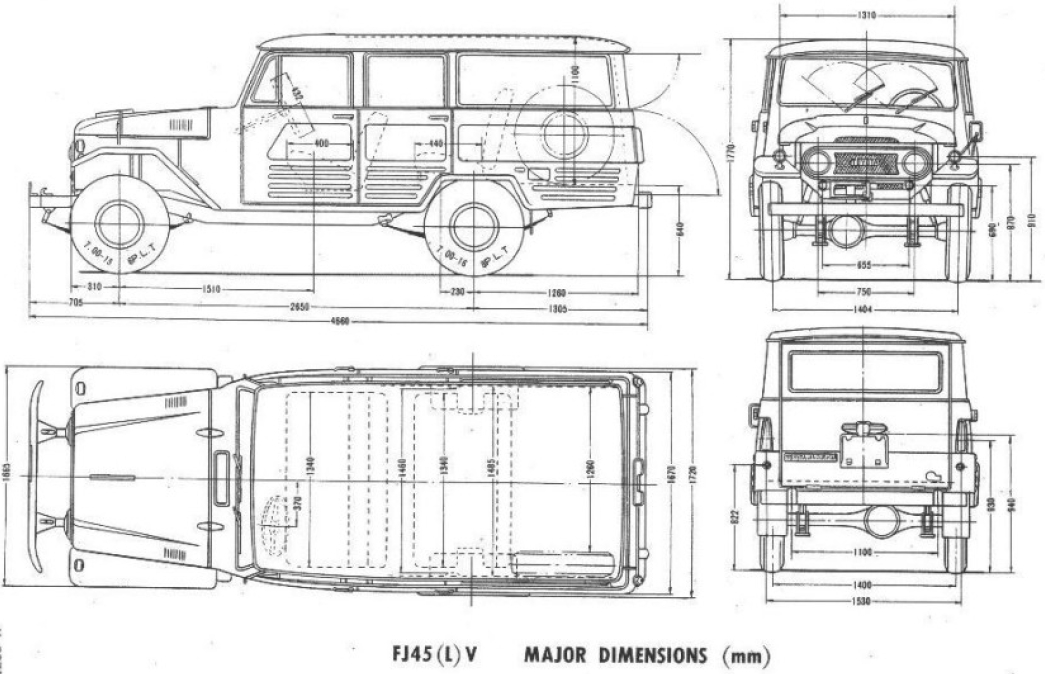
J45 specs. |
| Type | 4x4 pickup body or station wagon |
| Lenght | 3,840.5 mm (151.2 in) |
| Width | 1,666.2 mm (65.6 in) |
| Height | 1,950.7 mm (76.8 in) (softtop), 2,000 mm (78.8 in) (hardtop) |
| Wheelbase | LWB 2,650 mm (104.3 in), SLWB 2,950 mm (116.1 in) |
| Total weight | 1,480 kg (3,263 lb) softtop, 1,554 kg (3,427 lb) hardtop |
| Crew | 2+9 (station wagon) |
| Propulsion | 4.2 L 2F I6 petrol or 4.0 L 2H I6 (H45) |
| Layout | Front transverse, single axles |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual, 4-speed 1974, 5 speed 1984 |
| Suspension | Leaf springs |
| Speed (road) | 80 kph road, 50 kph off-road |
| Range | c800 km (diesel, road) |
| Armament | None, see notes |
| Production | 300,000+ |
| Manufacturer | Toyota City and others (see notes) |
Service

The Toyota FJ Land Cruiser stands among the most reliable, long-lasting, and nearly unbreakable vehicle a perfect "go anywhere" that cemented its legend on the civilian market, but no only. Since the BJ25 as Japan’s answer to the Jeep and Land Rover, and the first seeing action in the Korean War, the FJ became a trusted 4×4 and the backbone of the Toyota brand, the emissary of Japanese engineering and also interested other militaries, spreading worldwide to carry troops and cargo on poorly maintained roads or simple dust tracks in any latitudes, including running across the desert.
Not designed for the frontline, it was also often used as ambulance. Successive FJ models went for a rugged military style to a more cvilized one, ride with interior improvements notably softer springs. In "FJ", the “J” stands for “Jeep”, “F” the engine type.